Uterine fibroids - what is this disease and how to treat it? In ICD-10, this pathology is classified as leiomyoma under the code D25. In almost all cases, it is a benign tumor. However, even such neoplasms can lead to the development of serious complications requiring complex treatment.
Modern gynecologists can easily diagnose even microscopic tumors up to a centimeter, which are often detected quite by accident. Some women can even live with myoma all their lives and not face a single complication, while others are forced to undergo surgery to remove neoplasms due to all sorts of consequences.
Uterine fibroids - what kind of disease
Symptoms of this pathology depend primarily on the size of the tumor and the general health of the woman. Myoma is a neoplasm consisting of muscle tissue, which is characterized by slow growth and a benign character. Impressive tumors certainly do not develop in a few years. If the neoplasm grows rapidly, its malignant nature cannot be ruled out.
Uterine fibroids are a female disease, the exact mechanism of which is still not fully understood. In recent decades, the incidence rate has increased significantly among girls under 30 years old. This phenomenon is explained not only by harmful environmental conditions, but also by improved diagnostic methods.
Features
There are several important statements regarding uterine fibroids.
- It occurs exclusively in women of reproductive age, and gradually disappears during the menopause, as certain sex hormones are required for its development. If the neoplasm is diagnosed in a lady at the stage of menopause, one can suspect its malignant nature.
- About 80% of women with myoma have hormonal abnormalities - menstrual irregularities, polycystic symptoms, uterine polyps, malfunctioning of the thyroid gland.
- Often, pathology is combined with mastopathy. The chest and uterus are interconnected functionally. Abnormal changes in one organ often entail deviations in the work of another. That is why most women with myoma often have mastopathy at different stages. To treat such a condition should be comprehensive, and not separately.
- All the information that doctors have today does not make it possible to determine the real causes of the vice. All modern medicines can only temporarily stop the development of neoplasms and the corresponding consequences.
- In medicine, fibroids are called various terms. This is explained very simply. The uterus itself consists of connective and muscle tissue. It is impossible to determine specifically which tissue the tumor consists of before removal and histological analysis, even with CT, ultrasound and MRI. Although this nuance does not affect the treatment of women with myoma.
Using histological analysis, you can determine the nature of the tumor:
- leiomyoma - consists exclusively of smooth muscle structures;
- rhabdomyoma - from other muscle fibers;
- fibromyoma - from muscle and connective tissue;
- fibroma - a large area consists of connective cells.
Classification
Uterine fibroids - what is this disease? In the photo you can see what this pathology is. Although it is, of course, impossible to visually determine it, one should rely on other symptoms and one's own observations. If you suspect you have such a tumor, be sure to go to the gynecologist. Remember that curing this defect in the early stages is much easier than in a neglected state.
Uterine fibroids - what is this disease? This is one of the most common pathologies in women of reproductive age. This disease occurs in approximately 25-30% of modern women. The prevalence of the defect increases with age. The real peak of the disease occurs in 40-45 years.
Doctors divide myoma into several types.
- Small - one or several nodules up to 5 cm.
- Large - the presence of at least one neoplasm more than 5 cm or uterine parameters corresponding to 12 weeks of pregnancy (approximately 11-12 cm).
- Multiple - a history of uterine fibroids implies the presence of more than three nodes.
- Single - the presence of only one tumor.
- Submucous - the history of the disease of uterine fibroids involves the localization of the neoplasm with a protrusion into the uterine cavity, which contributes to its deformation.
- Subserous - the tumor is located above the surface of the uterus, protruding into the abdominal cavity.
- Interstitial - the node is located directly in the muscle wall.
- Mixed - often myoma grows in different directions, then doctors talk about a mixed type.
- Symptomatic - a tumor that appears on the background of some abnormal conditions, for example, due to bleeding with anemia.
- Cervical - the node is localized in the cervical zone, the frequency is about 6-7% of all diagnosed uterine fibroids.
What is this disease and how to identify it? Of course, the doctor at the appointment will tell you all this. However, the general symptoms of a pathology by which it can be suspected should be known to every woman.
