Good afternoon, dear readers! In recent articles, I talked about popular SLAM methods and visual odometry that have support in ROS. In this article I will deviate a little from the topic and talk about setting up and working with ROS on an
NVIDIA Jetson TK1 microcomputer. After installing everything you need, we connect and try to
strealabs ZED stereo camera . Who cares please under the cat.
About NVIDIA Jetson
To begin, consider the NVIDIA Jetson TK1 platform. NVIDIA Jetson TK1 is an NVIDIA microcomputer based on
Tegra K1 SOC (CPU + GPU on a single chip with CUDA support). NVIDIA Jetson boasts a 4-core ARM Cortex-A15 CPU with 2.3 GHz, has the same components as the Raspberry Pi (HDMI, USB 2.0 and 3.0, Ethernet) as well as PC-specific modules: SATA, mini-PCIe . The mobile
Tegra K1 processor has very similar properties and architecture to the desktop GPU, which allows it to withstand heavy loads with minimal power consumption. As they say on the
official page, the processor allows you to run on the board any demanding graphics tasks, such as face recognition, augmented reality, and even computer vision tasks for unmanned vehicles. More details about all the features of the platform can be found
here .
Embedded memory on NVIDIA Jetson TK1 is represented by a 16 GB eMMC module. By default, NVIDIA Jetson TK1 is pre-installed with Ubuntu 14.04 operating system.
A 12 V AC / DC adapter is used to power the microcomputer.

ZED stereo camera
The ZED stereo camera is a passive depth camera, consisting of two ordinary RGB cameras, 12 cm apart from each other, with an overview of up to 20 meters. Unlike active cameras (such as ASUS Xtion and Microsoft Kinect), the ZED stereo camera does not have an IR laser to measure distance. The camera is relatively inexpensive (costs $ 449). The advantage of the camera can be considered its small size (175 x 30 x 33 mm) and lightness (159 g).
The camera can be used to
create outdoor maps on the drone .
More information about the camera can be found
on the official page .
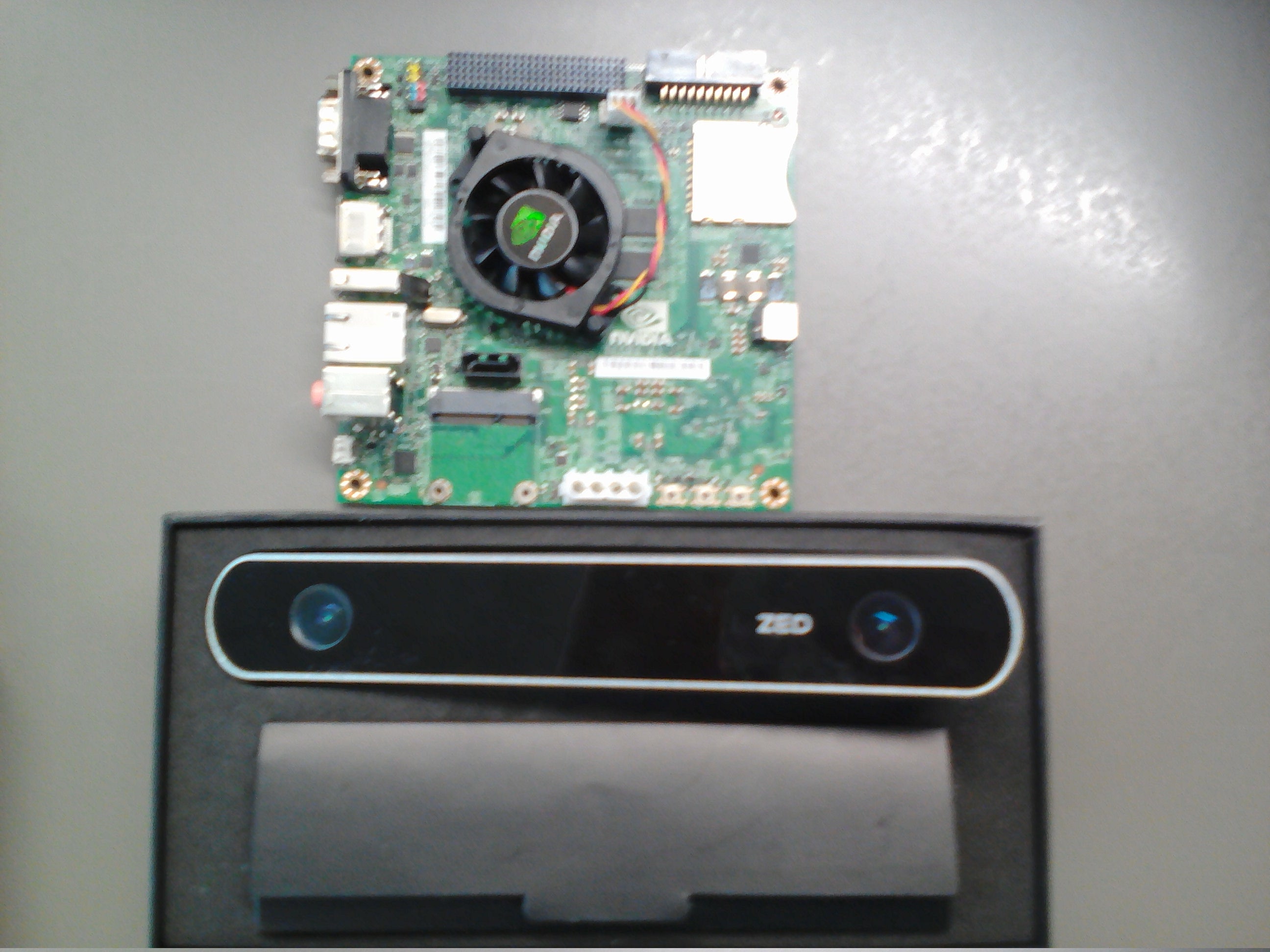

Configure Ubuntu on NVIDIA Jetson TK1
