
The rules for eye protection when working at a computer are well known: relax more, take short breaks, take your eyes off the screen every 20 minutes and look at the most distant objects in the perspective view for 20 seconds.
However, the displays have long gone beyond the desktop. We look at a laptop, smartphone, TV, tablet, e-book - everywhere we are surrounded by eye-catching light sources. Exercise and work breaks alone cannot solve the problem of eye strain. We face headaches, eye problems and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Fortunately, the developers at the software and hardware level have become more concerned about the health of the user. Appeared technology and software to minimize the light effects of displays.
Unwanted effects
 Computer visual syndrome
Computer visual syndrome is the official term coined by the American Optometrist Association. The syndrome is characterized by a decrease in visual acuity, difficulties in looking from close objects to faraway objects and back, doubling of visible objects, black flies and darkening of the eyes, excessive light sensitivity, etc.
17 times per minute, on average, our eyes blink, but when we look at the screen, we “forget” to blink, which often leads to a feeling of dryness or itching. We often sit, taking a difficult posture for the body, forget about rest, and relax just by opening another tab in the browser.
One of the causes of "computer syndrome" is the flickering of the display caused by the process of controlling the brightness of the backlight (pulse-width modulation,
PWM ). LED backlight does not shine constantly, but alternately turns on and off for the smallest fraction of a second. Screen flickering may occur, especially at low brightness levels.
This problem is typical not only for computer monitors, but also for
AMOLED displays of smartphones. Changes in the brightness of the backlight when it is turned on and off, even imperceptible at first glance, are a weighty reason for the emergence of computer visual syndrome. There are technologies that bypass possible PWM problems. For example, you can remove flicker by creating a permanent source of LED illumination.
