We continue to "gut" laptops in order to select the optimal CPU. In the
last publication, we focused on budget models. Now let's see how things are with their more expensive counterparts - costing from 30 to 50 thousand rubles. Under the cut - review, analysis, comparative tables and sound conclusions.
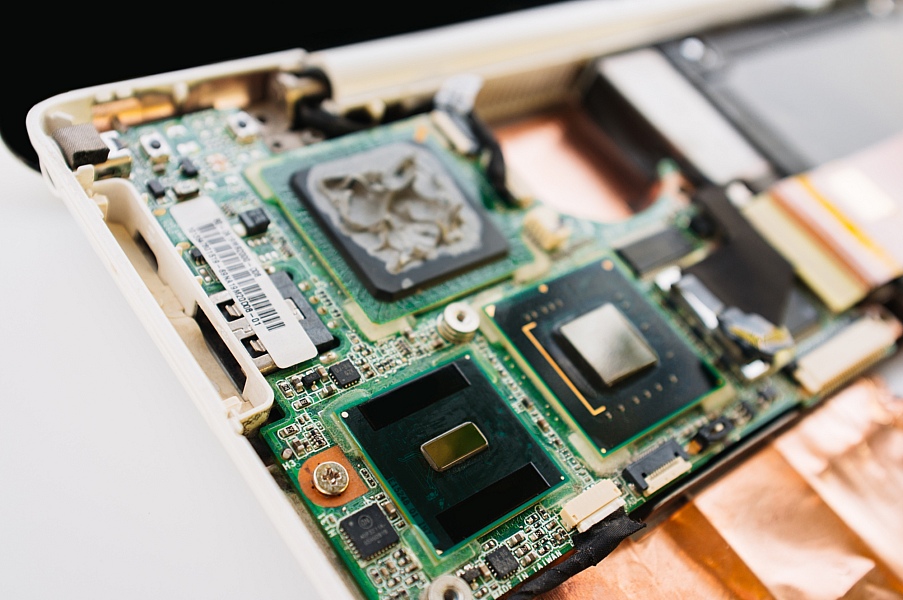

Alas, the reality is that in the past few years, the cost of laptops is constantly growing. What once you could afford for 30 thousand rubles now costs at least 50 thousand. It would seem that the situation is stalemate: spend more - and get less. But not everything is so sad in fact. For five years, progress has significantly moved towards a gradual reduction in power consumption and an increase in the frequency of the CPU. Yes, technologies are changing, yes, characteristics are improving, but behind all this veil of marketing remains the net performance, with which we measure the “processor-motherboard-memory” bundle.
Undoubtedly, with an integrated approach, special attention should be paid to the choice of platform. If we are talking about Intel, it is better to keep in mind at least four generations. With AMD, on the one hand, everything is simpler, since minor changes in the architecture did not bring major improvements in performance. On the other hand, the abundance of various processor naming schemes is confusing. For example, the parallel coexistence of APUs (the name of AMD processors with integrated video core) of business and leptop families with identical characteristics theoretically should not confuse you. However, manufacturers very often resort to tricks of a different plan - instead of a two-channel memory mode, they set one bar of a larger volume. On paper, everything seems to be fine, but in fact they lose to their brethren by about 10-15%. But we'll talk about this a little later - but for now let's analyze the processors in laptops of the price range starting for us.
Laptops price from 30 to 35 thousand rubles
A compromise (medium) version in this range is ultra low power processors. Intel representatives, of course, rule the ball, because as soon as this manufacturer offers truly energy-efficient solutions.
In total, we found five model lines on store shelves. Let's start with the processors with the Braswell architecture (Intel Pentium N3710 and Intel Pentium N3700) - which is a branch from the standard architectures for desktops and laptops and stands alone. In fact, these are sluggish processors with dual-channel DDR3 memory, but in 8 out of 10 cases only one memory channel with no expansion is used in notebooks from the factory.
It should be understood that the Braswell processors are the development of the Bay Trail direction, or, more precisely, the followers of Atom. In these processors, Intel has updated the integrated graphics core HD Graphics to the eighth generation. This means that the Braswell video core has become unified with the architecture of Broadwell. The bottom line is an attractive price and a long laptop life - but only with a good balance of the rest of the strapping in the system. At the same time, Intel does not change the strategy and continues to release sluggish turtles from Q1 2016.
Title
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / threads
| GHz frequency
| Cash MB
|
Intel Pentium N3710
| Q1'16
| 4/4
| 1.6-2.56
| 2MB
|
Intel Pentium N3700
| Q1'15
| 4/4
| 1.6-2.4
| 2MB
|
Next are real processors in the full sense of the word. Recall how architecture changed: Haswell -> Broadwell -> Skylake -> Kaby Lake.