Connect NVIDIA Jetson TK1 using HDMI to the monitor, connect the Ethernet cable to the appropriate connector, and finally use the 12 V AC / DC adapter to the power supply.
To install the system on NVIDIA Jetson, you may need to install JetPack TK1 (instructions can be found
here ). I got NVIDIA Jetson on my hands with JetPack already installed and Ubuntu 14.04, so here I am not considering installing it.
So the Ubuntu 14.04 system will start automatically. For authorization use the ubuntu login and password.
Find out the IP address of the Jetson host:
ifconfig
We get the hardware characteristics:
lscpu
The conclusion will be as follows:
Architecture: armv7l Byte Order: Little Endian CPU(s): 4 On-line CPU(s) list: 0-3 Thread(s) per core: 1 Core(s) per socket: 4 Socket(s): 1
There may be a problem with connecting to Jetson over SSH: ifconfig displays the IP address, but it is not possible to connect to Jetson at this address. To solve the problem, open the file / etc / network / interface from under the root:
sudo nano /etc/network/interface
and add the lines:
auto eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcp
We made a dynamic IP address assignment. Save the changes and execute:
sudo ifup eth0
Now everything should work. This decision was taken
from here .
Now connect to Jetson via SSH:
ssh -X ubuntu@<ip_address>
CUDA installation
To work with the ZED camera, we need the ZED SDK, which requires CUDA version 6.5 installed. Download the deb file for CUDA Toolkit 6.5 for L4T
from here (instruction taken
from here ):
wget http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/6_5/rel/installers/cuda-repo-l4t-r21.1-6-5-prod_6.5-14_armhf.deb
Install the repository metadata for CUDA for L4T, which has just been downloaded:
sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-l4t-r21.1-6-5-prod_6.5-14_armhf.deb
Download and install the CUDA Toolkit itself, including the OpenGL toolkit for NVIDIA:
sudo apt-get update
Install cuda-toolkit-6-5:
sudo apt-get install cuda-toolkit-6-5
Add the user ubuntu to the “video” group to provide access to the GPU:
sudo usermod -a -G video $USER
Here, $ USER is ubuntu.