Causes of occurrence
Until now, doctors can not determine the exact prerequisite for the development of uterine fibroids. What this disease is and why it arises is a secret for many scientists. It is believed that due to heredity, a uterine tissue site forms with too many receptors that perceive the influence of hormones. Such endings are more sensitive to progestogens and estrogens, compared with neighboring tissues. That is why over time, this site begins to develop more actively, unlike the others. The body gradually loses control over this process, a tumor appears, the size of which can reach more than 20 cm.
Risk group
In fact, uterine fibroids can appear without obvious causes and predisposing conditions. But most often this defect is diagnosed in women who:
- have a family history of similar diseases;
- subject to hormonal abnormalities;
- are overweight;
- subject to regular stress, chronic fatigue and lack of sleep;
- did not give birth;
- suffer from metabolic disturbances and diabetes;
- have undergone numerous IVF procedures or ovulation stimulation.
Some scientists believe that uterine fibroids are an environmental disease that occurs due to harmful environmental conditions. However, this statement is determined only by the increased incidence of women in recent years. But it has not been confirmed by clinical trials.
Among other things, the factors of increased risk of fibroids include the chronic absence of ovulation, inflammatory pathologies, curettage and abortion, as well as a genetic predisposition. By the way, contrary to popular belief, the use of oral contraceptives does not increase the likelihood of developing a defect. On the contrary, there is scientific evidence that the use of birth control pills reduces the risk and slows the growth of fibroids.
Clinical picture
Usually, the signs of pathology become noticeable only after the tumor reaches an impressive size - more than 2-3 cm subcumous neoplasm and about 5 cm subserous and interstitial nodes. Until this time, the history of the disease with uterine myoma can be characterized by a complete absence of pathological manifestations.
- Soreness. This is the most common symptom of the disease. Uterine fibroids provokes the appearance of pain at the stage of active development and involvement of other organs in the pathological process. Unpleasant sensations are localized in the lower back and lower abdomen. Pain can intensify many times during intimacy, exercise and before menstruation. As the nodes progress, the pain becomes constant. It is characterized by pulling sensations, reminiscent of the presence of a stone in the lower abdomen.
- Bleeding. Too plentiful menstruation also turn out to be frequent companions of myomas. They appear for a number of reasons. For example, if the tumor is submucous, it interferes with the complete rejection of the endometrium. If the node is too large, it deforms the uterine cavity, increases the area that bleeds, and prevents the normal contraction of the myometrium. Systematic blood loss entails the appearance of anemia with a pronounced clinical picture, which is characterized by apathy, lethargy, shortness of breath, pallor, dizziness.
- Infertility. The history of uterine fibroids can be characterized by such a sign. Small nodules have almost no effect on the course of pregnancy. But actively developing and too large tumors in the uterine cavity prevent the full formation of the embryo. Myoma, unlike normal myometrium, does not stretch well, due to which, with an intensive increase in the uterus, the risk of miscarriage and premature birth increases.
- Constipation If the tumor is too large or grows in the area of the rectum, it can be compressed, on the background of which such a symptom appears.
- Problems with urination. Such symptoms occur with the growth of a tumor on the front wall of the uterus. In this case, the woman may have incontinence or too frequent urges to empty the bladder.
Diagnostics
The most affordable and reliable way to identify pathology is considered to be an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. However, even during an ordinary gynecological examination, a specialist may suspect the presence of nodes if an enlarged uterus or its tuberous structure is noticeable.
To detect a neoplasm using ultrasound, several rules should be followed:
- do at the beginning of the cycle - during this period you can objectively assess the condition of the endometrium and the parameters of the nodes, 5-6 days - the optimal time;
- transvaginal procedure - makes it possible to detect even miniature neoplasms up to a centimeter;
- regularly monitor the dynamics - to monitor the development of the tumor, you need to do an ultrasound every six months.
If submucous neoplasms are suspected, a woman is prescribed hysteroscopy, which makes it possible to immediately remove small nodes.
CT or MRI is recommended for some patients to diagnose the disease in gynecology. Uterine fibroids with their help are determined more easily. In addition, these techniques make it possible to assess the location of nodes and their sizes as accurately as possible.
Even less commonly, hysteroscopy and laparoscopy are used to diagnose fibroids. True, such events are most often prescribed as medical procedures.