Let's not break the chronology and start with the 4th generation of chips - Haswell. There are several models in laptops: Intel Core i3 4030U, Intel Core i3 4005U, Intel Core i5 4210U and Intel Core i5 4200U. Marking U tells us about low power consumption (from 7.5 to 25 watts, depending on the settings).
These models appeared in 2013-14, but thanks to Hyper Threading technology and relatively high frequencies, they have an acceptable level of performance. Core i3 differs from Core i5 only in one chip - adaptive frequency control. In other words, Core i3 is constantly threshed under load at some kind of fixed frequency, and in Core i5 it dynamically changes in a certain range.
By the way, in many laptops, such processors are adjacent to a discrete graphics card. And this is an ideal solution: in simple scenarios, the integrated graphics core HD Graphics 4400 works, and in games and other resource-intensive tasks the video card is connected.
Title
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / threads
| GHz frequency
| Cash MB
|
Intel Core i5 4210U
| Q2'14
| 2/4
| 1.7-2.7
| 3MB
|
Intel Core i5 4200U
| Q3'13
| 2/4
| 1.6-2.6
| 3MB
|
Intel Core i3 4030U
| Q2'14
| 2/4
| 1.9
| 3MB
|
Intel Core i3 4005U
| Q3'13
| 2/4
| 1.7
| 3MB
|
Haswell is followed by Broadwell. In our case, these are Intel Core i5 5200U, Intel Core i3 5005U processors. In Broadwell, Intel introduced a truly breakthrough technology - the integrated video core Iris with an exclusive large-scale cache. But this did not affect our models - so they do not deserve special attention, even with the raised frequencies.
Title
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / threads
| GHz frequency
| Cash MB
|
Intel Core i5 5200U
| Q1'15
| 2/4
| 2.2-2.7
| 3MB
|
Intel Core i3 5005U
| Q1'15
| 2/4
| 2.0
| 3MB
|
We turn to more (or less) modern processors with current architectures. Skylake first. It is possible to list all the improvements long and dry, but the main thing is the graphics. More precisely, its multimedia part, which is responsible for decoding - it was significantly modified by the manufacturer to meet modern needs. And therefore, as it seems to us, a laptop in this price range without a discrete video card is worth taking at least with Skylake. You will not be able to play on the HD Graphics 5xx series cores, but it will be able to play videos with demanding codecs.
Using the integrated video core Skylake, you can hardware-encode and decode video in H.265 / HEVC, JPEG and MJPEG format. A block for image processing with support for up to four cameras with a resolution of 13 megapixels was registered in the micro-architecture. A pair can work simultaneously: encode and recognize faces, apply an HDR filter, etc.
In multimedia tests using AVX2 and FMA instructions, the Skylake architecture surpasses Haswell by an average of a quarter.
The time of the appearance of Skylake coincided with the flourishing of Windows 10, and the design of the processor took into account the features of this OS. So, thanks to the Speed Shift technology, the Skylake models have gained greater independence in managing their own energy-saving states. Engineers, realizing the importance of power consumption in transient conditions, divided the processor into smaller parts. Frequency switching is faster, and unused blocks automatically hibernate.
With the micro-architecture, there have also been changes (mainly in the initial stages of the formation of executive teams), aimed at increasing the number of concurrently performed operations. Unlike previous architectures, Skylake has increased the length of the queue of microinstructions from 192 to 224. Due to this, the degree of parallelism increases as they are executed and, consequently, the overall performance. But in this case it was necessary not to forget about the modifications of the branch prediction blocks and to improve the cycle of extraordinary execution of commands.
Compared with Haswell, Skylake noticeably accelerated cache responsiveness due to a twofold decrease in the associativity of the L2 cache. And its memory controller got support for DDR4.
To top it off, Skylake processors got a faster 2-mode ring bus - slow and fast. There is no exact data on the implementation of the mode in mobile processors, but, most likely, the processor itself decides which mode to use - based on the executable code and the loading depth of the execution units.
Title
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / threads
| GHz frequency
| Cash MB
|
Intel Core i5 6200U
| Q3'15
| 2/4
| 2.3-2.8
| 3MB
|
Intel Core i3 6100U
| Q3'15
| 2/4
| 2.3
| 3MB
|
Intel Core i3 6006U
| Q4'16
| 2/4
| 2.0
| 3MB
|
Intel Pentium 4405U
| Q3'15
| 2/4
| 2.1
| 2MB
|

The newest architecture is Kaby Lake. For the production of such processors, the blue giant uses an advanced process technology of 14 nm - that is, in fact, Kaby Lake has become a Skylake polish. The delayed transition to 14 nm technical process has failed in the usual sequence of cycles, and "tick-tac" has become a "tick-tac-soooo." The latter should be taken as an optimization of the already improved architecture, sorry for the tautology. Due to an improved process technology, Intel was able to increase the frequency without deterioration in consumer properties. But the hardware component of the changes almost did not touch - only some parts of the processor pulled up to the actual characteristics.
