
Both products are designed to detect unauthorized user actions, suspicious activity and configuration control in the Microsoft infrastructure.
Quest Change Auditor and
Netwrix Auditor are direct competitors who are quite struggling with each other for a place on customers' servers. Under the cut, we revealed the features of the solutions of both vendors.
Product versions under investigation: Quest Change Auditor 7.0.3 (written about it
here ), Quest Enterprise Reporter 2.5.1 (written about it
here ) and Netwrix Auditor 9.8 (we have not written about it yet, but we will write soon).
Why does Quest have two products, but Netwrix has one? The fact is that in Quest, change control is performed using Change Auditor, and configurations - Enterprise Reporter. In Netwrix's Auditor, these two functions are in the same console.
We will analyze the products according to the following properties regarding change control and Active Directory configurations: supported technologies, architecture, integration capabilities, interface elements and general conclusions.
Supported Technologies
Details are in the table below.
Architecture
The first and main difference between the products is the collection method.
Netwrix makes this an agentless method, i.e. uses native auditing tools (Windows logs). Before starting work, in order for the audit data to be sufficient, a number of settings must be made at the operating system level.
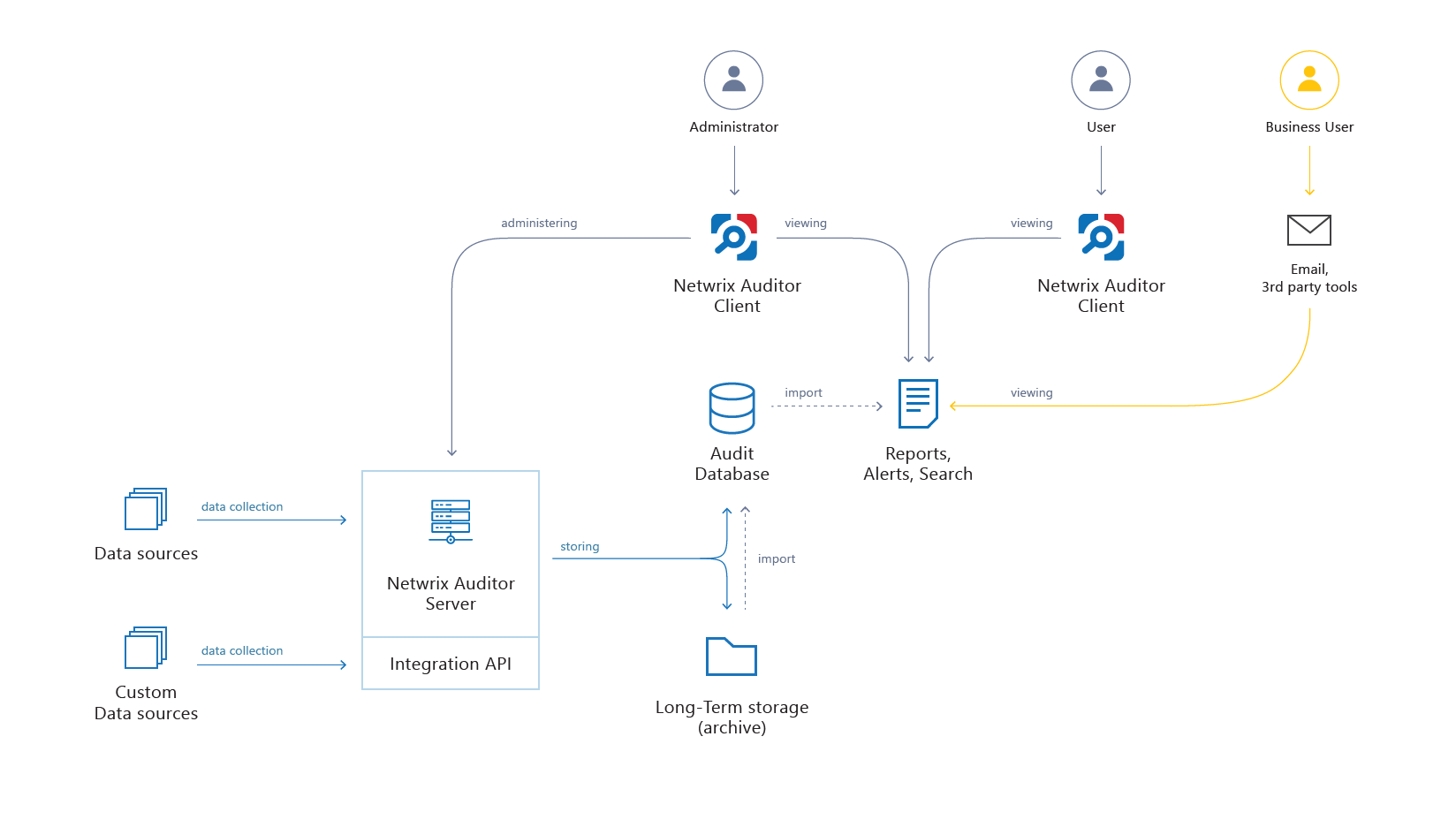 Netwrix Auditor Architecture
Netwrix Auditor ArchitectureThus, the architecture of Netwrix Auditor consists of a central server, database and consoles. The system scales vertically by increasing the power of the central server.