Add the paths to the CUDA installation folder to the .bashrc script and execute it in the current terminal:
echo "export PATH=/usr/local/cuda-6.5/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export $PATH=/usr/local/cuda-6.5/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
Check that the CUDA Toolkit is installed on the device:
nvcc -V
USB 3.0 Setup on Jetson TK1
By default, the USB 3.0 port is configured by the system on the Jetson TK1 as USB 2.0. We need to configure it as USB 3.0. To do this, open the file / boot / extlinux / extlinux.conf as root:
sudo vi /boot/extlinux/extlinux.conf
Find the string 'usb_port_owner_info = 0'. If this line occurs twice, then we change the last inclusion. Rewrite 'usb_port_owner_info = 0' to 'usb_port_owner_info = 2'.
Installing the ZED SDK
The installation procedure looks the same as on desktop Linux. It is worth noting that OpenCV is already installed when installing JetPack in order to use Tegra optimization for it. Therefore, manual installation of OpenCV is not required.
To use the ZED stereo camera, we need to install the ZED SDK 1.2. As an installer, a special Jetson TK1 .run file is used. Download the installer:
wget https://www.stereolabs.com/developers/downloads/archives/ZED_SDK_Linux_JTK1_v1.2.0.run
Set the permissions for the file and run it in the terminal:
sudo chmod +x ZED_SDK_Linux_JTK1_v1.2.0.run ./ZED_SDK_Linux_JTK1_v1.2.0.run
Accept the terms of the license agreement, press 'q' and then 'Y'. Next, perform the procedure following the instructions.
Run ZED Explorer on Jetson itself (does not work when connecting remotely via SSH):
/usr/local/zed/tools/ZED\ Explorer
