Oracle VM Server for SPARC for Dummies (How-to)
A small How-to for beginners to work with
Solaris and the
Oracle VM Server for SPARC virtualization platform, formerly known as Sun Logical Domains.
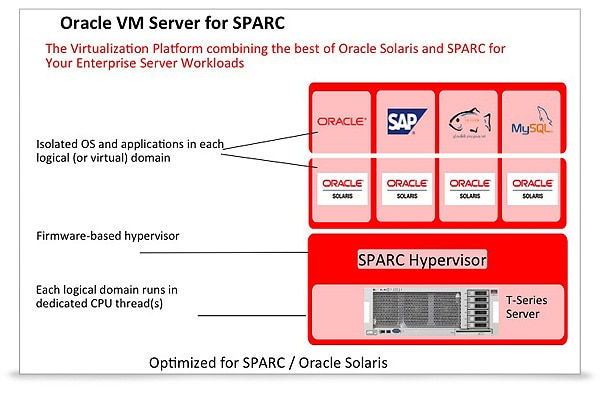
Logical Domains is a virtualization and physical resource sharing technology for the SPARC V9-based UNIX line of servers introduced in May 2007 by Sun Microsystems.
It is possible to control the hypervisor from the command line or visual control interfaces, the latter will not be considered here.
Examples are given for
Solaris 10 OS, in
Solaris 11 it is worth considering the features of network configuration.
In Sun terminology, virtual machines are referred to as domains; there are several types of domains.
Domain roles
- Control Domain - The control domain, in which Oracle VM Server works, is created during installation by default from the system where Oracle VM Server is installed, it is called primary. There can only be one management domain.
- Service Domain - The domain of virtual devices such as virtual switches, virtual disks, etc. Any domain can be configured as a Service Domain; by default, the Control Domain is already a Service Domain.
- I / O Domain - A domain that has access to physical PCIe devices on the server. May provide access to these devices if configured as a Service Domain. It has better performance compared to Guest Domain, almost comparable to a non-virtualized server. The maximum number of domains is limited by the number of PCIe buses on the server. The use of such domains complicates migration. By default, the Control Domain acts as an I / O Domain.
View available PCIe buses and devices:
- Root Domain - The root domain has more advanced access to the architecture of physical PCIe server devices than the I / O Domain. It has access to all services provided by PCIe devices, for example, to the fabric error handling factory. The number of root domains depends on the server architecture.
- Guest Domain - The guest domain has only virtual devices.
Virtual device and service designations
- vnet - Virtual Network. Virtual network card.
- vsw - Virtual Switch. Virtual switch.
- vds - Virtual Disk Server. Virtual hard disk. The disk usage model is built on a client-server architecture, therefore, the vdc client is used to access the disk, and vds is a service for accessing physical disks or their images.
- vdc - Virtual Disk Client. Provides access to a virtual hard disk. Despite the fact that virtual disks belong to the Guest Domain, most operations with them are performed on the Service Domain.
- vcc - Virtual Console Concentrator. Typically, this virtual device has a Control Domain (primary). It provides access to virtual machine consoles. The svc: / ldoms / vntsd: default service provides access to virtual machine consoles, launched in the Control Domain.
An example of creating basic services
Typically, device services are created in the Control Domain, but you can select a separate domain for this - the Service Domain.
- We create a console concentrator in the primary domain, with the name primary-vcc0 and the range of ports used 5000-5100:
- Create a virtual hard disk server in the primary domain, called primary-vds0:
- We create a virtual switch in the primary domain, called primary-vsw0 and bind it to the nxge0 network interface. Use mac address of network card:
The specified mac address is used:
- View a list of primary domain services:
Setting up a Control Domain and releasing resources from it for other domains
- View a list of cryptographic devices. Used in SPARC systems, the presence of these devices in the domain does not allow you to dynamically reconfigure the number of CPUs:
- Naturally set this parameter to 0, or do not touch this command at all:
- Set the number of cores to the primary domain:
- We start reconfiguration of the primary domain or just reboot the server:
- Set the amount of RAM for the primary domain:
- Save the current domain configuration as initial:
- View a list of domain configurations (initial [next poweron] means that the configuration will be used the next time the hypervisor is loaded):
- Reboot the hypervisor:
By default, there is no network connection between the Control Domain and other domains, this is due to the fact that the Control Domain uses a physical interface (eg: nxge0), and the rest of the domains are virtual (eg: vsw0).
Configuring a virtual switch as the main interface in Control Domain
- List of various network interfaces to the system:
- We include the necessary virtual switch:
- Turn off the physical interface:
- We set the IP address and mark the interface of the virtual switch on:
Or you can use DHCP:
- Do not forget to register the network interface settings in the configuration files:
When using DHCP:
Creating Guest Domain
- Creating the ldg1 domain:
- Adding processors to the ldg1 domain:
- Adding RAM to the ldg1 domain:
- Adding the vnet1 network interface connected to the vsw0 switch in the ldg1 domain:
- Add the physical hard drive / dev / dsk / c2t1d0s2 to the primary-vds0 virtual disk server named vol1.
Or:
- Creating a file system with a mount point:
- Creating a file system of a certain size:
- Add the ZFS partition as a virtual disk to the disk server:
Or:
- Create a 10 gigabyte file:
- Add the file as a virtual disk:
- Add the virtual disk vol1 @ primary-vds0 to the ldg1 domain as vdisk1:
- We set autoload for the ldg1 domain when the server starts:
- Install the disk from which the ldg1 domain will be loaded:
- Bind the ldg1 domain to the Control Domain:
- View information about the ldg1 domain, the CONS column will indicate the port on which to connect to the domain:
- View all resources associated with the ldg1 domain:
- Connect to the domain console listening on port 5000:
- Start the ldg1 domain if it is stopped:
Install Oracle Solaris 10 from a DVD
- Stop the volume management service:
- We stop the necessary domain:
- Exclude from the list of managed domains:
- Add the drive / dev / dsk / c0t0d0s2 to the primary-vds0 virtual disk server under the name dvd_vol:
- We connect the virtualized drive to the ldg1 domain under the name vdisk_cd_media:
- View all resources associated with the ldg1 domain:
- Bind the ldg1 domain to the Control Domain:
- Launch ldg1 domain:
- Connect to the domain console:
- Browse domain device aliases for vdisk_cd_media:
ok devalias
- Boot from disk:
ok boot vdisk_cd_media:f
Install Oracle Solaris 10 from an image
- Stop necessary domain:
- Exclude from the list of managed domains:
- Add the solaris10.iso image to the primary-vds0 virtual disk server named iso_vol:
- Connect the virtualized drive to the ldg1 domain as vdisk_iso:
- View all resources related to the ldg1 domain:
- Associate ldg1 domain with Control Domain:
- Launch ldg1 domain:
- Connect to the domain console:
- Browse domain device aliases for vdisk_iso:
ok devalias
- Boot from the image:
ok boot vdisk_iso:f
Domain Deletion
- Stop ldg1 domain:
- Unlink ldg1 domain:
- Delete ldg1 domain:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/468163/
All Articles