Uterine fibroids treatment
What is this disease and how to get rid of it? This question comes first for most women who have been diagnosed with a tumor. Like any other growth, the fibroid does not disappear by itself. However, its development can stop and even regress with:
- breastfeeding and pregnancy;
- menopause.
This phenomenon is explained by cardinal changes in the hormonal background at these stages of a woman's life. In all other cases, specific therapy is required.
How to treat the disease? Uterine fibroids are not really amenable to conservative therapies. Usually, medication is only temporary, and simply stops the development of the tumor. Although even after removal of all neoplasms, after a while new nodules may appear.
Conservative treatment
To slow the development of a neoplasm or reduce its area before surgery, drugs of the following categories can be used:
- analogues of the hormone gonadotropin-releasing (Diferelin, Decapeptil, Buserelin, Zoladex) inhibit the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle at all levels, causing a specific state of temporary menopause, as a result, the myoma and the uterus itself decrease by about 30-50 %, but after the withdrawal of the remedy, the symptomatology returns;
- antigestagens ("Ginepriston", "Mifepristone") - inhibit the effect of progesterone;
- "Esmiya" - has an effect similar to antigestagens;
- antigonadotropic drugs ("Gestrinon", "Danazol", "Lucrin Depot") - inhibit the production of gonadotropic hormones, that is, FSH and LH, which inhibits the activity of the ovaries;
- combined birth control pills ("Yarina", "Regulon", "Jess") - reduce the production of LH and FSH, suppress the work of the ovaries;
- gestagens ("Utrozhestan", "Dufaston", "Vizanne") - are used to regulate the menstrual cycle, are ineffective in the treatment of fibroids.
With the development of all kinds of complications, for example, tumor necrosis or inflammation, antibiotics, antispasmodics, as well as analgesics in the form of suppositories, injections or tablets are used.
Surgical intervention
Indications for surgery for uterine fibroids:
- the size of the tumor is more than 5 cm;
- symptomatic type of education;
- preparation for IVF;
- growth necrosis or torsion of the legs;
- active development of nodes within six months;
- the presence of legs;
- concomitant defects of the endometrium and ovarian cysts.
The method of surgical intervention is selected taking into account the age of the woman and the presence of concomitant diseases.
- Laparoscopy. Most often used to remove subserous and interstitial tumors. This technique is deservedly considered one of the safest interventions. In addition, modern technology makes it possible, with appropriate indications, to completely remove the uterus.
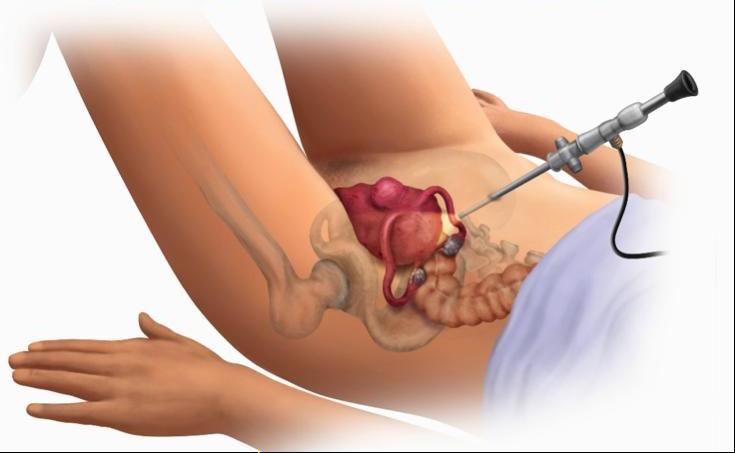
- Laparotomy The traditional way to remove leiomyoma nodes. The operation may involve excision of some nodules, partial removal of the uterus or the whole organ.
- Uterine vessels embolization. The technique is aimed at blocking the arteries of the neoplasm, due to which it significantly decreases in size, and sometimes disappears completely. To achieve this result, an angiosurgical intervention is performed - bringing a special solution to the uterine arteries.
- FUS tumor ablation. By means of MRI, the location of the growths and their sizes are specified, after which a strong ultrasonic pulse is applied to this area. Gradually, the neoplasm heats up and burns down. True, the technique has a number of contraindications. For example, FUS-ablation is prohibited for large myomas and their localization near the bones of the pelvis.