The rapid development of electronics and the unification of software solutions led to the emergence of smart devices (Smart Devices), which have become an integral part of our lives. If we talk about the Internet of things (IoT), this is still a concept. It assumes the presence of many objects around us that will get access to the Internet and will interact with each other. Interaction, according to the concept of the Internet of Things, is a distinctive factor compared to existing solutions of smart electronics (Smart Electronics), for example, fitness bracelets that are quite popular now, household smart weights, and in general, such systems as smart home and much another.
 Alexa - voice control your smart home. Image: Amazon
Alexa - voice control your smart home. Image: AmazonOne way or another, but the whole idea of the Internet of things revolves around social networks and a new round of their development. Already today you can share the results of your pedometer on Twitter, but modern social networks are hardly transformed into the concept of social IoT. Too much data and too different tasks will have to be solved by such services. But what happened before and are there prerequisites for creating a Social IoT as a separate solution?
Back in 1999, Bill Gates, in his book Business at the Speed of Thought, proposed the idea of a digital nervous system of an enterprise. Then the basis of such a nervous system became e-mail and rapidly developing web technologies. The idea of interaction at the enterprise or organization level was focused on the manager receiving feedback from employees, with a preference towards the flow of information about problems or obstacles in their work. In general, then it allowed to increase the efficiency of business decisions.
Later in 2005, Tim O'Reilly proposed the term Web 2.0 as a new stage in the development of web technologies. In the concept of Web 2.0, the main user and user content is becoming, which creates competition for famous glossy magazines and professional journalistic resources. Now the Web has transformed again, because we already live in the world of social networks and short message delivery services, while there are opinions that our time should be considered the era of the semantic Internet. In any case, at the moment, already many paper publications have ceased to exist, traffic on web portals has decreased and has moved into the direction of communication in social networks. But the post, as it was, and there is, are popular mass of static sites, as well as bloggers give a lot of interesting content, which we refer to from social networks.
