
Introduction
Good afternoon friends! I was surprised to notice that there are not many articles on Habré devoted to the products of such a vendor as
Extreme Networks . To fix this and introduce you closer to the Extreme product line, I plan to write a short series of several articles and want to start with switches for Enterprise.
The cycle will include the following articles:
- Extreme Enterprise Layer Overview
- Enterprise Network Design on Extreme Switches
- Configuring Extreme Switch Settings
- Overview comparison of Extreme switches with equipment of other vendors
- Warranty, Technical Support and Service Contracts for Extreme Switches
I invite you to read the series of articles of all those who are interested in this vendor, and just network engineers and network administrators who are faced with the choice or configuration of these switches.
About company
To begin with, I want to introduce you to the company and its history more closely:
Extreme Networks is a telecommunications company founded in 1996 to promote advanced Ethernet technology solutions and the development of the Ethernet standard. Many Ethernet standards for network scaling, QoS, and fast recovery are open patents of Extreme Networks. The headquarters is located in the city of San Jose (California), USA. At the moment, Extreme Networks is a public company focused specifically on the development of Ethernet.
As of December 2015, the number of employees was 1300 people.
Extreme Networks offers wired and wireless network solutions that meet the requirements of the modern mobile world with the constant movement of users and devices, as well as the migration of virtual machines both inside the data center and beyond - to the cloud. Using a single ExtremeXOS operating system allows you to create advanced solutions for both telecom operators, data center networks, and local / campus networks.
Company partners in the CIS
- Extreme Networks has four official distributors in Russia - RRC, Marvel, OCS and Comptek, as well as more than 100 partners, whose number is constantly growing.
- Extreme Networks has three official distributors in Belarus - Solideks, IUK and Abris. Solidex has the status of an authorized training partner.
- Official distributors in Ukraine - Information Merezhivo, MUK and Abris.
- In the countries of Central Asia, as well as in Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan, the official distributors are RRC and Abris.
Well, we met, and now let's see what of the switches this vendor can offer us for our Enterprise network.
And he can offer us the following:

The figure above shows the models of switches depending on the type of operating system that controls the switches and the technologies supported by the ports (vertical arrow on the left):
- 1 Gigabit Ethernet
- 10 Gigabit Ethernet
- 40 Gigabit Ethernet
- 100 Gigabit Ethernet
Let's look at Extreme switches in more detail and start with the V400 series.
V400 Series Switches
These are switches using Virtual Port Extending technology (based on the IEE 802.1BR specification). The switches themselves are called Virual Port Extenders.
The essence of this technology is that all the control and dataplane functionality is taken out from the switch to the aggregating switches - Controller Bridges / CB.
As the Controller Bridge of the switch, only model switches can be used:
Before describing typical switching schemes for these switches, I will describe their specifications:

As can be seen from the table above, depending on the number of GE access ports 24 or 48, the switches have 2 or 4 10GE SFP + uplink ports.
There are also switches with PoE ports for connecting and powering PoE devices using 802.3af (up to 15 W per port) and 802.3at (up to 30 W per port) technologies.
Below are 4 typical wiring diagrams for the V400 and CB switches:

Benefits of Virtual Port Extending Technology:
- ease of maintenance - if one of the V400 switches fails, it will be enough to simply replace it and the new switch will be automatically detected and configured for CB operation. Therefore, there is no need to configure each access switch.
- the entire configuration is located only on CB, V400 switches are visible only as additional CB ports, which simplifies the management of these switches
- when working with V400 in conjunction with Controller Bridge, you get all the functionality of Controller Bridge on V400 switches
Technology limitation - up to 48 Port Extenders of V400 switches (2300 access ports) are supported.
X210 and X220 Series Switches
The E200 family of switches has a fixed number of 10/100/1000 BASE-T ports, operates at L2 / L3 levels, and is intended for use as Enterprise access switches. Depending on the model, the switches have:
- PoE / PoE + ports
- 2 or 4 pcs 10 GE SFP + ports (X220 series)
- stacking support - up to 4 switches per stack (X220 series)
Below I will give a table with the configuration and some features of the X200 series switches