Now about the multimedia part of the CPU. Kaby Lake taught the hardware to encode and decode 4K video in HEVC format with a Main10 profile. Now for this you do not need to use the main graphics core in parallel with the media gate. Accordingly, the power consumption of the processor as a whole has decreased.
Added support for VP9 codec with 8 and 10-bit depth. What is this codec and why did it suddenly become so important? Watch YouTube? So, he completely switched to it. In addition, improvements will be felt by streamer players who can simultaneously play and stream video without dropping frames and losing some CPU performance. The Video Quality unit, which is responsible for the operation of the hardware encoder, has expanded its functionality by introducing support for HDR content with a 4: 2: 0 color profile.
Title
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / threads
| GHz frequency
| Cash MB
|
Intel Core i5 7200U
| Q3'16
| 2/4
| 2.5-3.1
| 3MB
|
Intel Core i3 7100U
| Q3'16
| 2/4
| 2.4
| 3MB
|
Intel Pentium 4415U
| Q1'17
| 2/4
| 2.4
| 2MB
|
In principle, in terms of competition, AMD did not pose a threat to Intel until the advent of the Zen architecture. But as an alternative, consider AMD processors. The company has an original approach to naming architectures. It uses not one sequence, but several - dividing them by scope.
Mobile APU: Llano → Trinity → Richland → Kaveri → Carrizo → Bristol Ridge
Platform
| Year of issue
| Technical process
| CPU architecture
| Memory support
| Graphics core
|
Bristol ridge
| 2016
| 28 nm
| 4th generation Bulldozer
| DDR4
| 3rd generation, GCN Radeon R9 285, R9 380, R9 380X,
|
Carrizo
| 2015
| 28 nm
| 4th generation Bulldozer
| DDR3L / DDR3
| 3rd generation, GCN Radeon R9 285, R9 380, R9 380X,
|
Kaveri
| 2014
| 28 nm
| 3rd generation Bulldozer
| DDR3L / DDR3
| 2nd generation, GCN Radeon R7 260 / 260X, R9 290/290X, R9 295X2, R7 360, R9 390 / 390X
|
Richland
| 2013
| 32 nm
| 2nd generation Bulldozer
| DDR3L / DDR3
| VLIW4, Radeon HD 6900
|
Trinity
| 2012
| 32 nm
| 2nd generation Bulldozer
| DDR3L / DDR3
| VLIW4, Radeon HD 6900
|
Llano
| 2011
| 32 nm
| AMD K10.5
| DDR3L / DDR3
| VLIW5, Radeon HD 5000
|
Ultra mobile APU: Brazos → Kabini → Beema → Carrizo-L → Stoney Ridge
Platform
| Year of issue
| Technical process
| CPU architecture
| Memory support
| Graphics core
|
Stoney ridge
| 2016
| 28 nm
| 4th generation Bulldozer
| DDR4
| 3rd generation, GCN Radeon R9 285, R9 380, R9 380X,
|
Carrizo-l
| 2015
| 28 nm
| Puma +
| DDR3L
| 2nd generation, GCN Radeon R7 260 / 260X, R9 290/290X, R9 295X2, R7 360, R9 390 / 390X
|
Beema
| 2014
| 28 nm
| Puma
| DDR3L
| 2nd generation, GCN Radeon R7 260 / 260X, R9 290/290X, R9 295X2, R7 360, R9 390 / 390X
|
Kabini
| 2013
| 28 nm
| Jaguar
| DDR3L
| 2nd generation, GCN Radeon R7 260 / 260X, R9 290/290X, R9 295X2, R7 360, R9 390 / 390X
|
Brazos
| 2011
| 40 nm
| Bobcat
| DDR3L
| VLIW5, Radeon HD 5000
|
But often under a similar name completely different generations of architectures are hidden. For example, Carrizo and Carrizo-L. The first is based on the architecture of the Excavator processor cores (the fourth and last optimization of the Bulldozer architecture), the second took the Puma + core. In addition, these areas have completely different graphic modules: Carrizo was produced with the third generation GCN (Radeon R9 285, R9 380, R9 380X), and Carrizo-L - only with the second GCN (Radeon R7 260 / 260X, R9 290 / 290X , R9 295X2, R7 360, R9 390 / 390X).
In the notebook segment from 30 to 35 thousand rubles there are models with APU based on five generations of architectures - these are ultra mobile Stoney Ridge, Carrizo-L and mobile Bristol Ridge, Carrizo, Kaveri.