Obviously, the social Internet of things as a service will become an effective addition to existing solutions and expand the scope of interaction of both people and machines. For the time being, we can only consider current technical solutions for interaction in the Social IoT world in order to understand what lies ahead. At the same time, we ourselves can take part in the transformation of the Internet and the technology of the attached devices.
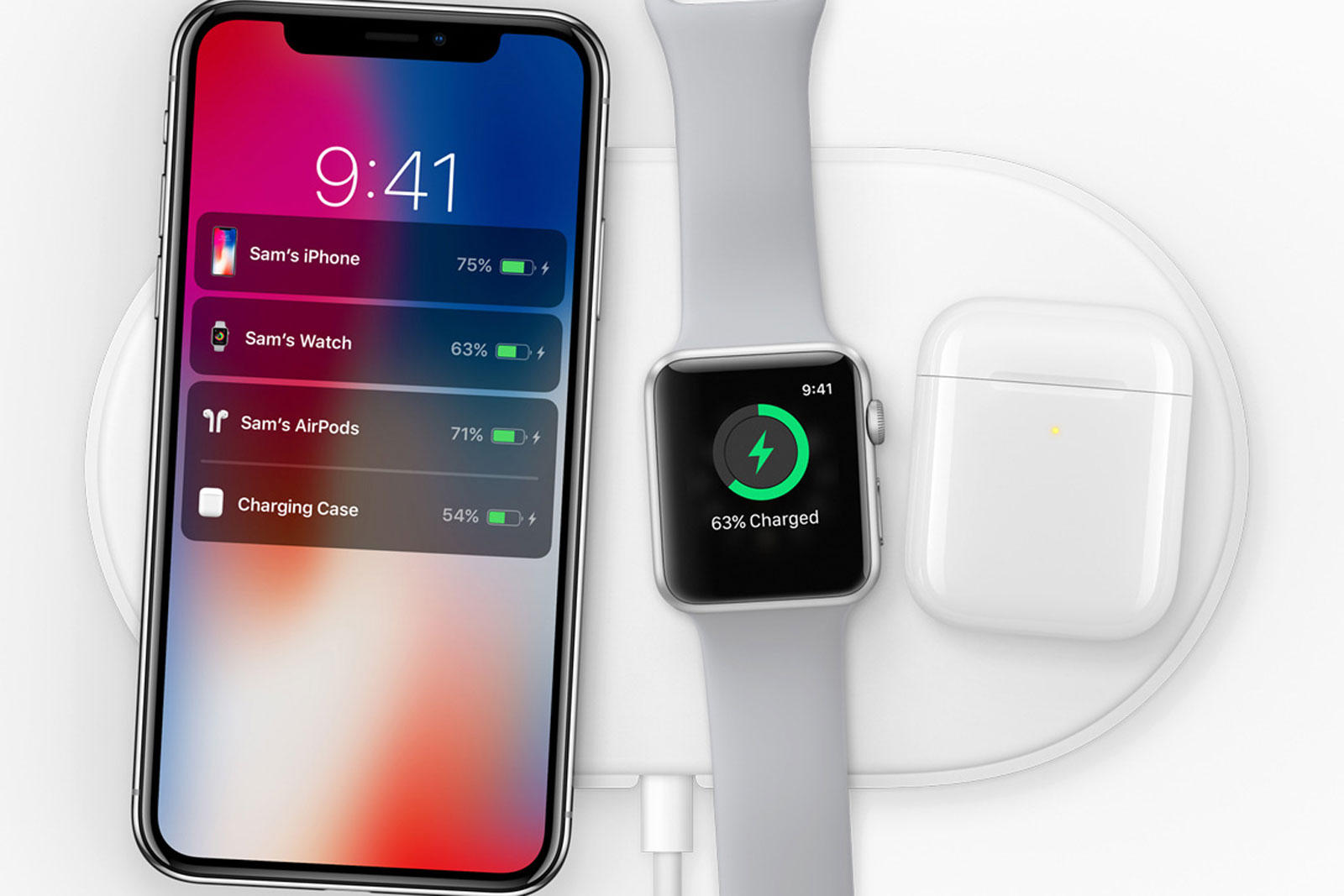 iPhone X wireless charging. Photo: Apple
iPhone X wireless charging. Photo: AppleAfter mentioning Gates and O'Reilly, it is impossible not to recall the recent presentation of Apple. Judging by the Facebook feed, many at the time of the wireless charging show decided that this was another of the company's “innovations”, expressing the irony in the comments. The wireless charger is not new, relatively slow in charge time, but still, this is quite a convenient technology. The most interesting thing is the presentation frame, where it is shown how the phone “sees” the process of charging other gadgets of the company. Here, really, what should be strived for - the actual interaction of devices is “transparent” for the end user.
For example, at the level of interaction between the components of a smart home, we can say that this is the current state of the Internet of things. But still, these are local solutions, limited by the physical space of the room. For example, devices managed by Amazon Echo are primarily aimed at interacting with a person, but not among themselves, and even more so, the boundaries around a single home are not particularly blurred, and at the same time do not combine home comfort with an office workspace, etc., although all technology is aimed at exactly that.
As an exception to the rule, some components of the smart home can "agree" among themselves. A typical example of the interaction of such devices is the third generation of the trained Nest Learning Thermostat thermostats. Also recently appeared cheaper model Thermostat E without the function "Farsight", including the display when someone passes by. But we should not forget that in fact it is possible to independently "program" the corresponding algorithms of device interaction at the level of a smart hub (Smart Hub) of a smart home.
