There was always more emotion than fact around the topic of communication quality. Not calling a friend or colleague in a critical situation is always a shame, as is the failure of the Internet at the time of sending an important letter.
And such precedents rightly caused attacks on operators who always have excuses ready: “Your phone is old”, “Yes, there was a malfunction on your site, but we have it every 10 years, but in general our quality here is at the level All industry studies speak about this ”,“ You were in a tunnel (or in a room made of concrete walls, or in a subway, etc.) and therefore could not reach you. Sorry, but we have nothing to do with it. ” Well, the subscriber had to agree, because he could not prove the bad signal quality, compare it with other operators.
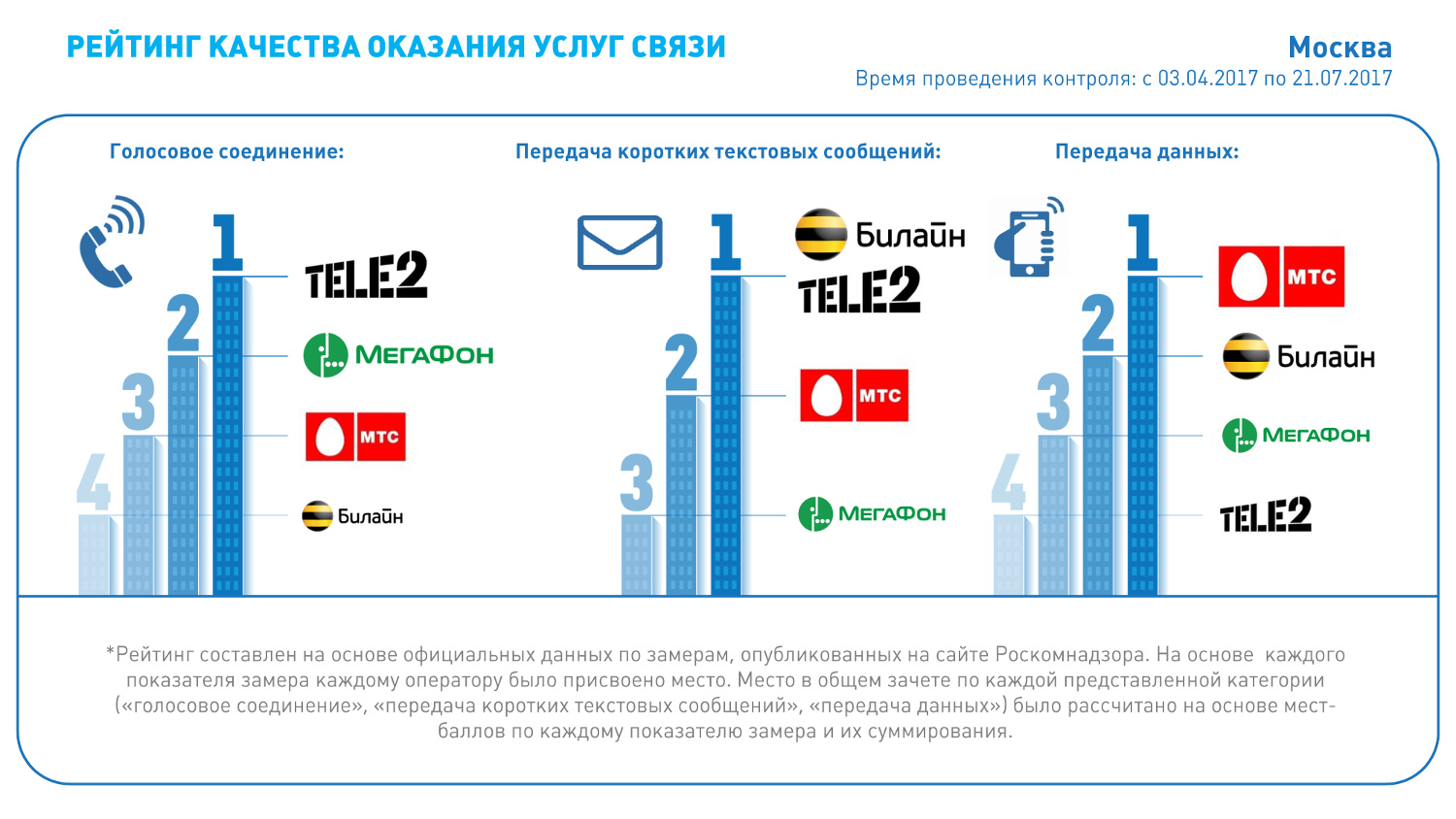
In early September, Roskomnadzor published the results of its own monitoring of the quality of communications in Moscow. I will not go into the details of this particular measurement, they are set out in the
material of the Merchant.
