Compared with last month in September, Dr.Web server statistics recorded an increase in the total number of threats by 19.96%. At the same time, the share of unique threats decreased by 50.45%. Most often, users were attacked by adware programs, as well as software downloaders and installers. In the mail traffic, threats again prevailed, which use Microsoft Office document vulnerabilities to infect devices.
The number of user requests to decrypt files affected by encryption Trojans has increased. At the same time,
Trojan.Encoder.858 became the most active encoder - it accounted for 16.60% of all incidents. In addition, almost twice as many Internet addresses were added to the database of non-recommended and malicious sites than in August.
According to Doctor Web statistics servers
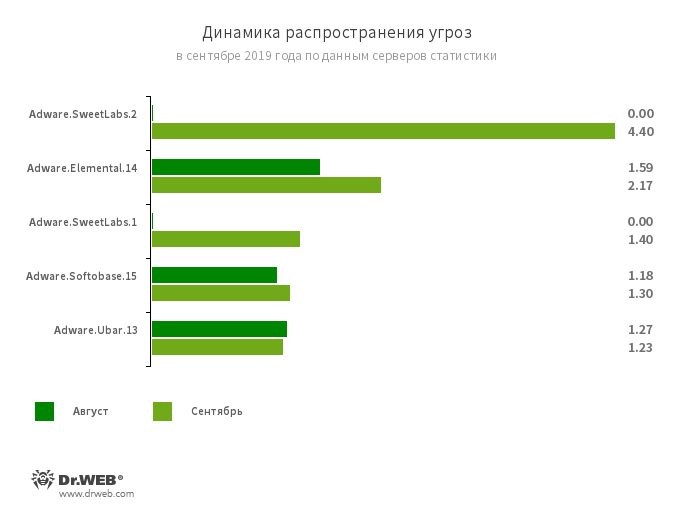
The most common threats of September:
- Adware.SweetLabs.1
- Adware.SweetLabs.2
An alternative application catalog and add-in to the Windows GUI from the creators of
Adware.Opencandy .
Detection of advertising programs that, by substituting links, are downloaded from file-sharing services when trying to download certain files from them. Instead of the expected files, the victims receive these applications, which display advertisements, and also install unnecessary software.
An installer that distributes legacy software. Changes browser settings.
A torrent client that installs unwanted software on a device.
Email traffic statistics
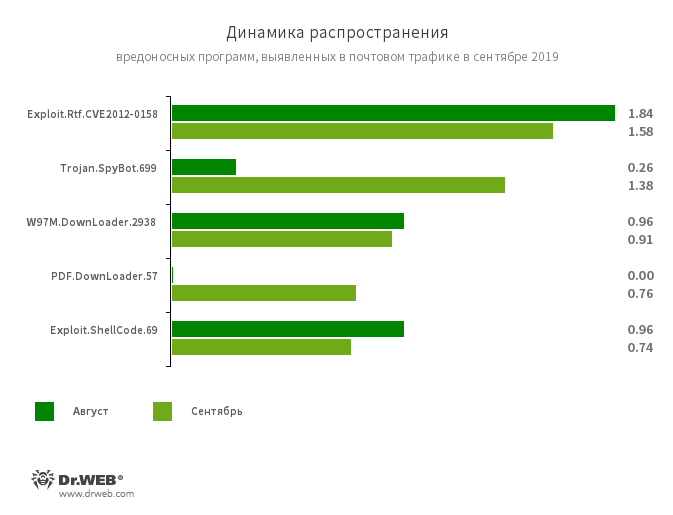
A modified Microsoft Office Word document that uses the CVE2012-0158 vulnerability to execute malicious code.
A spyware Trojan capable of intercepting characters entered on the keyboard (keylogger).
A family of downloader Trojans that exploit vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office documents. Designed to download other malicious programs to the attacked computer.
A representative of the family of downloader Trojans that are distributed in specially formatted PDF documents.
Malicious Microsoft Office Word document. Uses vulnerability CVE-2017-11882.
Cryptographers
Compared to August, in September Doctor Web technical support received 14.59% more requests to decrypt files from users affected by encryption Trojans.
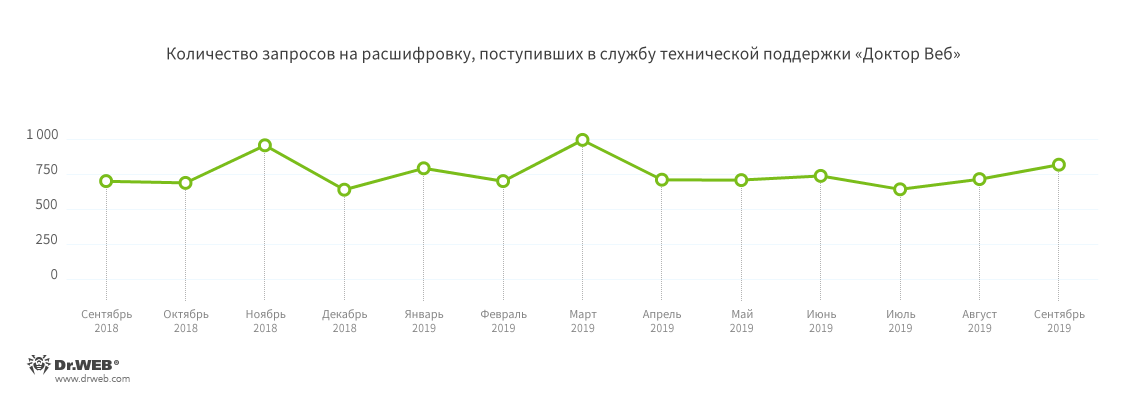
Most often, the calls were related to the following encoders:
Dangerous sites
During September 2019, 238,637 Internet addresses were added to the database of non-recommended and malicious sites.
Malicious and unwanted software for mobile devices
During September, a lot of malware was detected on the Google Play directory. Earlier this month, Doctor Web virus analysts detected the banking Trojan
Android.Banker .347.origin, which attacked users from Brazil. He intercepted SMS messages with one-time codes and could download fraudulent websites at the command of attackers. Another banker, found at the end of the month, was named
Android.Banker .352.origin. He stole the credentials of users of the YoBit cryptocurrency exchange.
Among the threats spread via Google Play were the
Android.DownLoader .920.origin and
Android.DownLoader .921.origin downloaders, which downloaded other malicious applications. In addition, virus analysts have detected
Android.HiddenAds adware Trojans. In addition to them, our experts discovered several modifications of the Trojans of the
Android.Joker family. They subscribed users to expensive services, could intercept SMS, and transmitted data from the phone book of infected devices to cybercriminals. Also, these Trojans downloaded and then launched auxiliary modules and were able to execute arbitrary code.
In addition, virus analysts have identified new versions of potentially dangerous programs designed for cyber espionage.
The most notable events related to the "mobile" security in September:
- malware distribution through the Google Play directory;
- Detection of new versions of cyber espionage software.
Read more about the virus situation for mobile devices in September
in our review .