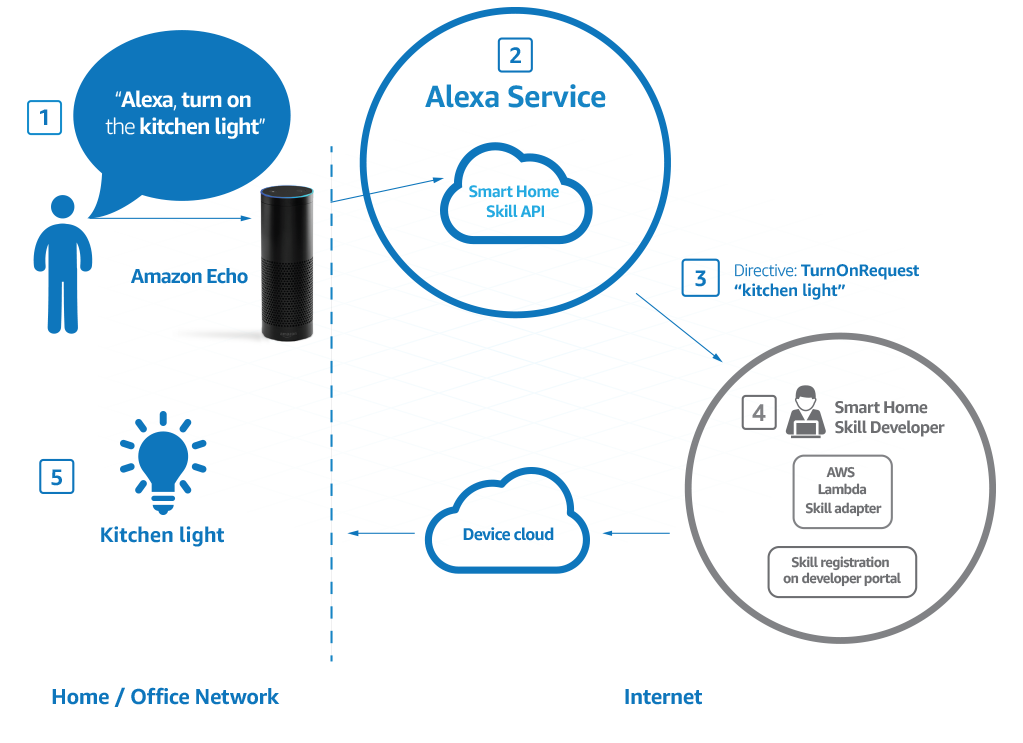 Alexa device control process. Image: Amazon
Alexa device control process. Image: AmazonUsing the Alexa Skills Kit (ASK), it is quite prosaic to add new features in the behavior of smart home devices. All computing and data processing, including speech recognition, is performed at the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud level. Device behavior is programmed at the AWS Lambda service level, and the
Alexa Skills ready-made application platform is also available. Anyway, the skills, behavior or, rather, the interaction of devices and humans depends on predefined scripts. An interesting option is the addition of Machine Learning technologies to this environment as a cloud service, as well as integration with third-party services based on the IFTTT MASK service, which allows you to combine your actions and device behavior between different services and social networks.
If we talk about the interface of “smart things” and a person, an interesting option is with a smart lock, for example, August Smart Lock, which can issue temporary access codes for guests. On the other hand, if it is difficult to program intelligent voice assistants for Amazon Alexa, Google Home, or chat bot, you can always use the services of the Conversation.one platform.
Speaking of smart voice assistants, a smart hub of a smart home, I immediately want to note: what can they do if there is no smart water supply equipment in a regular kitchen, a household gas stove turns on a piezo ignition that is controlled by a mechanical handle and we are surrounded by good old outgoing systems in the past of the industrial world? How does such a smart system know about what is happening in the house? One of the solutions is the installation of video surveillance. But how many cameras will you need to install all over the house, and would it not be easier to retool plumbing, etc.?