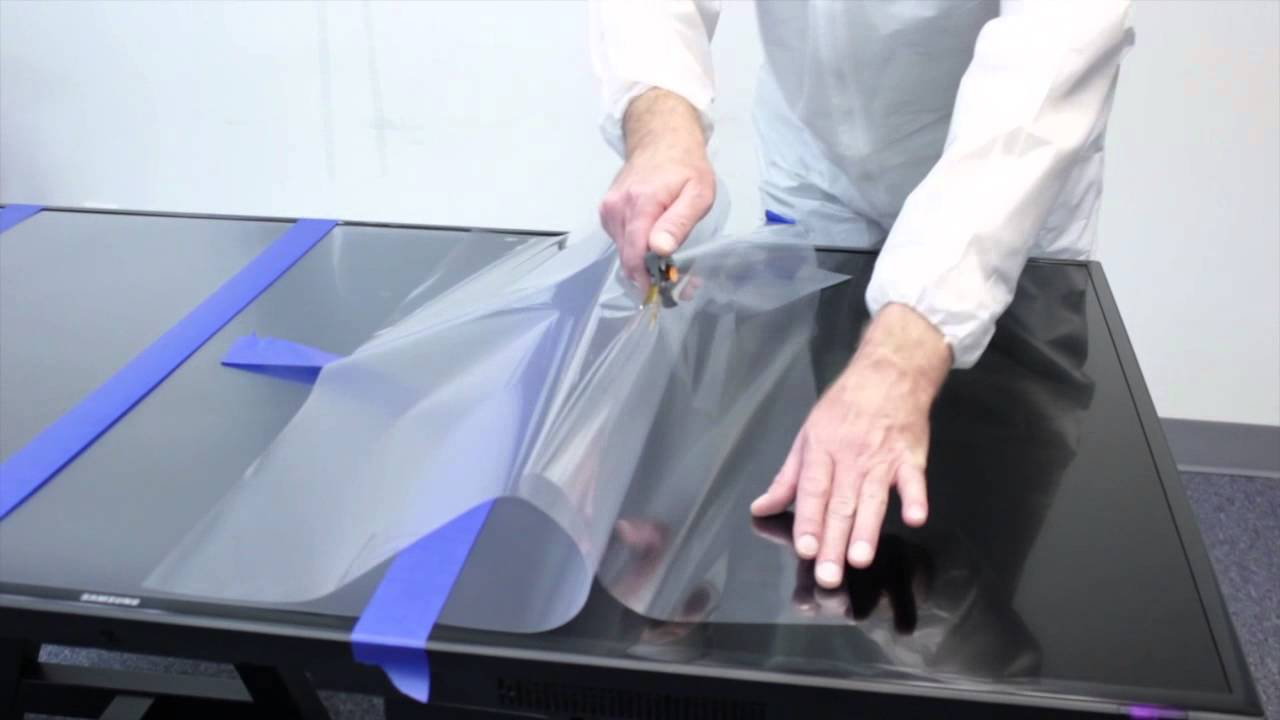 Anti-glare protective film
Anti-glare protective filmAnother problem (which many do not take seriously) is a glossy screen coating that reflects light. "Gloss" leads to unpleasant reflections and glare, which cause overexertion and eye fatigue. Anti-reflective (or matte) coating removes this disadvantage. You can get rid of the glare using a film or an external hinged screen, and the second option often has an additional useful function - it does not allow you to pry from the side.
Well-known glass maker Corning also plans to produce
Gorilla Glass with a new anti-reflective coating . Improved glass should facilitate the use of the smartphone in direct sunlight. Most displays today have low peak brightness or high reflectivity, or both. Light bounces off glass, making the display dark or dim. You have to strain your eyes to see the picture.
The Corning prototype protective glass with a special anti-reflective coating reflects only 1% of the incident light (most solutions have about 5%), which is pretty close to the physical limit. A thin film on glass not only reduces the intensity of light waves, but also improves the accuracy of color reproduction.
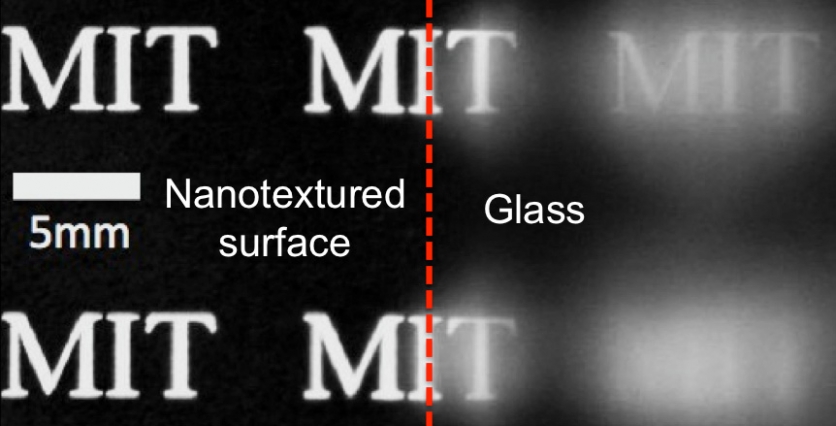
Science also does not stand still. Researchers at MIT have even created a special
glass on which glare almost does not occur. The surface of the glass was covered with conical nanostructures that repelled water, dirt and eliminated glare under direct sunlight. This technology will allow in the future to finally solve the problems of glossy surfaces.
To make your eyes less tired, it’s not enough to choose the display color that suits you personally. You need to adjust the brightness to change the background color from bright white to cool gray. The screen brightness should not be contrasted with the ambient light - forget about working in complete darkness. If you are working in a bright room, increase the brightness of the image; If the room is dim, reduce the brightness.