As can be seen from the table, the E210 and E220 series switches are intended for use as access switches. Thanks to the presence of 10 GE SFP + ports, the X220 series switches can support stacking - up to 4 units per stack, with a stack bandwidth of 40 Gb.
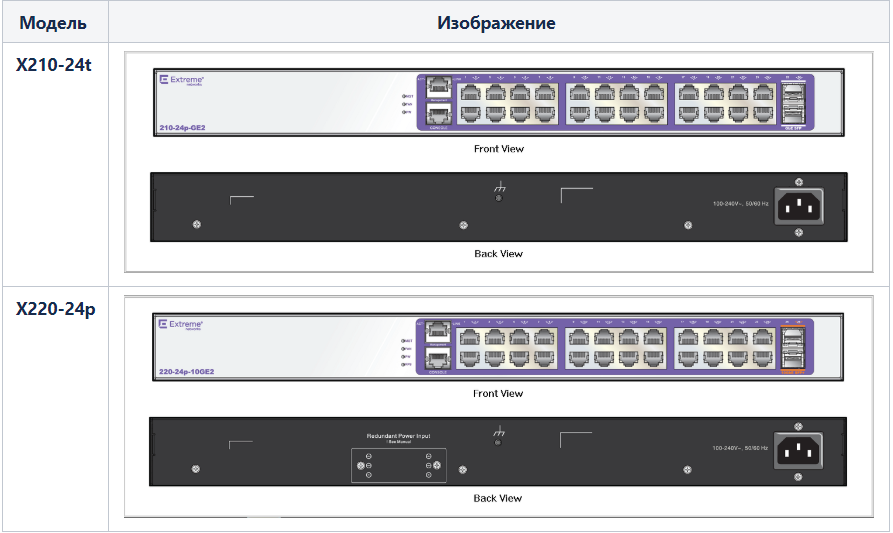 The switches are controlled by the EOS operating system.
The switches are controlled by the EOS operating system.ERS Series Switches
The switches in this series are more powerful than the switches in the younger E200 series.
First of all, it is worth noting:
- These switches have more advanced stacking capabilities:
- up to 8 switches per stack
- depending on the model, both SFP + ports and dedicated ports for stacking can be used
- ERS series switches have a larger PoE budget compared to the E200 series
- ERS Series Switches Have More L3 Functionality Compared to E200 Series
I propose to begin a more detailed discussion of the ERS switch family with the younger line - ERS3600.
ERS3600 Series
The switches in this series are represented by the following configurations:

As can be seen from the table, the ERS 3600 switches can be used as access switches, have a larger stack capacity, a larger PoE budget and a wider range of L3 functions, although of course they are limited only by RIP v1 / v2 dynamic routing protocols, as well as the number of interfaces and routes involved in him.
The picture below shows the front and rear views of the 50-port switch series ERS3600:

ERS4900 Series
The configuration and functionality of the ERS4900 series switches can be briefly described in the following table:

As we can see, these switches implement dynamic routing protocols, such as RIPv1 / 2 and OSPF, there is a gateway reservation protocol - VRRP, and also supports IPv6 protocol.
Here I have to make an important note - * additional functionality of L2 and L3 (OSPF, VRRP, ECMP, PIM-SM, PIMSSM / PIM-SSM, IPv6 Routing) is activated by purchasing an additional license - Advanced Software License.
The front and rear views of the 26 port switch of the ERS4900 series and the option of stacking them are shown in the pictures below:

As can be seen from the pictures, the switches of the ERS4900 series have dedicated ports for stacking - Cascade UP / Cascade Down, and they can also be equipped with redundant power supplies.
ERS5900 Series
The latest and oldest models in the ERS series are the ERS5900 switches.
From the interesting:
- in some switches of the series, Universal PoE is implemented - the ability to output 60 W on the port to power specialized devices and small switches / routers
- there are 100 port switches with a total PoE budget of 2.8 kW
- ports with support for 2.5GBASE-T (standard 802.3bz) are available
- support for MACsec functionality (802.1AE standard)
The configuration and functionality of the series switches are best described by the following table:


*
5928GTS-uPWR and 5928MTS-uPWR switches support the so-called Four-Pair PoE initiative (aka Universal PoE - uPoE) - the ability to power devices with consumption up to 60 W, for example, some types of video communication systems, thin VDI clients with monitors, small PoE powered switches or routers, and even some IoT systems (such as intelligent lighting control systems).**
PoE budget of 1440 W is achieved by installing 2 power supplies. When you install 1 power supply in the switch, the PoE budget will be - 1200 watts.***
PoE budget of 2880 W is achieved when installing 4 power supplies. When you install 1 power supply in the switch, the PoE budget will be - 1200 watts. When installing 2 power supplies in the switch, the PoE budget will be 2580 watts.Additional functionality of L2 and L3 as in the case of the ERS4900 series is provided by the purchase and activation of the corresponding switch licenses:

The pictures below show the front and rear views of the 100-port switch of the ERS5900 series and the option of stacking 28 and 52 port switches:

** All switches in the series are managed by the ERS operating system. **
Friends, as you probably noticed, at the end of the description of the series I indicate which operating system they are running, and so - I do it for a reason. As many have already guessed, the fact is that managing a particular operating system means an individual set of syntactic commands and settings blocks for each operating system.
Example:
As fans of Avaya switches have probably noticed, in the description of the L2 functionality of the ERS series switches, there is the line MLT / LACP Groups characterizing the maximum possible number of groups for combining interfaces in them (aggregation and reservation of communication links). The
MLT designation is typical for link aggregation in Avaya Holding switches, where it is used directly in the command syntax when configuring link aggregation.
The thing is that ExtremeNetworks, in accordance with its development strategy, bought Avaya Holdings in 2017-2018, which at that time had a line of its switches. Thus, the ERS series is essentially a continuation of the Avaya switch line.
EXOS Series Switches
The EXOS series is considered the flagship Extreme series. In the switches of this line, the most powerful functionality is implemented - both the set of standard protocols and the set of “own” Extreme protocols, which I will try to describe in the future.
In it you can find switches for every taste:
- for any network level - access, aggregation, core, data center switches
- with any set of 10/100/1000 Base-T, SFP, SFP +, QSFP, QSFP + ports
- with or without PoE support
- with support for several types of “stacking” and support for “clustering” to ensure fault tolerance of critical network nodes
Before starting the review of this series with the youngest line - X440, I would like to explain the licensing policy of the EXOS operating system.
EXOS licensing (since version 22.1)
EXOS has 3 main types of licenses - Edge License, Advanced Edge License, Core License.
The table below describes the license usage options depending on the line of EXOS series switches:
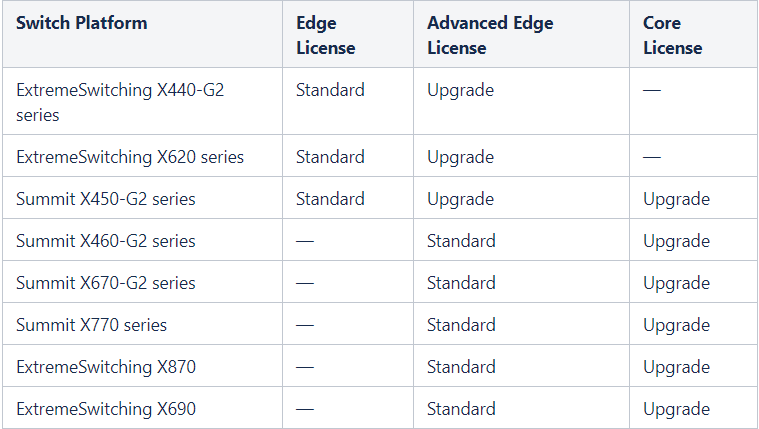
- Standard is the EXOS version of the operating system that comes standard with the switch
- Upgrade is the ability to expand the EXOS operating system to any level.
The functionality of each type of license and its support on various platforms of the series can be found in the tables below.
To activate MPLS functionality, there are separate Feature Packs, which I will talk about below.
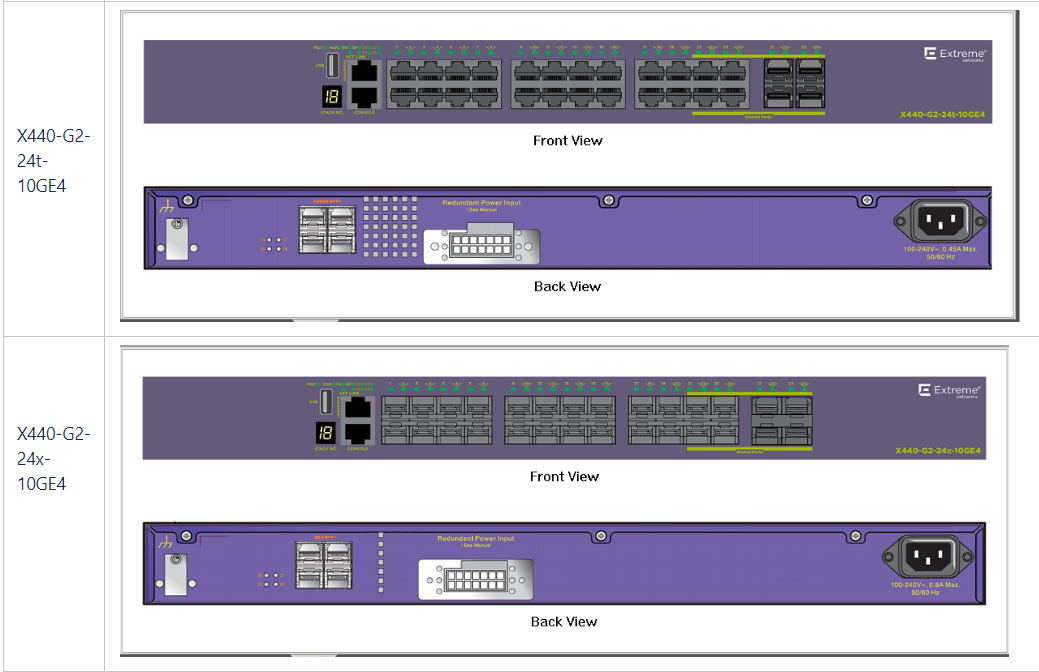
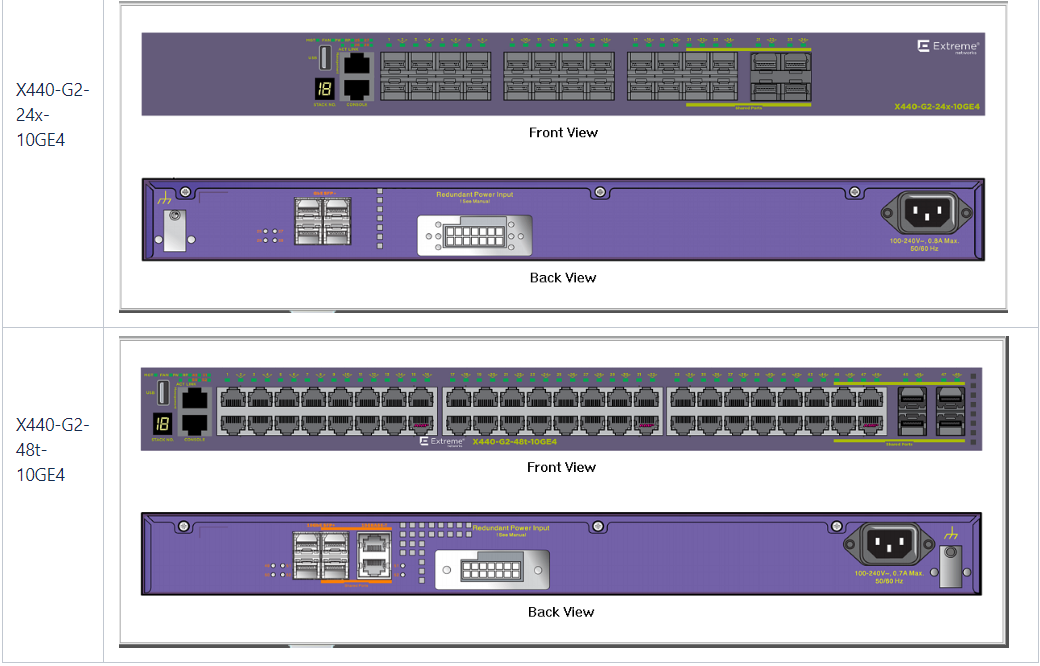
X440-G2 Series
I propose starting the discussion of EXOS switches with the switches of this series, which clearly describe the concept of "pay-as-you-grow" (pay as you grow), which is actively supported by ExtremeNetworks.
The main idea of this concept is to gradually increase the productivity and functionality of purchased and installed equipment without the need to replace both the equipment itself and its parts.
For clarity, I will give an example:
- Suppose you initially need a 24 or 48 port switch with copper or optical access ports, which will first occupy 50% of the access ports (12 or 24 pieces) and the total traffic of the trunk ports in one of the directions (usually this is downlink for working machines) will be up to 1 Gb / s
- Suppose you initially selected an X440-G2-24t-10GE4 or X440-G2-48t-10GE4 switch that has 24 or 48 1000 BASE-T access ports and 4 GigabitEthernet SFP / SFP + ports with the option of expanding them to 10 GigabitEthernet
- You configured and installed the switch, included it with 1 trunk port in the kernel or aggregation (depending on the structure of your network), connected users to it - everything works, you and the management are satisfied
- Over time, your campaign and network grows - new users, services, equipment appear