In the context of this, the experience and vision of the problem by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, the laboratory of the Future Interfaces Group, who suggest using a single “synthetic” or combined sensor, is interesting. The proposed Synthetic Sensor combines sensors: AMG8833 temperature, TCS34725 colors, magnetometer (3-axis magnetic field sensor) MAG3110, atmospheric pressure with BME280 hygrometer, 6-axis orientation sensor (combined 3-axis gyroscope and accelerometer) MPU-6500, signal quality Wi-Fi, movement AMN211, microphone ADMP401, electromagnetic radiation. However, it seems that everything that engineers had at hand fell into this universal sensitive element of a smart home. On the basis of data recording, a kind of “cardiogram” of what is happening in the room is recorded and, for example, it is concluded that the water tap is turned on, the gas stove is turned on, the blender is working. Immediately I remembered the publication about the speech of the professor and author of the book “Funky Business” Kjell Nordstrem about the future: “Everything that can be digitized will be digitized.”
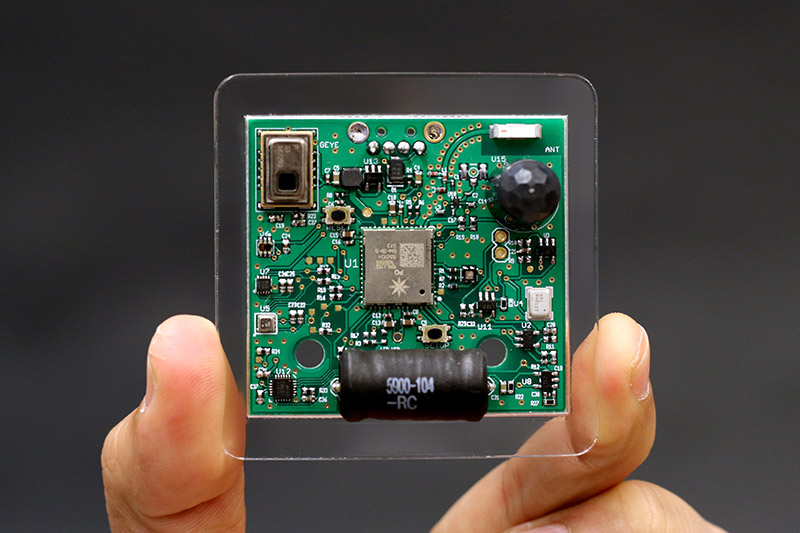 Synthetic Sensor. Photo: Gierad Laput
Synthetic Sensor. Photo: Gierad LaputAt the same time, the term “smart space” looks very bright and colorful and is practically realizable at the level of individual decisions. Still, I would like to note that the concept of the Internet of Things must take into account not only the interaction, but also the self-organization of the objects around us (Connected Devices). Such synergistic interaction will provide an opportunity to move to a new level of digital life, where there is no need to study instructions for electronic devices, they will become maximum safe, will be able to adjust to a specific situation and, at the same time, will be less noticeable as separate objects. At the same time, we will get comprehensive data on the operation and status of such attached devices.
Speaking of terminology, it can be noted that if the concept of embedded systems (Embedded Systems) was used everywhere, now they are not conceivable without being connected to the Internet. Moreover, such a connection is reduced to the use of a chip for a couple of dollars, which may well become the “core” of an intelligent sensor or control system. For example, the well-known module based on esp8266 and more modern esp32 of the company Espressif or a similar solution from other manufacturers.
Such a module is based on a fairly powerful 32-bit processor, usually combined on a microboard with external program memory and allows you to access wi-fi or another wireless data channel. But it is noteworthy that in fact these modules have access to the Internet "out of the box."
The same feature of the modules is the ability to program them in a simple script-oriented language or even use the Arduino IDE and its programming language, similar to simple C / C ++. The modules have few general-purpose input / output ports, which can be expanded by hardware, and interfaces, for example, SPI, UART, are used to connect to digital sensors or to actuators.