To match the brightness of the display surrounding the working space,
you need to compare the white background on the monitor with a sheet of paper - the brightness of the sheet and your desktop should be close. The lighting of the room where the display is installed can change dramatically in the morning, afternoon and evening, so the brightness of the screen should change accordingly. In an office with a normal brightness of 300-500 lux, the display brightness should be adjusted to approximately 100-150 cd / m2.
Threat of blue light

Radiation with wavelengths in the range of 440-485 nm is one of the main problems of modern civilization. Redundancy of blue light in cities disrupts the brain and upsets the natural cycle of sleep and wakefulness. Several scientific papers - among which “
Effect of Light on Human Circadian Physiology ” can be particularly highlighted - convincingly prove the destructive effect of blue light on the human’s 24-hour biological cycle.
For millions of years, life exists under the same conditions: in the morning the sun rises and in the evening darkness descends. The daily cycle of light and darkness regulates changes in the behavior and physiology of most species. Studies have shown that these changes are regulated by a biological clock, which in mammals are located in two areas of the brain, called the
suprachiasmatic nuclei . The circadian cycles established by this watch are found everywhere in nature and have a period of about 24 hours.
Circadian cycles can be synchronized with external time signals, but they are preserved even in the absence of such signals. In many months of
underground experiments , subjects experienced a transition of biological hours from 24 hours to 48 hours (36 waking hours and 12 hours of sleep).
Studies have shown that the internal clock consists of an array of genes and protein products that regulate various physiological processes throughout the body. Disruption of biological rhythms can impair health and general well-being.
Biological clocks are also responsible for ensuring that physiological changes take place in coordination with each other. And of course they determine when to stay awake and when to sleep. And for this biological clock needs an “external source of information” - light. If it is light around, you have to act, get food. When darkness comes, the body goes into "sleep mode" to accumulate strength, heal, etc.
However, light itself is not a signal that triggers a circadian rhythm. Only the blue part of the spectrum is responsible for this. Blue light helps us maintain vigor, improves mood, improves performance. Studies have shown that it is easier for our eyes to filter the light of the green and red spectrum (yes, as in RGB). However, a high level of energy in blue light has a more noticeable effect on a person.
There is a lot of blue radiation in the sunlight, but the Sun is not its only source. The problem begins in the evening, when the sun goes beyond the horizon, and the light remains. Light bulbs, monitors, smartphone displays emit blue light, interfering with the production of the sleep hormone - melatonin. From the point of view of the body, everything is logical - once we see the light, it means that it is still day and you need to keep vigor.
It seems that this is great news: without making special efforts, we become more efficient for a period exceeding daylight hours. This is especially true in winter. However, suppression of melatonin in the evening, at best, causes increased fatigue, and at worst,
depression ,
obesity and
cancer .
The way out of this situation is quite simple - to eliminate the blue light in the evening.
Blocking radiation

Simple glasses with amber (orange) glasses
deceive the brain and make it produce as much melatonin as it "produces" in complete darkness. Orange filter removes any light with a wavelength of less than 530 nm.

With such glasses make glasses for working at a computer - for example, the Gunnar Optiks series. They reduce glare and increase contrast, the eyes get less tired with long-term work.
What matters is not only the color of the glass, but also the type of lens. Bifocal and trifocal spectacle lenses allow you to see objects at any distance well. Bifocal and multifocal lenses reduce the efforts of the muscles of the lens when focusing when you are trying to examine objects at close range, which is especially important when working at a computer.
Professional "progressive" lenses lack the lack of bifocal lenses - "image jump". In glasses with bifocal lenses, a person, looking from a distant object to a near one and back, feels a “jump” - a sharp shift of visible objects. "Progressive" lenses allow you to feel more comfortable when working behind the display, but are not recommended for prolonged use.
Auto Light Adjustment

Not everyone can walk with glasses every night or tweak the display settings of all available devices. Another effective way to increase melatonin synthesis is to use special computer programs that automatically adjust color and brightness. If your smartphone does not have a built-in protection mode, you can select one of the available applications - for example (under Android)
Twilight .
The Android application
Eye Relax will remind you to take a break. The application reminds of the need to arrange short rest slots every 30 minutes (there is also a desktop version). It also has a tool for relaxing the eyes: two circles will appear on the screen - the user’s task is to make each eye look at a separate circle: the left eye on the left circle, the right eye - on the right one. Circles will gradually move away from each other, which indicates the relaxation of the medial muscles of the eyes.

The easiest way to optimize eye strain when working on a PC is to use
F.lux . This free application automatically changes the display settings to pre-determined color temperatures that match your lighting environment, based on where the Sun is now located.
In the afternoon, f.lux selects settings with a default color temperature of 6500K — this corresponds to a standard daytime white light source close to noon sunlight. It is during this time that your eyes receive blue light from the display. At night, f.lux chooses the color temperature of the warmer and yellow glow of 3400K - in real life, we see such light when the sun is at the horizon. You can also choose from presets (halogen lamp, fluorescent and daylight, etc.) or customize settings to suit other preferences.
Finally, ASUS Splendid technology, familiar to owners of ASUS smartphones, laptops and desktop monitors, not only improves the picture quality, but also allows you to adjust the color temperature. For this there is a special mode that reduces the intensity of the blue color.
And yet let's not forget that the best rest for the eyes is to look at distant objects that are not the source of light themselves. For an adult, the danger of working at a computer is greatly exaggerated, and by observing all the recommendations listed above, it is possible to level possible harm.