Installing ROS drivers for ZED stereo cameras
I used in my experiments ROS Indigo. Install the dependencies for the ROS driver:
sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-tf2-ros ros-indigo-image-transport ros-indigo-dynamic-reconfigure ros-indigo-urdf
Install ROS wrapper for ZED camera:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src git clone https://github.com/zastrix/zed-ros-wrapper.git git checkout ef3ad46f14cf62ff21083829a1fa6879d20246de cd ~/catkin_ws catkin_make
Run zed_wrapper by executing the following commands in different windows of the terminal:
roscore roslaunch zed_wrapper zed.launch
Show active topics:
rostopic list
In the list, in addition to the standard topics, we will see topics with the / zed prefix:
/zed/depth/camera_info /zed/depth/depth_registered /zed/joint_states /zed/left/camera_info /zed/left/image_raw_color /zed/left/image_rect_color /zed/odom /zed/point_cloud/cloud_registered /zed/rgb/camera_info /zed/rgb/image_raw_color /zed/rgb/image_rect_color /zed/right/camera_info /zed/right/image_raw_color /zed/right/image_rect_color
Run rqt_image_view:
rosrun rqt_image_view rqt_image_view
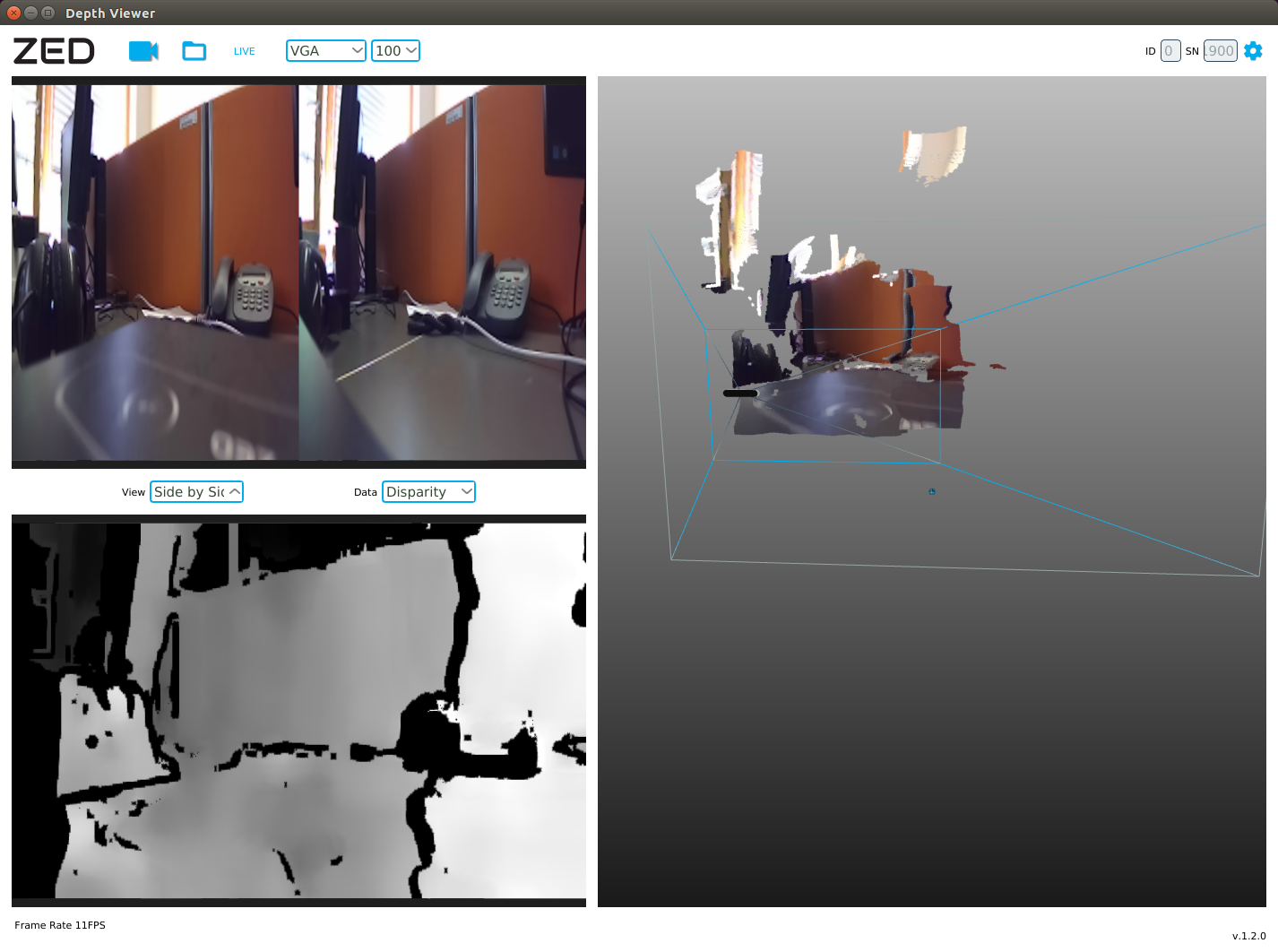
When choosing the topic / zed / depth / depth_registered, we get a depth map:

RGB image from the left camera (/ zed / left / image_raw_color):
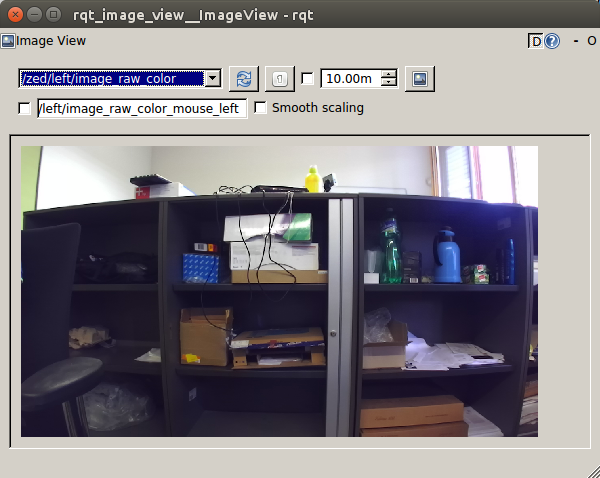
And finally the RGB image from the right camera (/ zed / right / image_raw_color):
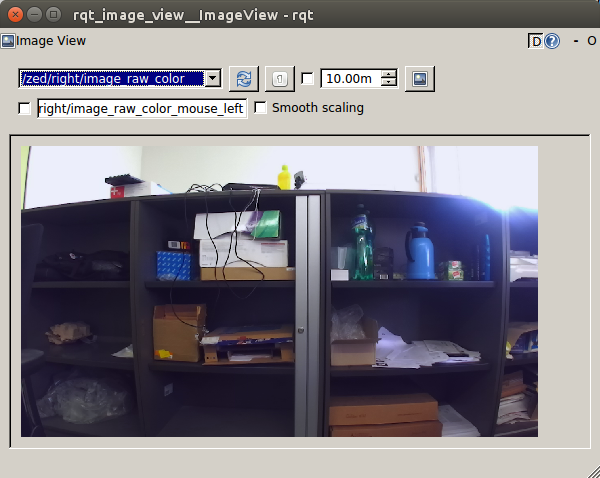
Data from the camera is published in / zed / rgb / image_raw_color and / zed / depth / depth_registered topics with a frequency of 15Hz.