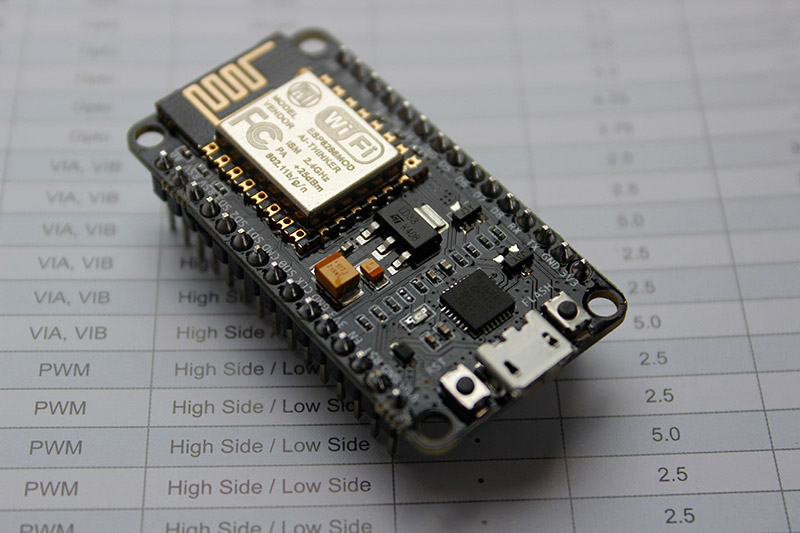 The ESP8266 WiFi Module is a self-contained SOC with integrated TCP / IP. Photo: Vowstar / Wikipedia
The ESP8266 WiFi Module is a self-contained SOC with integrated TCP / IP. Photo: Vowstar / WikipediaSo, if earlier, to provide access to the Internet at the microcontroller level, it was necessary to programmatically implement the TCP / IP stack or use an additional chip on the board, for example, a W5100 with hardware support for a wired Ethernet network, now wireless access to the Internet has become part of the microprocessor module, greatly simplifying development Although this adds security problems at the level of the end device, this issue is completely solved within the global concept of the Internet of Things.
The Internet is changing the interface between human and smart device. If now the main interaction tool is a smartphone, then soon the voice control, Augmented Reality and just an autonomous intelligent button will firmly take their place in our life. For example, the Amazon Dash Button allows you to instantly make a predetermined order in a well-known online store. A slightly different AWS IoT button, you can program to interact with people, devices, the cloud and various services.
Approximately, as with the Alexa Skills technology, all programming comes down to use without AWS Lambda server cloud technologies.
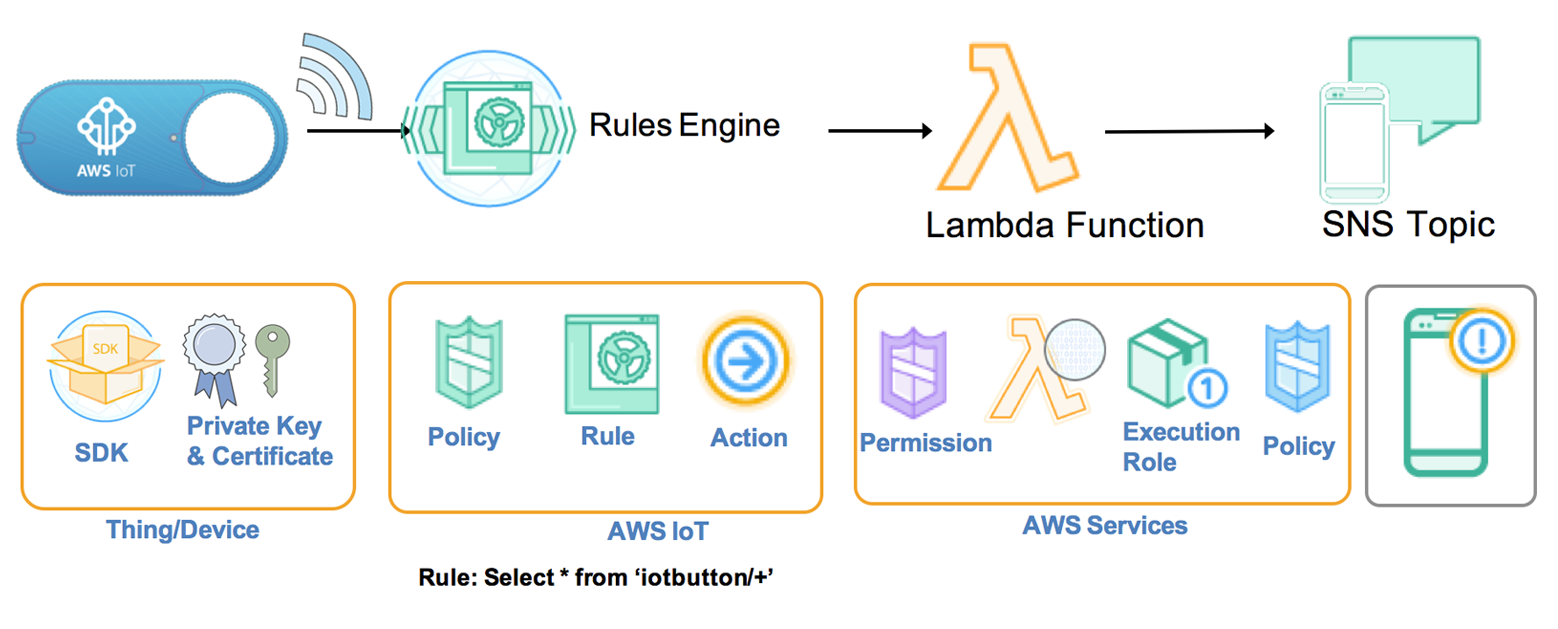 Route Clicks to AWS Services. Image: Amazon
Route Clicks to AWS Services. Image: AmazonAnother interesting idea and, as the development of the concept of the cloud button, the project of the laboratory of the Fluid Interfaces of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology allows you to bind the physical buttons and actuators to each other using the technology of augmented reality. An innovative mobile application for Android and iOS platforms called Reality Editor 2 is proposed. This application