- As a result, traffic growth at various network levels is possible, including on the switch we are considering. This can happen for various reasons - you connect new devices to the switch, or users begin to consume more and more traffic from various services, and as a rule, both happen simultaneously
- Over time, you notice that the switch trunk port load has reached 1 Gb / s
- Not a problem, you think, because you have 3 more GigabitEthernet ports that you can use to aggregate communication links between the switch and aggregation (core) - you raise another optical or copper link between them and configure the aggregation, for example, using the protocol Lacp
- Time passes and there is a need to install one or more switches
- Several situations may arise that make it necessary to enable a new switch through your existing X440 switch:
- lack of aggregation ports or kernels for inclusion - in this case it will be necessary to buy additional aggregation level or kernel switches
- the remoteness of the switch from the aggregation nodes or the lack of existing capacity of the cable route, for example optical fibers, will require the construction of new communication lines and significant additional costs
- in the worst case, two options are possible simultaneously
- After analyzing the network diagram and additional costs with the management, you decide to connect the new X440 switch to the network through the existing one. Not a problem - for this you have several options:
- Option 1 - Stacking:
- You can stack 2 switches into a stack using SummitStack-V technology using the 2 remaining trunk ports on the first X440 switch and 2 trunk ports on the second X440 switch.
- Depending on the distance, you can use either short DAC cables or SFP + transceivers up to several tens of kilometers
- Thus, the stacking of the switches will go through 2 ports allocated for stacking from 4 trunk ports (usually these are ports 27, 28 on 24-port models and ports 49, 50 on 48-port models). The bandwidth of the stacking ports on each port will be 20Gb (10Gb one way and 10Gb the other)
- A license to expand trunk ports from 1 GE to 10 GE is not required in this case
- Option 2 - use of trunk trunk ports with the possibility of their further aggregation:
- You can enable the second switch using 1 or 2 (if aggregated) of the remaining trunk ports on the first X440 and 1 or 2 trunk ports on the new X440
- A license to expand trunk ports from 1 GE to 10 GE is also not required here
- You turned on one or more switches in series, or by star, from the first X440 switch as you planned