Let's start to solve the quest with the names of the lower models: AMD A9-Series 9420, AMD A9-Series 9410 and AMD A8-Series 7410. A8-series based on Carrizo-L - with a slow core and good graphics (among all the shortcomings AMD has one dignity - GP with GCN architecture).
On the A8, graphics of the second generation were set up, analogs of which are video cards for desktop systems of the Radeon R7 260 / 260X, R9 290 / 290X, R9 295X2, R7 360, R9 390 / 390X series.
To ensure that the APU was not too voracious, AMD had to reduce the number of actuators to the minimum values. So, in the A8-Series 7410, the ratio of stream processors to texture units and rasterization units is 128: 8: 4. When comparing the frequency and total memory, it turns out that the DDR3 A8-Series 7410 is 1/8 part of the Radeon HD 7790 in terms of performance.
The older models on the Stoney Ridge core received support for DDR4 memory, a more or less current version of the Buldozzer processor and the third generation GCN. A9-Series 9420/10 equipped with a large number of stream processors with a ratio of 192: 12: 4. Thanks to the two channels of DDR4 memory, the graphics are already inflamed with low-end discrete graphics cards 3-4 years old. But manufacturers do not always use both channels and prefer to install one module of a larger volume. Because of this, the speed of processor computing drops sharply, and even more - graphics performance.
Full-fledged APUs, similar in characteristics to desktop processors, are also represented by a pair of architectures: Kaveri and Bristol Ridge. The AMD A10-Series 7300 is built on Kaveri, but we dismiss it immediately: despite the second-generation GCN graphics, this chip has an outdated video core without the support for encoding and decoding of modern standards.
AMD A12-Series 9720P, 9700P and AMD A10-Series 9620P, 9600P received support for DDR4 memory, third-generation GCN (HEVC, H.265 v1 hardware decoding and encoding with a resolution of up to 4K and 8-bit representation) with a large number of stream processors (up to 512: 32: 8). In this version of the APU on an equal footing with Intel processors and easily overtake them in games.
Model
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / threads
| Frequency, GHz
| Kesh, MB
|
AMD A12-Series 9720P
| Q1'16
| 4/4
| 2.7-3.6
| 2MB
|
AMD A12-Series 9700P
| Q1'16
| 4/4
| 2.5-3.4
| 2MB
|
AMD A10-Series 9620P
| Q1'17
| 4/4
| 2.5-3.4
| 2MB
|
AMD A10-Series 9600P
| Q1'16
| 4/4
| 2.4-3.3
| 2MB
|
AMD A10-Series 7300
| Q2'14
| 4/4
| 1.9-3.2
| 4MB
|
AMD A9-Series 9420
| Q1'16
| 2/2
| 3.0-3.6
| 1MB
|
AMD A9-Series 9410
| Q1'16
| 2/2
| 2.9-3.5
| 1MB
|
AMD A8-Series 7410
| Q3'15
| 4/4
| 2.2-2.5
| 2MB
|
In this category of prices, it is preferable not to focus only on the processor, but to choose a balanced system with DDR4 memory sitting on two channels. If the laptop is designed for gaming, it is difficult to say who is better than Intel or AMD. If we are talking about a laptop without a discrete video card, you can safely take a model with an APU AMD Bristol Ridge. If you are considering a device with a separate video card, it is better to look at models with processors on the architecture of Kaby Lake and Skylake.
In order to approximately estimate the performance of all the above models, we have collected for you typical test results from the Geekbench 4 online database.
Model
| Single-core
| Multi-core
|
Intel Core i5 7200U
| 3941
| 7871
|
Intel Core i5 6200U
| 3732
| 7157
|
Intel Core i3 7100U
| 3288
| 6465
|
Intel Core i3 6100U
| 3266
| 6368
|
Intel Core i5 5200U
| 3374
| 6152
|
Intel Core i5 4210U
| 3184
| 5725
|
Intel Pentium 4415U
| 2949
| 5647
|
Intel Core i5 4200U
| 2938
| 5574
|
Intel Core i3 6006U
| 2803
| 5535
|
AMD A12-Series 9720P
| 2303
| 5399
|
Intel Core i3 5005U
| 2647
| 5045
|
Intel Pentium 4405U
| 2618
| 5002
|
AMD A12-Series 9700P
| 2294
| 5256
|
AMD A10-Series 9620P
| 2192
| 5233
|
AMD A10-Series 9600P
| 2172
| 5215
|
Intel Core i3 4030U
| 2466
| 4693
|
Intel Core i3 4005U
| 2247
| 4333
|
AMD A10-Series 7300
| 1971
| 4039
|
AMD A9-Series 9420
| 2314
| 3513
|
AMD A9-Series 9410
| 2258
| 3482
|
AMD A8-Series 7410
| 1422
| 3835
|
Intel Pentium N3710
| 1189
| 3639
|
Intel Pentium N3700
| 1136
| 3452
|
Laptops price from 35 to 40 thousand rubles
Strangely enough, but the increase of five thousand to the price of a laptop only slightly expands the list of processors that may be in it.