allows, in the space captured and taken by the camera of the smartphone and supplemented with virtual connection lines, select interfaces of various Internet things using predefined QR codes, linking them together. For example, virtually connect an independent button and a lighting lamp, etc.
Augmented reality helps a startup Hayo to visualize the place of binding action to smart objects of a smart home. In this project, on the basis of a special 3D sensor, an infrared sensor and software in the cloud, it is planned to give the opportunity to control the “behavior” of a smart home with ordinary gestures and interaction with surrounding objects. And augmented reality allows you to train the system in your phone and install virtual tags. It is interesting, of course, how in this project it is planned to deal with false alarms on gestures, but obviously, big data and processing on the cloud side should help in solving this task.
What is interesting is not only super-innovative projects that develop the concept of interaction between devices and people based on augmented reality, but also the usual developments, for example, the MeteoLogic climate system from GlobalLogic, which uses an augmented reality interface to visualize sensor data.
Undoubtedly, now is a great time to launch startups with projects in the field of the Internet of things, using speech management, augmented reality, various ready-made solutions in the clouds of well-known vendors. For this, the architecture of the social Internet of things may not be completely ready, especially in the area of security, as well as in ensuring application portability. Obviously, applications can run in the cloud and use the interface of a regular browser or mobile device. But perhaps the launch of the application should adapt to the end platform and, for example, instead of the browser, go into the native mode of the smartphone application or smart watch.