Quest uses an agent method. Change Auditor receives events through deep integration into calls within AD and, as the vendor himself writes, this method detects changes even in deeply nested groups and brings less load than when writing and reading logs. You can check at high load. The consequence of this low-level integration is that in Quest Change Auditor you can veto certain changes for certain objects, even users at the Enterprise Admin level.
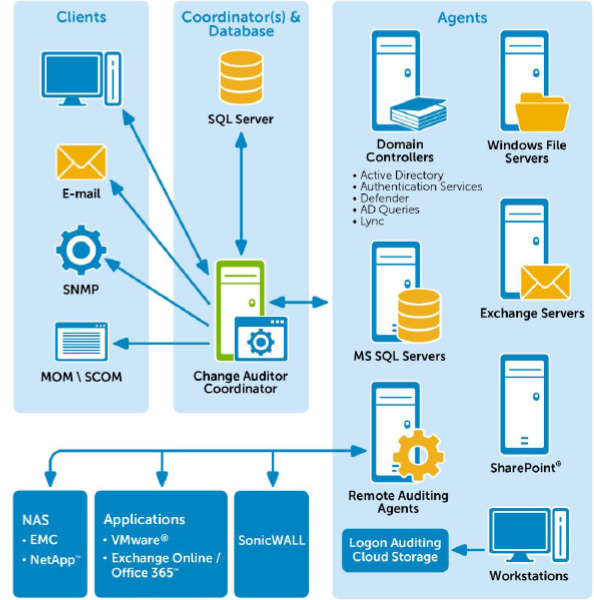 Quest Change Auditor Architecture
Quest Change Auditor ArchitectureThe image above shows that the core of the system is the coordinator and the database. The architecture of Quest Change Auditor allows you to perform horizontal scaling and host coordinating servers on various virtual (or physical) machines, thereby ensuring high availability of the solution using the solution itself.
The Enterprise Reporter architecture is represented by a central server and nodes that are responsible for aggregating configuration data. Like Change Auditor, Enterprise Reporter runs on a SQL Server database.