To the previously described processors added "hybrids" AMD, on the architecture of Kaveri and Carrizo, and even those "not the first freshness." It is clear that, choosing between the APU released in 2014 and 2015, it is better to look towards the models on the Bristol Ridge.
Title
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / threads
| Frequency, GHz
| Kesh, MB
|
AMD FX-Series FX 7500
| Q2'14
| 4/4
| 2.1-3.3
| 4MB
|
AMD A10-Series 8700P
| Q1'15
| 4/4
| 1.8-3.2
| 2MB
|
AMD A10-Series 8700B
| Q1'15
| 4/4
| 1.8-3.2
| 2MB
|
So why with a similar processor laptops are more expensive? The answer to this question lies on the surface. Either this is a stale product, or the manufacturer installs more capacious hard drives or uses * VA / IPS instead of TN panels. In the latter case, the laptop becomes more attractive.
Generic Geekbench 4 test results for the entire category are:
Model:
| Single-core
| Multi-core
|
Intel Core i5 7200U
| 3941
| 7871
|
Intel Core i5 6200U
| 3732
| 7157
|
Intel Core i3 7100U
| 3288
| 6465
|
Intel Core i3 6100U
| 3266
| 6368
|
Intel Core i5 5200U
| 3374
| 6152
|
Intel Core i5 4210U
| 3184
| 5725
|
Intel Pentium 4415U
| 2949
| 5647
|
Intel Core i5 4200U
| 2938
| 5574
|
Intel Core i3 6006U
| 2803
| 5535
|
AMD A12-Series 9720P
| 2303
| 5399
|
Intel Core i3 5005U
| 2647
| 5045
|
Intel Pentium 4405U
| 2618
| 5002
|
AMD A12-Series 9700P
| 2294
| 5256
|
AMD A10-Series 9620P
| 2192
| 5233
|
AMD A10-Series 9600P
| 2172
| 5215
|
AMD A10-Series 8700P
| 2113
| 5058
|
Intel Core i3 4030U
| 2466
| 4693
|
AMD A10-Series 8700B
| 2075
| 5038
|
AMD FX-Series FX 7500
| 2037
| 4617
|
Intel Core i3 4005U
| 2247
| 4333
|
AMD A10-Series 7300
| 1971
| 4039
|
AMD A9-Series 9420
| 2314
| 3513
|
AMD A9-Series 9410
| 2258
| 3482
|
AMD A8-Series 7410
| 1422
| 3835
|
Intel Pentium N3710
| 1189
| 3639
|
Intel Pentium N3700
| 1136
| 3452
|
Laptops price from 40 to 45 thousand rubles
Finally, we got to really powerful configurations, when the number of cores increases to four, and the number of simultaneously executed threads - to eight. And this segment is opened by an Intel Core i7 4700MQ processor.
 Intel Core i7 4700MQ. Photo: hardwareluxx.ru
Intel Core i7 4700MQ. Photo: hardwareluxx.ruAlthough it was released in 2013 on the 22 nm process technology, in performance it is significantly superior to all previously described models. A significant disadvantage of such a choice is the power consumption that is crazy by the standards of laptops (TDP 47 W). In a thin case, respectively, it is not inserted, therefore, laptops with such a processor should rather be considered as a replacement for the desktop.
Title
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / threads
| Frequency, GHz
| Kesh, MB
|
Intel Core i7 4700MQ
| Q2'13
| 4/8
| 2.4-3.4
| 6MB
|
Intel Core i7 7500U
| Q3'16
| 2/4
| 2.7-3.5
| 4MB
|
Intel Core i7 6500U
| Q3'15
| 2/4
| 2.5-3.1
| 4MB
|
For compact models, there is a pair of efficient ones in the issue of power consumption of i7 7500U processors (TDP 15 W) and i7 6500U. Both are fast, but they only have two cores. The first is based on the architecture of Kaby Lake, the second is on Skylake. As you have already guessed, there are not so many differences between them, therefore, if you want to save and equal other characteristics, feel free to choose the one that is cheaper.
From AMD, you can consider a single APU with the strange name FX-Series FX 9800P. The FX series are Bristol Ridge's most powerful APUs, equipped with powerful integrated graphics. Due to 512 stream processors (for comparison, in the APU Bristol Ridge A10 and A12 are 384), the GPU speed in the FX series processors reached the level of Radeon R7250.
Title
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / threads
| GHz frequency
| Cash MB
| Those. Pr-s. Nm
|
AMD FX-Series FX 9800P
| Q1'16
| 4/4
| 2.7-3.6
| 2MB
| 28
|
The performance of processors (including previous models) according to the results of testing in single-threaded and multi-core mode according to Geekbench 4.
