| Biological | Nuclear |
|---|
| Cost of receipt | + / ++ | ++++ |
| Technical difficulty | + | +++ |
| Dual-use potential (military / civilian) | +++ | +++ |
| Destructive potential | +++ | +++ |
| Difficulty tracking | +++ | ++ |
Legend: + = low, ++ = medium, +++ = high, ++++ = very highThe Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scientists Support (or the Wilson Center) prepared the report “
Intellectual and Internet-connected biolabs of the future: perspectives and dangers of the Fourth Industrial Revolution ”. The experts conducted a fundamental analysis of the situation, which is emerging on the background of rapid development and convergence of several technologies:
• genetic editing;
• Artificial Intelligence;
• automation;
• cloud computing;
• and etc.
The convergence and further development of these technologies, according to experts, will lead to the emergence of Internet-connected intelligent biolaboratories with a high degree of automation of actions. Powerful synthetic biology tools (such as the CRISPR genetic editing technique) will combine with AI, which will allow you to create new effective drugs and vaccines, but at the same time create risks of genetic engineering of very powerful new toxins. Grow GMO arbitrary composition will be easier than ever.
Already, there are more and more research areas where automatic and remote tasks can be accomplished with a few mouse clicks. There is no doubt that scientific and technical progress will not stop and the functionality of such autonomous biological laboratories will grow, especially if AI is used for their work. It is even theoretically possible that a person needs only to set a list of properties for GMOs that he wants to create - and the artificial intelligence system will select the appropriate structure of the genome and synthesize GMOs on request. Editing techniques like CRISPR will become available to a wide range of customers, and not just a small number of competent and qualified specialists, as now.
Experts point out that governments of different countries understand the threat of biological weapons. In particular, some measures have already been taken to limit the access of potential intruders to pathogens or tools that can be used to create biological weapons. However, a very fast pace of scientific and technological progress opens up new loopholes for villains, and government regulation does not keep pace with them. According to experts, one of the best ways to proactively protect against the misuse of new technologies is government funding for promising startups in areas such as artificial intelligence and genome sequencing.
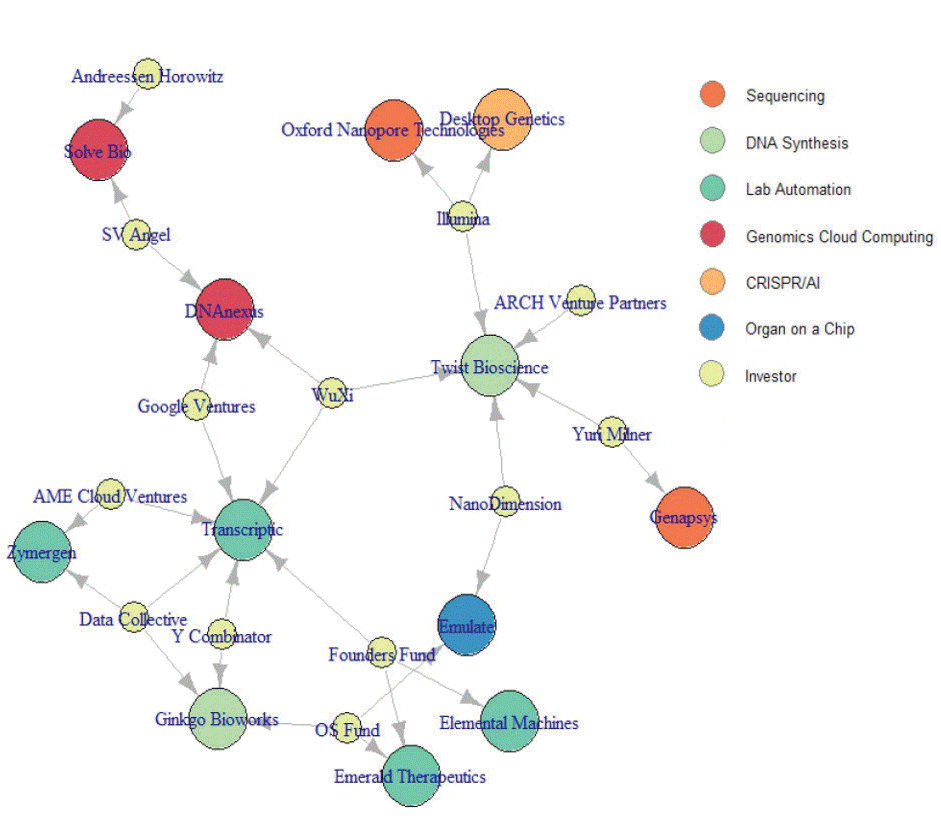 Investments in technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution: genome sequencing, DNA synthesis, automation of laboratory activities, genomic cloud computing, CRISPR and artificial intelligence, organ growing on microchips. Green Circles Marked Investment Funds
Investments in technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution: genome sequencing, DNA synthesis, automation of laboratory activities, genomic cloud computing, CRISPR and artificial intelligence, organ growing on microchips. Green Circles Marked Investment FundsAt the time of the adoption
of the Biological Weapons Convention (1972) and other government regulations aimed at preventing the threat of biological warfare, the greatest threat seemed to be the leakage of a biological agent from a BSL-4 class laboratory, that is, the fourth maximum level of biosafety.
 The location of all biological laboratories class BSL-4, capable of releasing biological weapons
The location of all biological laboratories class BSL-4, capable of releasing biological weaponsBut the threat becomes much more serious. For example, the remaining smallpox strains are stored in only two BSL-4 laboratories in the world - one in the United States and the other in Russia. Now it is enough to guard these two laboratories. But the smallpox genetic code is freely available on the Internet, and in the future nothing can enable an attacker to reproduce the
Variola major genetic code of variola virus with a mortality of 20–90% or create a genetically modified version with a mortality rate closer to 100% on its basis. In nature, the variola virus evolved 16−68 thousand years ago, but genetics are able to continue the process of its evolution.
Recently, Canadian geneticists have been
able to restore the horse pox virus , which was considered lost a long time ago. Curiously, in their work they used DNA synthesis by request in a remote laboratory. This is a prototype of how automatic laboratories will work on the synthesis of organisms in the future. You just point out the DNA chain you need - and you get the sample by mail.
For example, three mutations in the H7N9 avian influenza virus are enough to adapt this virus to spread among people like ordinary flu. Given the death rate of 40%, one can imagine the chaos that will occur in society after the start of the epidemic of such a flu.
The risk of creating biological weapons grows with the cheapening and spread of modern technologies of synthetic biology. Wilson Center experts warn that the civil defense system should be prepared to repel bioterrorism attacks not only from known viruses (as now), but also from unknown strains from which there are no vaccines yet. That is, it is necessary to work out a system for rapid collection of samples and removal of the vaccine in the shortest possible time.
We need to prepare for the fact that bioterrorism will become an everyday part of our daily life. So that in case of another attack, there would be no panic, and all citizens would act according to instructions.