- Time passes and you notice that the traffic on the trunk ports of the first X440 switch has reached 2 Gb / s and you need:
- or more ports for link aggregation between the aggregation and the first X440 switch, which in turn can lead to the same problems as installing the new X440 switch, which I described above - lack of ports on the aggregation equipment or cable infrastructure capacity
- either use 10 GigabitEthernet trunk ports between aggregation equipment and the first X440 switch
- At this point, the ability of the X440 switches to extend the bandwidth of its trunk ports from 1 GigabitEthernet to 10 GigabitEthernet will come to your aid, using the appropriate license. Depending on the options, you decide:
- For option 1 (stacking) - use the Dual 10GbE Upgrade License. You activate the license on the first X440, which will expand the throughput of 2 of its trunk ports from 1 GigabitEthernet to 10 GigabitEthernet (the other 2 ports, as we recall, are used for stacking)
- For option 2 (trunk trunk ports), use the Dual 10GbE Upgrade License or Quad 10GbE Upgrade License depending on the load on the trunk ports between the first X440 and the second X440. There may also be several options:
- first you can activate Dual 10GbE license on the first X440
- then, as the traffic on the second X440 grows, connected with connecting one more or several switches sequentially to it, you activate another Dual 10GbE license on the first X440 and Dual 10GbE license on the second X440 switch
- and so sequentially on the switch branch
- It takes some time, your organization continues to grow both horizontally - the number of network nodes increases, and vertically - the network structure becomes more complicated, new services appear that require specific protocols.
- Depending on the needs of your organization, you may decide to opt out of the L2 level on your switches and go to the L3 level. The needs that may affect your decision can be very different:
- network security requirements
- network optimization (for example, reduction of broadcast domains, accompanied by the introduction of dynamic routing protocols such as OSPF)
- introduction of new services requiring specific protocols
- any other reasons
- No problems. X440 switches will continue to be relevant, as you can additionally purchase and activate a license for them that extends their functionality - Advanced Software License.
, X440 ( ) «pay-as-you-grow». .
.
, X440 , , :