Model:
| Single-core
| Multi-core
|
Intel Core i7 4700MQ
| 4159
| 13171
|
Intel Core i7 7500U
| 4461
| 8891
|
Intel Core i5 7200U
| 3941
| 7871
|
Intel Core i7 6500U
| 3919
| 7717
|
Intel Core i5 6200U
| 3732
| 7157
|
Intel Core i3 7100U
| 3288
| 6465
|
Intel Core i3 6100U
| 3266
| 6368
|
Intel Core i5 5200U
| 3374
| 6152
|
Intel Core i5 4210U
| 3184
| 5725
|
Intel Pentium 4415U
| 2949
| 5647
|
Intel Core i5 4200U
| 2938
| 5574
|
Intel Core i3 6006U
| 2803
| 5535
|
AMD FX-Series FX 9800P
| 2381
| 5364
|
AMD A12-Series 9720P
| 2303
| 5399
|
Intel Core i3 5005U
| 2647
| 5045
|
Intel Pentium 4405U
| 2618
| 5002
|
AMD A12-Series 9700P
| 2294
| 5256
|
AMD A10-Series 9620P
| 2192
| 5233
|
AMD A10-Series 9600P
| 2172
| 5215
|
AMD A10-Series 8700P
| 2113
| 5058
|
Intel Core i3 4030U
| 2466
| 4693
|
AMD A10-Series 8700B
| 2075
| 5038
|
AMD FX-Series FX 7500
| 2037
| 4617
|
Intel Core i3 4005U
| 2247
| 4333
|
AMD A10-Series 7300
| 1971
| 4039
|
AMD A9-Series 9420
| 2314
| 3513
|
AMD A9-Series 9410
| 2258
| 3482
|
AMD A8-Series 7410
| 1422
| 3835
|
Intel Pentium N3710
| 1189
| 3639
|
Intel Pentium N3700
| 1136
| 3452
|
Laptops price from 45 to 50 thousand rubles
We are close to a denouement and to the most controversial processors.
On the part of Intel, the most advanced and fast 4-core processors on the Skylake architecture - Intel Core i7 6700HQ and 6300HQ - appear in this category. Both heat up very quickly (TDP 45 W) and require a massive cooling system. Therefore, as is the case with the Core i7 4700MQ, laptops with an Intel Core i7 6700HQ and 6300HQ will be big, hot and heavy, but still quite productive.Title
| Date of issue
| Number of cores / Pot s
| GHz frequency
| Cash MB
|
Intel Core i7 6700HQ
| Q3'15
| 4/8
| 2.6-3.5
| 6MB
|
Intel Core i5 6300HQ
| Q3'15
| 4/4
| 2.3-3.2
| 6MB
|
What will AMD show us? And here - attention - the previously unknown types of APUs from the business line appear - these are AMD A10-Series 8730B and AMD A8-Series 9600B. The AMD A10-Series 8730B is based on the Carrizo PRO architecture - essentially the usual Carrizo with DDR4 memory support. Alas, in the pursuit of profit, this processor is often equipped with a single-channel memory, which dramatically affects the performance as a whole. At the heart of the AMD A8-Series 9600B is the architecture of Bristol Ridge and is also found in combination with single-channel memory in 9 out of 10 cases. In other words - the APUs are not bad, but you can stumble upon a laptop with a terrible imbalance in the configuration.Total
The optimal processor in the category from 30 to 35 thousand rubles:
Intel Core i5 7200U and Intel Core i5 6200U with good performance and low power consumption. The second is equipped, for example, Lenovo V110-15ISK or Lenovo IdeaPad 310 . Additionally, you will get normal support for modern multimedia formats. And if you find a configuration with a discrete graphics card - then a decent gaming performance with a long battery life. Adherents of AMD products will appeal to the AMD A12-Series 9720P. It does not have enough stars from the sky, but at the same time it provides quite good gaming capabilities without a discrete video card.The optimal processor in the category from 35 to 40 thousand rubles:
The choice remains the same - Intel Core i5 7200U and Intel Core i5 6200U. This may be, for example, Lenovo IdeaPad 320-15IKB . “Additional five thousand” is an overpayment mainly for a more spacious hard drive, a fast discrete graphics card, or a good LCD matrix.The optimal processor in the category from 40 to 45 thousand rubles:
In the course goes heavy artillery in the face of 4-core 8-stream processor Intel Core i7 4700MQ. Undoubtedly, in this case will have to make concessions, because Placing such a hot processor requires a good cooling system and a spacious case. But in the end you will get a good replacement for the average desktop. If "size matters", look at the current new product - Intel Core i7 7500U or Intel Core i7 6500U. Both are great for thin laptops, and those who like to play should choose a configuration with a discrete graphics card.The optimal processor in the category from 45 to 50 thousand rubles:
Here, out of competition "hot guys" with the architecture of Skylake. Moreover, if we really want to bet on performance, then I’ll be picking up an Intel Core i7 6700HQ - for example, in an Acer Aspire V5-591G-75ZA laptop .The results of Geekbench 4 for all processors in our review:Model:
| Single-core
| Multi-core
|
Intel Core i7 6700HQ
| 4633
| 14392
|
Intel Core i7 4700MQ
| 4159
| 13171
|
Intel Core i5 6300HQ
| 4199
| 11469
|
Intel Core i7 7500U
| 4461
| 8891
|
Intel Core i5 7200U
| 3941
| 7871
|
Intel Core i7 6500U
| 3919
| 7717
|
Intel Core i5 6200U
| 3732
| 7157
|
Intel Core i3 7100U
| 3288
| 6465
|
Intel Core i3 6100U
| 3266
| 6368
|
Intel Core i5 5200U
| 3374
| 6152
|
Intel Core i5 4210U
| 3184
| 5725
|
Intel Pentium 4415U
| 2949
| 5647
|
Intel Core i5 4200U
| 2938
| 5574
|
Intel Core i3 6006U
| 2803
| 5535
|
AMD FX-Series FX 9800P
| 2381
| 5364
|
AMD A12-Series 9720P
| 2303
| 5399
|
Intel Core i3 5005U
| 2647
| 5045
|
Intel Pentium 4405U
| 2618
| 5002
|
AMD A12-Series 9700P
| 2294
| 5256
|
AMD A10-Series 9620P
| 2192
| 5233
|
AMD A10-Series 9600P
| 2172
| 5215
|
AMD A10-Series 8700P
| 2113
| 5058
|
Intel Core i3 4030U
| 2466
| 4693
|
AMD A10-Series 8700B
| 2075
| 5038
|
AMD FX-Series FX 7500
| 2037
| 4617
|
Intel Core i3 4005U
| 2247
| 4333
|
AMD A10-Series 7300
| 1971
| 4039
|
AMD A9-Series 9420
| 2314
| 3513
|
AMD A9-Series 9410
| 2258
| 3482
|
AMD A8-Series 9600B
| 1433
| 4150
|
AMD A10-Series 8730B
| 1655
| 3824
|
AMD A8-Series 7410
| 1422
| 3835
|
Intel Pentium N3710
| 1189
| 3639
|
Intel Pentium N3700
| 1136
| 3452
|
And the general table of characteristics:Segment 30-35 thousand. Rub.
|
Title
| Number of cores / Pot s
| Frequency, GHz
| Those. pr-s, nm
| Nth, W
| Memory (type / frequency / channels)
| Architecture
| Graphics
|
Intel Core i5 7200U
| 2/4
| 2.5-3.1
| 14
| 7.5-25
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Kaby lake
| HD Graphics 620
|
Intel Core i5 6200U
| 2/4
| 2.3-2.8
| 14
| 7.5-25
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Skylake
| HD Graphics 520
|
Intel Core i5 5200U
| 2/4
| 2.2-2.7
| 14
| 7.5-25
| DDR3L, LPDDR3 / 1333-1600 / 2
| Broadwell
| HD Graphics 5500
|
Intel Core i5 4210U
| 2/4
| 1.7-2.7
| 22
| 7.5-25
| DDR3L, LPDDR3 / 1333-1600 / 2
| Haswell
| HD Graphics 4400
|
Intel Core i5 4200U
| 2/4
| 1.6-2.6
| 22
| 7.5-25
| DDR3L, LPDDR3 / 1333-1600 / 2
| Haswell
| HD Graphics 4400
|
Intel Core i3 7100U
| 2/4
| 2.4
| 14
| 7.5-25
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Kaby lake
| HD Graphics 620
|
Intel Core i3 6100U
| 2/4