Find out the frequency of publishing point clouds in the topic / zed / point_cloud / cloud_registered:
rostopic hz /zed/point_cloud/cloud_registered
average rate: 4.146 min: 0.202s max: 0.371s std dev: 0.04798s window: 11 average rate: 4.178 min: 0.191s max: 0.371s std dev: 0.04306s window: 16
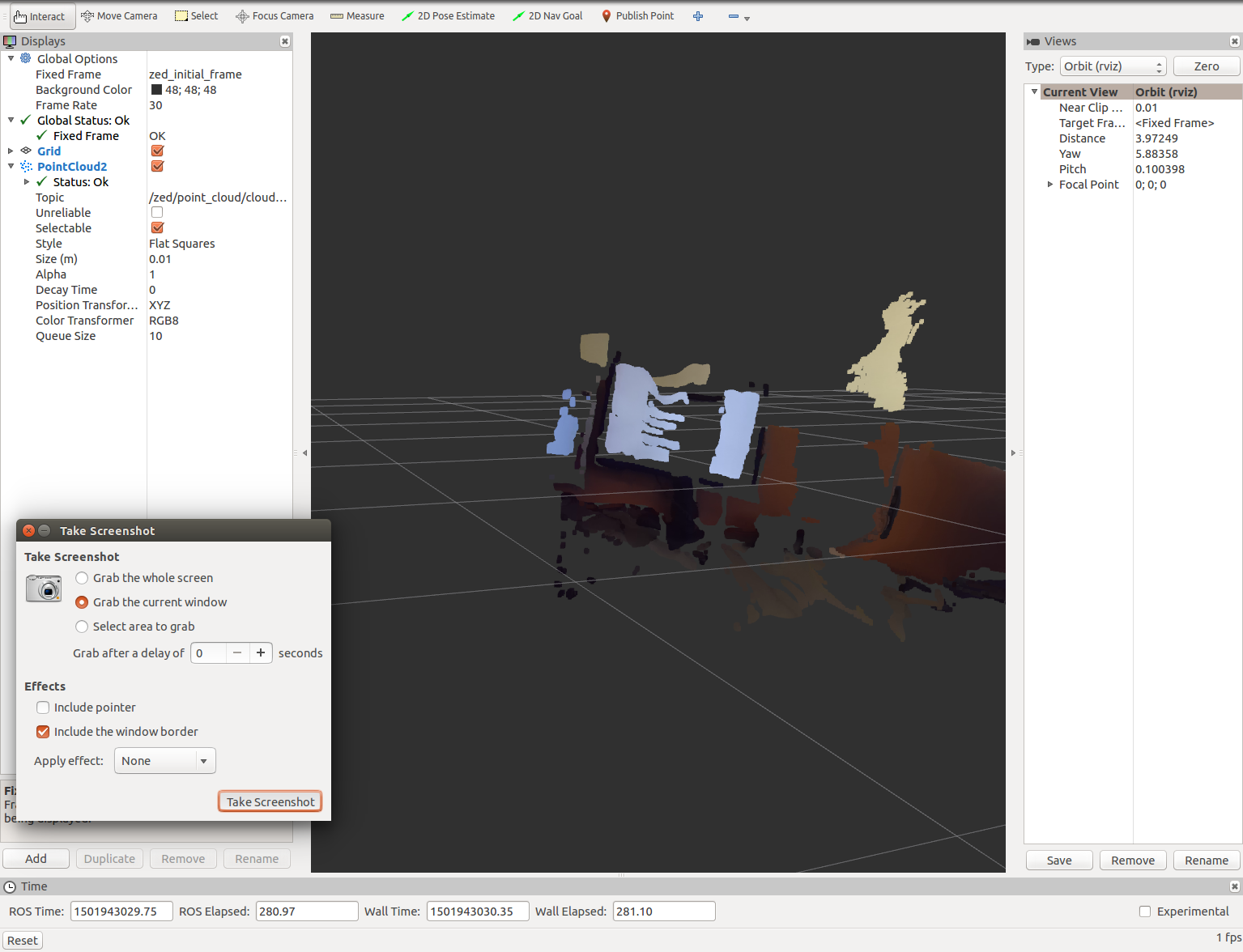
Run rviz on Jetson itself (I could not successfully launch it when connecting via ssh with the -x option):
rosrun rviz rviz
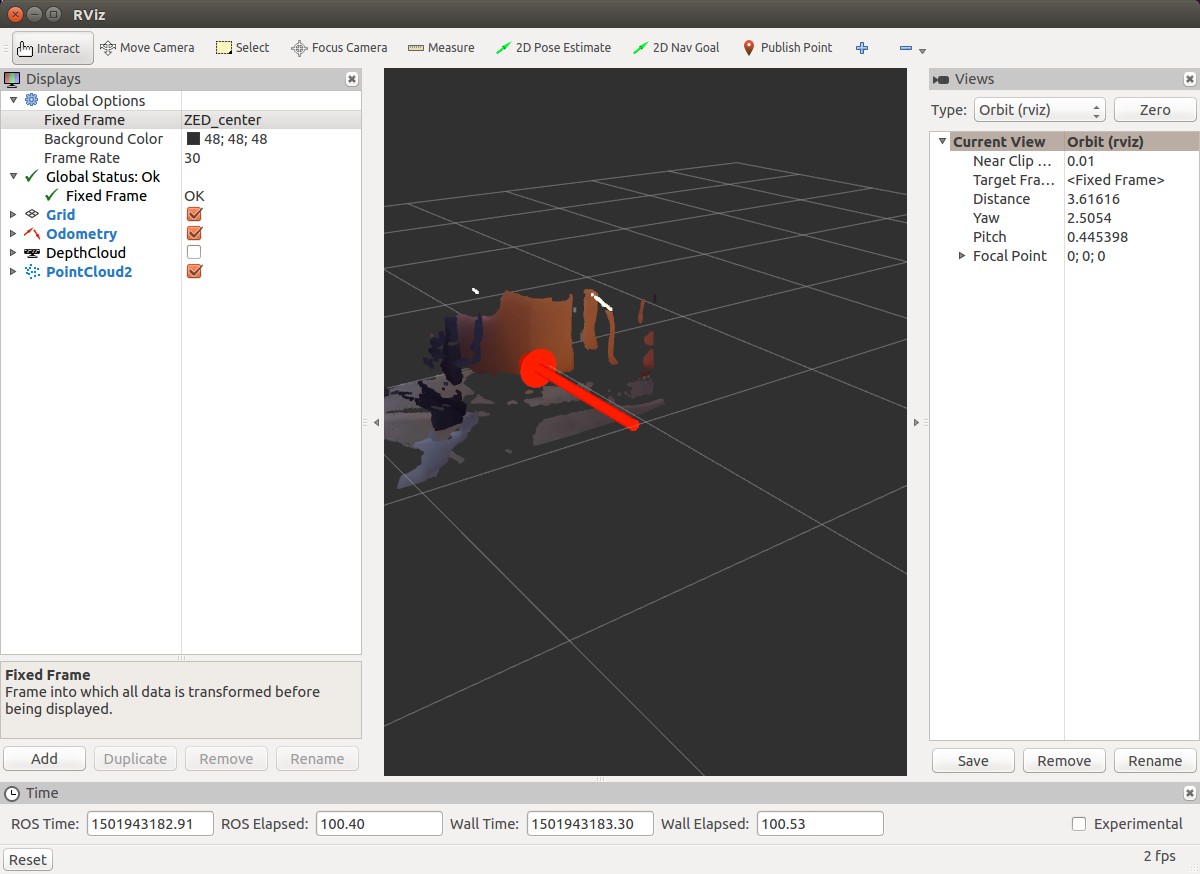
SLAM On NVIDIA Jetson with ZED Stereo Camera