How it all began?On February 6, 2013, Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev instructed the Ministry of Communications and Mass Media to develop a set of measures to improve the quality of mobile radiotelephone services in Moscow.
In June 2014, at the meeting of the commission, the Minister of Communications Nikolay Nikiforov proposed to create a system of public control over the quality of communications. According to the minister, the state should gradually move away from regulating the quality of communication — the market should do this, but for this it is necessary that the subscriber has the opportunity to consciously choose an operator.
In response, Deputy Prime Minister Arkady Dvorkovich instructed regulators, including the Ministry of Communications and Mass Media, together with cellular operators to develop a methodology for monitoring the quality of communications.
In October of the same year, the draft methodology developed at the Research Institute of Radio, the Ministry of Communications and Mass Media, was
sent for consideration to the heads of MTS, VimpelCom, MegaFon, Tele2.
In December 2014, the methodology was signed. In the spring of 2015, the first measurement was made.
The technique is published, it can be found
here .
How is the quality of communication measured?Measuring mobile complex RFC CFD, subordinate to Roskomnadzor center, moves along pre-compiled routes, which include the main urban highways and central streets.
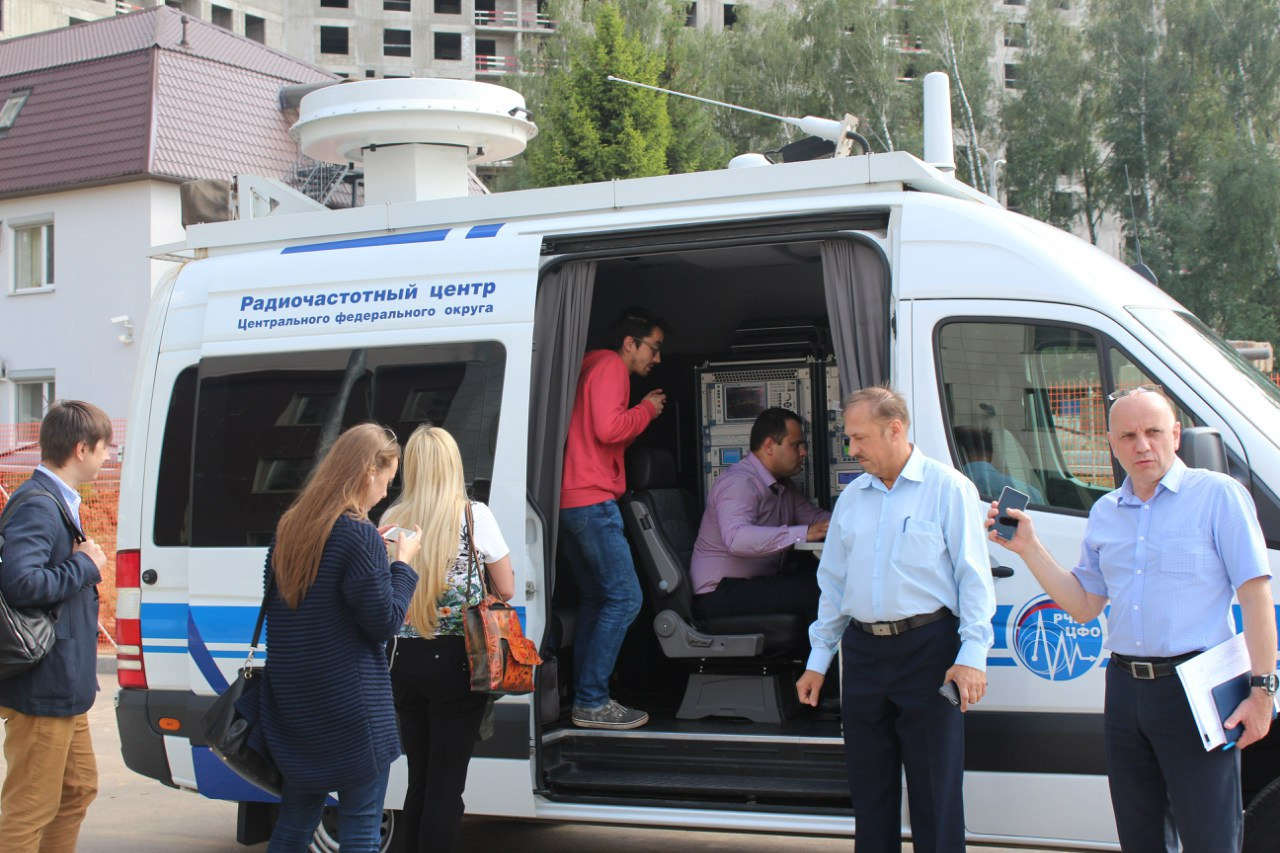

Control calls are made using the ASCOM TEMS Automatic complex to a fixed telephone number (call-generator in the territory of the RFC), which is also connected to the digital E1 lines of the fixed communication network (PSTN). At the same time, the complex includes 4 identical devices for calls, equipped with sims of four federal operators. Thus, calls are made synchronously at the same time, from the same place, which excludes the privileged conditions for any operator.