| 2.3
| 14
| 7.5-25
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Skylake
| HD Graphics 520
|
Intel Core i3 6006U
| 2/4
| 2.0
| 14
| 7.5-25
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Skylake
| HD Graphics 520
|
Intel Core i3 5005U
| 2/4
| 2.0
| 14
| 7.5-25
| DDR3L, LPDDR3 / 1333-1600 / 2
| Broadwell
| HD Graphics 5500
|
Intel Core i3 4030U
| 2/4
| 1.9
| 22
| 7.5-25
| DDR3L, LPDDR3 / 1333-1600 / 2
| Haswell
| HD Graphics 4400
|
Intel Core i3 4005U
| 2/4
| 1.7
| 22
| 7.5-25
| DDR3L, LPDDR3 / 1333-1600 / 2
| Haswell
| HD Graphics 4400
|
Intel Pentium 4415U
| 2/4
| 2.4
| 14
| 10-15
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Kaby lake
| HD Graphics 610
|
Intel Pentium 4405U
| 2/4
| 2.1
| 14
| 10-15
| DDR4, LPDDR3 / 1600-1866 /2
| Skylake
| HD Graphics 510
|
Intel Pentium N3710
| 4/4
| 1,6-2,56
| 14
| 4-6
| DDR3L / 1600/2
| Braswell
| HD Graphics 405
|
Intel Pentium N3700
| 4/4
| 1,6-2,4
| 14
| 4-6
| DDR3L / 1600 /2
| Braswell
| HD Graphics
|
| | | | | | |
|
AMD A12-Series 9720P
| 4/4
| 2,7-3,6
| 28
| 12-15
| DDR4, DDR3 / 1600-1866 /2
| Bristol Ridge
| R7
|
AMD A12-Series 9700P
| 4/4
| 2,5-3,4
| 28
| 12-15
| DDR4, DDR3 / 1600-1866 /2
| Bristol Ridge
| R7
|
AMD A10-Series 9620P
| 4/4
| 2,5-3,4
| 28
| 12-15
| DDR4, DDR3 1600-1866 /2
| Bristol Ridge
| R5
|
AMD A10-Series 9600P
| 4/4
| 2,4-3,3
| 28
| 12-15
| DDR4, DDR3 / 1600-1866 /2
| Bristol Ridge
| R5
|
AMD A10-Series 7300
| 4/4
| 1,9-3,2
| 28
| 15-19
| DDR3U, DDR3L, DDR3 / 1333-1600 /2
| Kaveri
| R6
|
AMD A9-Series 9420
| 2/2
| 3,0-3,6
| 28
| 10-15
| DDR4 / 2133 /1
| Stoney Ridge
| R5
|
AMD A9-Series 9410
| 2/2
| 2,9-3,5
| 28
| 10-15
| DDR4 / 2133 /1
| Stoney Ridge
| R5
|
AMD A8-Series 7410
| 4/4
| 2,2-2,5
| 28
| 12-25
| DDR3L / 1866 /1
| Carrizo-L
| R5
|
35-40 . .
|
Title
| - /-
| Frequency, GHz
| Those. -.,
| -., .
| Memory
| . -
| Graphics
|
AMD FX-Series FX 7500
| 4/4
| 2,1-3,3
| 28
| 15-19
| DDR3U, DDR3L, DDR3 / 1333-1600 /2
| Kaveri
| R7
|
AMD A10-Series 8700P
| 4/4
| 1,8-3,2
| 28
| 12-35
| DDR3 / 1600-2133 /2
| Carrizo
| R6
|
AMD A10-Series 8700B
| 4/4
| 1,8-3,2
| 28
| 12-35
| DDR3 / 1600-2133 /2
| Carrizo
| R6
|
40-45 . .
|
Title
| - /-
| Frequency, GHz
| Those. -.,
| -., .
| Memory
| . -
| Graphics
|
Intel Core i7 4700MQ
| 4/8
| 2.4-3.4
| 22
| 35-47
| DDR3L / 1333-1600 / 2
| Haswell
| HD Graphics 4600
|
Intel Core i7 7500U
| 2/4
| 2.7-3.5
| 14
| 7.5-25
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Kaby lake
| HD Graphics 620
|
Intel Core i7 6500U
| 2/4
| 2.5-3.1
| 14
| 7.5-25
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Skylake
| HD Graphics 520
|
| | | | | | |
|
AMD FX-Series FX 9800P
| 4/4
| 2.7-3.6
| 28
| 12-15
| DDR4 / 1866/2
| Bristol ridge
| R7
|
45-50 thousand rubles.
|
Title
| Number of cores / Pot s
| Frequency, GHz
| Those. pr-s., nm
| Nth., Watts.
| Memory
| Code. called
| Graphics
|
Intel Core i7 6700HQ
| 4/8
| 2.6-3.5
| 14
| 35-45
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Skylake
| HD Graphics 530
|
Intel Core i5 6300HQ
| 4/4
| 2.3-3.2
| 14
| 35-45
| DDR4, LPDDR3, DDR3L / 1600-2133 / 2
| Skylake
| HD Graphics 530
|
| | | | | | |
|
AMD A10-Series 8730B
| 4/4
| 2.4-3.3
| 28
| 12-35
| DDR4 / 2400/2
| Carrizo pro
| R5
|
AMD A8-Series 9600B
| 4/4
| 2.4-3.3
| 28
| 12-15
| DDR4 1866/2
| Bristol ridge
| R5
|
You may also be interested in:- Processors in budget laptops: what to choose?