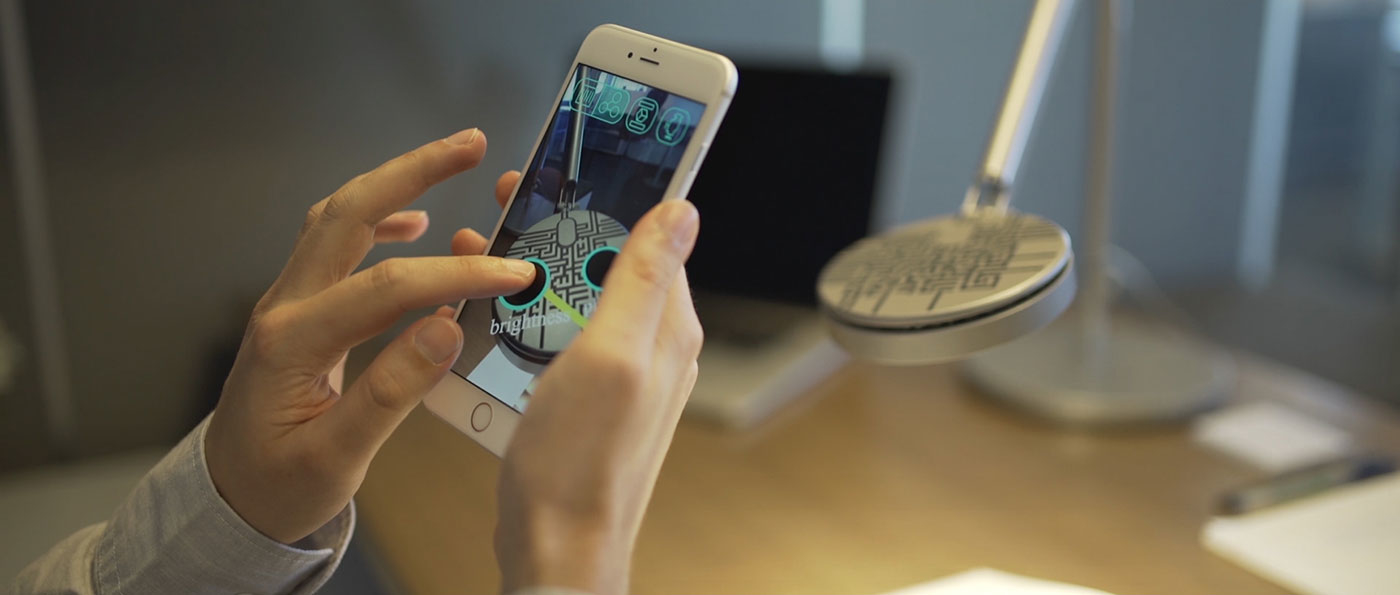 Reality Editor 2 - a web-based tool for controlling the physical world. Video screenshot: Realityeditor
Reality Editor 2 - a web-based tool for controlling the physical world. Video screenshot: RealityeditorSocial Internet of Things is, above all, reliability and security, supported by user confidence in smart devices. There will always be supporters of unprecedented security, who will seal the tablet's camera with tape and block wireless networks. However, it should be so, because any technology should not violate the boundaries of personal life, but coexist with the world of people, complementing and simplifying the ways of solving routine tasks. Information security of IoT devices now completely depends on the reliability of Internet protocols, data transfer technologies, cryptoalgorithms, authorization methods, and the authentication of people and devices. For now, this is mostly centralized systems. Perhaps the rapid development of distributed methods for building information systems based on the blockchain technology will fundamentally solve both the security of the Internet of Things and users' confidence in smart hubs and a variety of connected devices.
In this review, we wanted to consider modern projects and the state of the issue of interaction among the Internet of Things, as well as the impact of user socialization on the development of interfaces with electronics and smart devices. Of course, only in passing the question of the interaction of machines, but the references and reflections around the problem, allow us to conclude that the Social IoT concept is feasible in the near future.
It is now interesting and exciting to observe the development of various innovative projects and to design and develop smart devices and software components to support them. There is no doubt that this review could not cover all the nuances of the interaction of machines and people, as well as the relevant projects and ideas of startups. We hope for your comments with examples of the implementation of such ideas and directions for the development of smart devices.
Interesting resources and links:
Augmented RealityBlockchain & IoT