Let's now try the ZED camera on a practical task. On NVIDIA Jetson, you can easily run the SLAM RTAB-MAP algorithm. First, install the ROS wrapper for RTAB-MAP:
sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-rtabmap-ros
Now run rtabmap using the ZED camera. If we are not running zed_wrapper, then run it:
rosrun zed_wrapper zed_wrapper_node
Run rtabmap:
rtabmap
Select the ZED camera in the rtabmap window as the source:
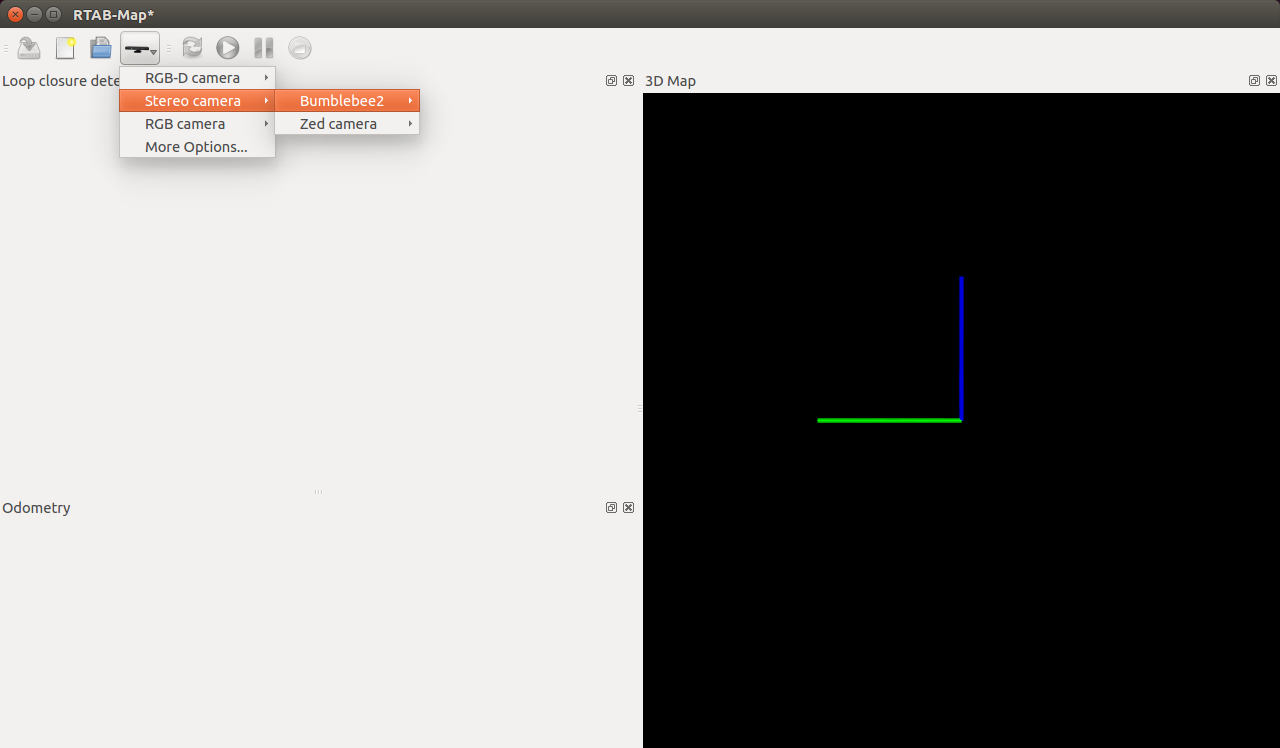
I did not test the RTAB-MAP on NVIDIA Jetson, so I leave you, dear readers, the opportunity to try this SLAM algorithm. You can read about using RTAB-MAP in my last two articles (
here and
here ).
I hope this article will be a good starting point for you to use the ZED stereo camera and the NVIDIA Jetson microcomputer. I wish you good luck in your experiments and see you soon!
PS: I am interested in your opinion on the choice of an inexpensive stereo camera for experiments. ROS support doesn't matter much, the main thing is the price. Please write your options in the comments to the article.
PS (Upd): I would like to try passive stereo cameras such as ZED. Preferably able to work with Raspberry Pi 3.