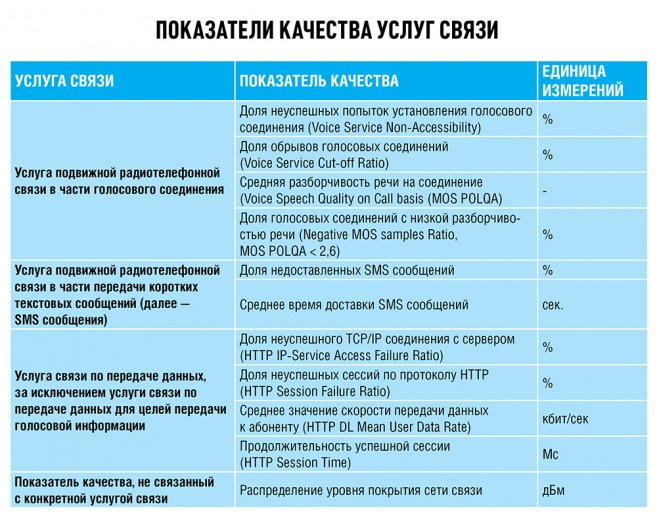
Voice quality tests fix the following parameters:
- Voice quality . It includes the proportion of unsuccessful attempts to establish a connection, the proportion of dropped calls, speech intelligibility. Speech quality is measured using the POLQA (Perceptual Objective Listening Quality Assessment) technology, approved by the International Telecommunication Union. Each voice call is evaluated for three minutes. The result of the “Big Four” telephone calls is a combination of log-files of measuring complexes. Each voice call is evaluated for 3 minutes.
- Delivery of sms-messages (the share of messages that did not reach the addressee, as well as the average delivery time).
- Data transfer : the proportion of unsuccessful TCP / IP connection to the server (HTTP IP-Service Access Failure Ratio); share of unsuccessful HTTP sessions (HTTP Session Failure Ratio); average data transfer rate to the subscriber (HTTP DL Mean User Data Rate) in kbps; the duration of a successful session (HTTP Session Time) in ms. The procedure is performed for three standards: GSM (2G), UMTS (3G) and LTE (4G). The file size for downloading via HTTP for GSM and UMTS is 3 MB, and for LTE 100 MB.
- Total scan coverage , presence and signal level (measured in dBm).
The materials obtained are analyzed, a protocol is formed, after which they are sent to the site of communication quality. Then the resource publishes the data.
Measurements cannot be carried out during an abnormal load on the network: for example, on holidays, during public events or major incidents. Also it is impossible to spend night measurements.
 What is the difference from crowdsourcing
What is the difference from crowdsourcingIt is believed that special services, such as the SpeedTest application, can demonstrate more reliable results. After all, measurements in this case are made by the many thousands audience of the application in all environments, in the most different periods of time and in any rooms.
But despite all these advantages, crowdsourcing measurements contain one big minus: their results are very easy to dispute. The operator can always refer to signal distorting factors. After all, a simple user, in contrast to the special laboratory, will not be able to measure the “pure signal”.
Mobile laboratories conduct simultaneous parallel testing in the networks of all telecom operators using the same type of equipment. Thus, the evaluation results are not affected by such factors as the various capabilities of the subscriber equipment and different profiles of subscriber traffic in time and space.
Sources:
1. Website Roskomnadzor. Materials on measuring the quality of communication .
2. Interview with the head of the radio monitoring organization and development department of the FSUE “RFC CFA” Valery Ivanenko . Rspectr.com, 11.09.2017.
3. " As a radio frequency service, the quality of communication measured ." Geektimes.ru, 06/15/2016.