*
X440-G2 SummitStack-V - X450-G2, X460-G2, X670-G2 and X770. — EXOS .**
. Edge License.— redundant power input RPS .
X440-G2 :

X440 :

X450-G2
ExtremeNetworks Summit X450-G2 .
X450-G2 X440-G2 :
- ( ) — Edge License, Advanced Edge License, Core License
- QSFP ,
- PoE
- 10GE SFP+ 1 10


*
SummitStack-V84 X450-G2.**
X440-G2 SummitStack-V - X440-G2, X460-G2, X670-G2 and X770. — EXOS .***
. Edge License.PoE — redundant power input RPS .
. .
X450-G2 :

X450-G2 :

X460-G2
X460-G2 QSFP+ . :
- VIM VIM- — SFP+, QSFP+,
- 2.5GBASE-T (802.3bz)
- MPLS
- Synchronous Ethernet TM-CLK
:

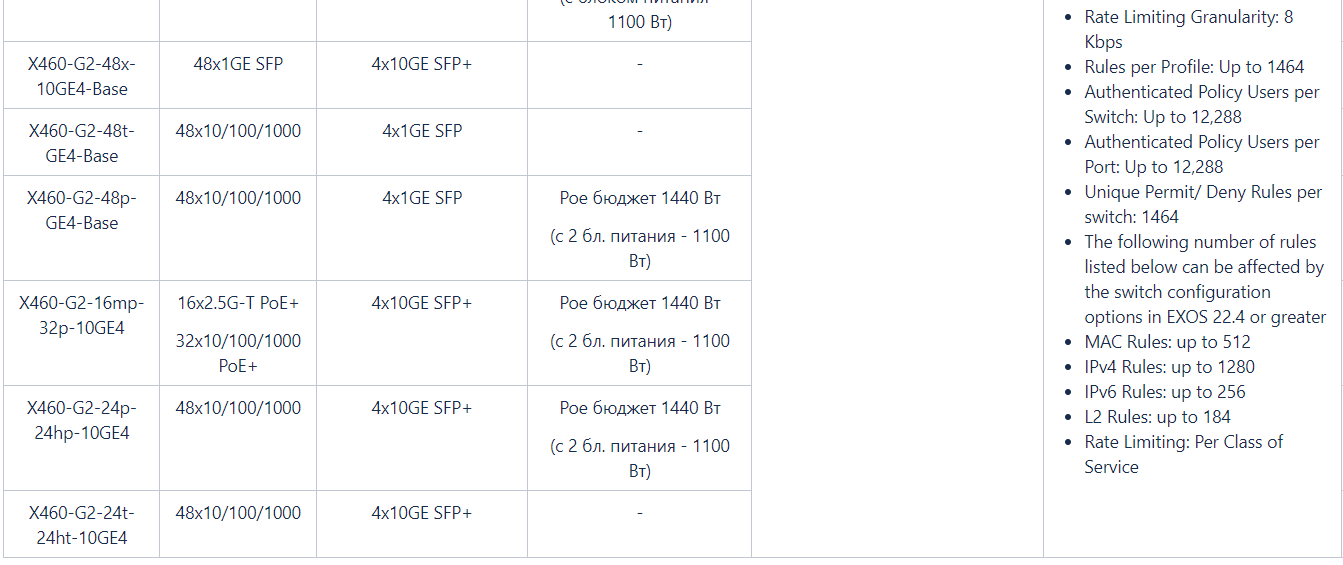
*
, VIM-. .**
X440, X460, X460-G2 X480,***
X440, X440-G2, X450, X450-G2, X460, X460-G2, X480, X670, X670V, X670-G2 X770 ,****
X460-G2, X480, X670V, X670-G2 X770,2- — front-to-back back-to-front, .
VIM- , X460-G2 :
:

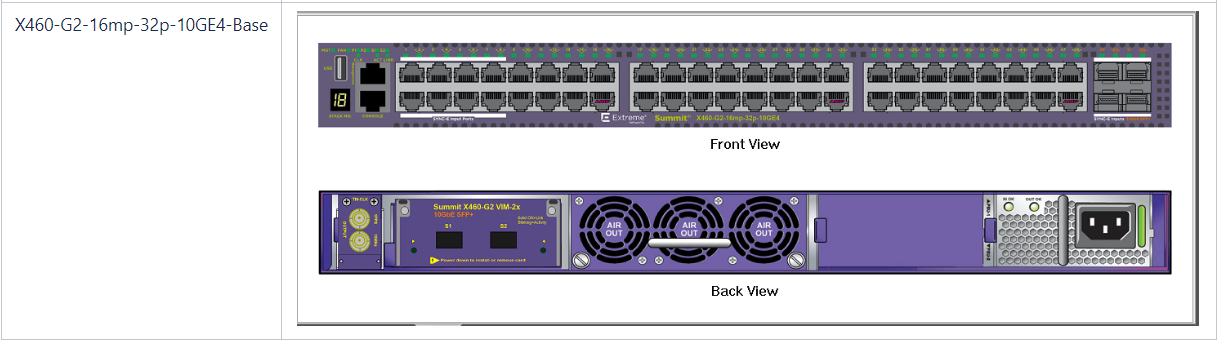
X620-G2
X620-G2 10 GE . 2- — Edge License Advanced Edge License.
SummitStack-V - X440-G2, X450-G2, X460-G2, X670-G2 X770 2x10 GE SFP+ — Data/Stacking.
PoE+ 60W 802.3bt 4-Pair PoE++ — Type 3 PSE. .
:



:

:


X670-G2
X670-G2 1RU , Controller Bridge V400. 48 72 10 GE SFP+ 4 QSFP+ .
2- — Advanced Edge License ( ) Core License 4 — SummitStack-V, Summit-Stack-80, SummitStack-160, SummitStack-320.
- MPLS Feature Pack, LSR LER - L2VPN (VPLS/VPWS), BGP-based L3VPNS, LSP LDP, RSVP-TE, Static provisioning - VCCV, BFD CFM.
2- :
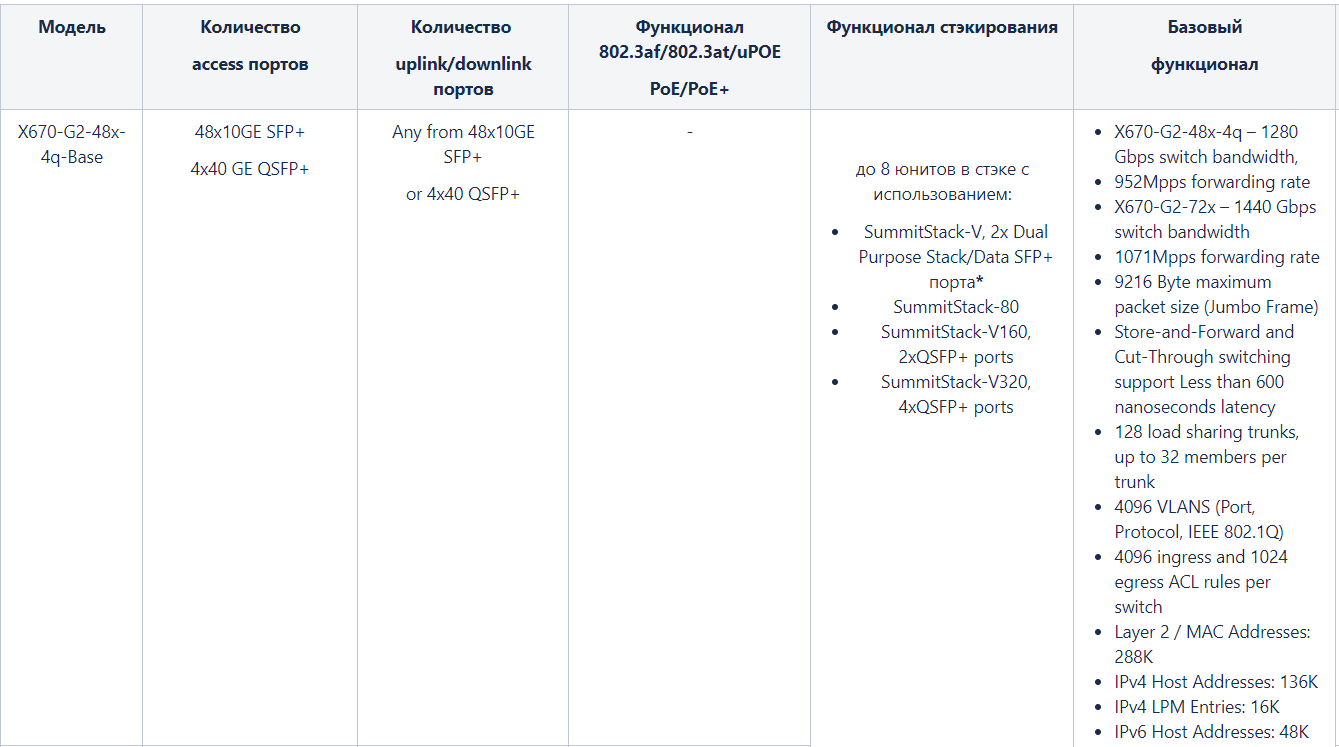

*
— X440, X440-G2, X450, X450-G2, X460, X460-G2, X480, X670, X670V, and X770— . :
:

2 :

X590
1GE/10GE/25GE/40GE/50GE/100GE :
- Controller Bridge V400
- top-of-rack
2- — SFP BASE-T 2- :


*
X690 X870.— . :
:

:

X690
1GE/10GE/25GE/40GE/50GE/100GE X590 :
- Controller Bridge V400
- top-of-rack
2- — SFP BASE-T 2- :


*
X590 X870.— . :
:

:

X870
X870 100Gb Enterprise spine/leaf .
— Advanced, Core MPLS -.
x870-96x-8c-Base «pay-as-you-grow» — Upgrade ( 6 , 4- ).
2- 2- :


*
X590 X690.— . :
:

2- , :

Conclusion
, , , .
, ExtremeNetworks :
- VSP (Virtual Services Platform) ,
- VDX SLX,
, .
— , Extreme SFP/SFP BASE-T/SFP+/QSFP/QSFP+ , (, , Cisco) — , .
. , «», :
—
Telegram—
Facebook—
VK—
TS Solution Blog