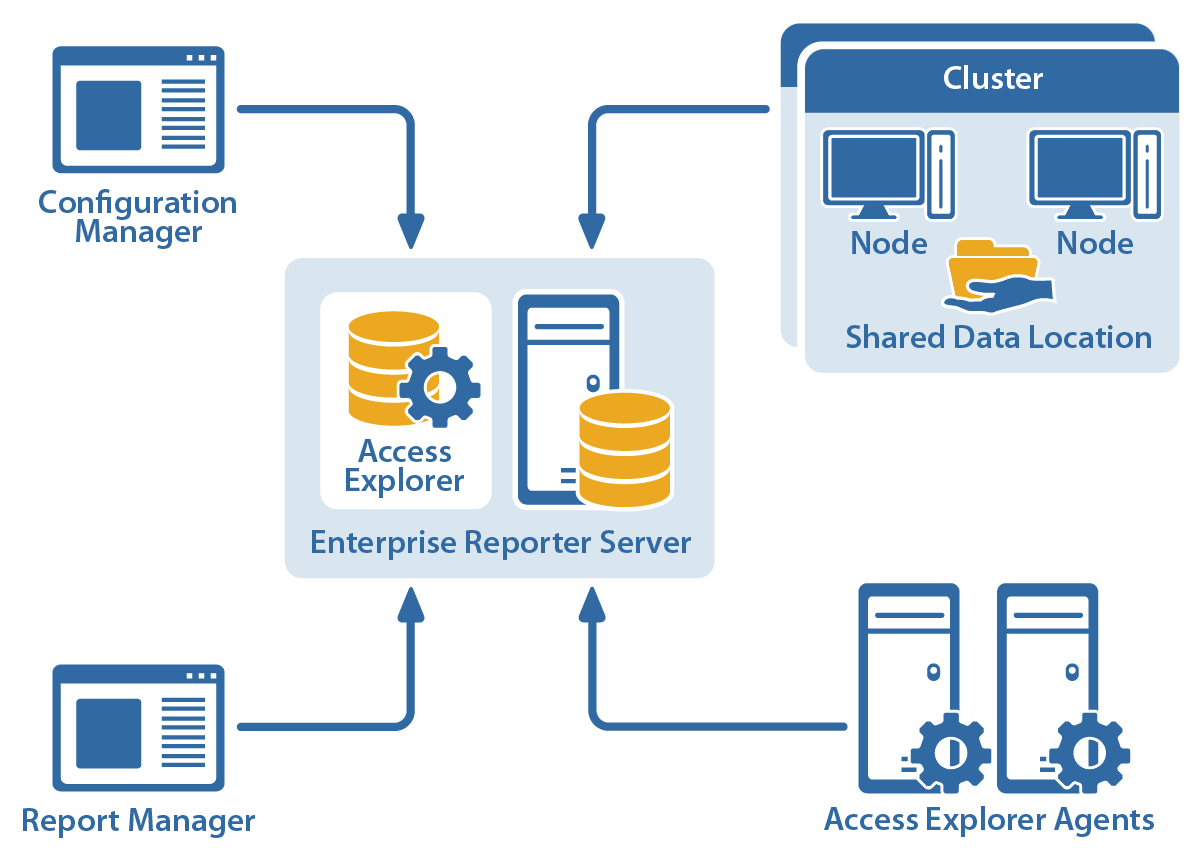 Quest Enterprise Reporter Architecture
Quest Enterprise Reporter ArchitectureIn addition to the above, Quest has a separate IT Security Search umbrella console with google-like search, which combines the first two products and displays events from Change Auditor in conjunction with reports from Enterprise Reporter. IT Security Search is free.
Another difference is the availability of the product from Quest, in addition to the "thick" client web console with the ability to adapt to mobile devices. Netwrix Auditor has only a "thick" client.
As Quest writes in its materials, the development of various products is their conscious choice, not historical circumstances. The company claims to deepen and develop each product individually, and does not make a one-stop solution.
Another functionality of both products has not been analyzed in the architecture diagram: it is the restoration of modified objects to their previous state. In Change Auditor, this feature is available from the same interface, and in Netwrix Auditor, for the same operation, you need to run a separate console.
Integration
Both manufacturers have standard integrations with SIEM systems: ArcSight, Splunk, IBM QRadar and universal integration through web services. In addition to the above, Netwrix integrates out of the box with ServiceNow, LogRhytm, Alien Vault, Solarwinds and
others , and Quest has a plug-in for sending events to SCOM.
To export data to external systems in Change Auditor, you must use access through the database, and in Netwrix you can use both the database and the RESTful API.
Interface elements
Consider all the interfaces that offer to use both vendors in their work. Both products have predefined reports in various sections, as well as by types of compliance (SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, etc.). Let's start with Quest.
Quest
As mentioned above, Quest uses two separate products to audit changes and control configurations: Change Auditor and Enterprise Reporter.
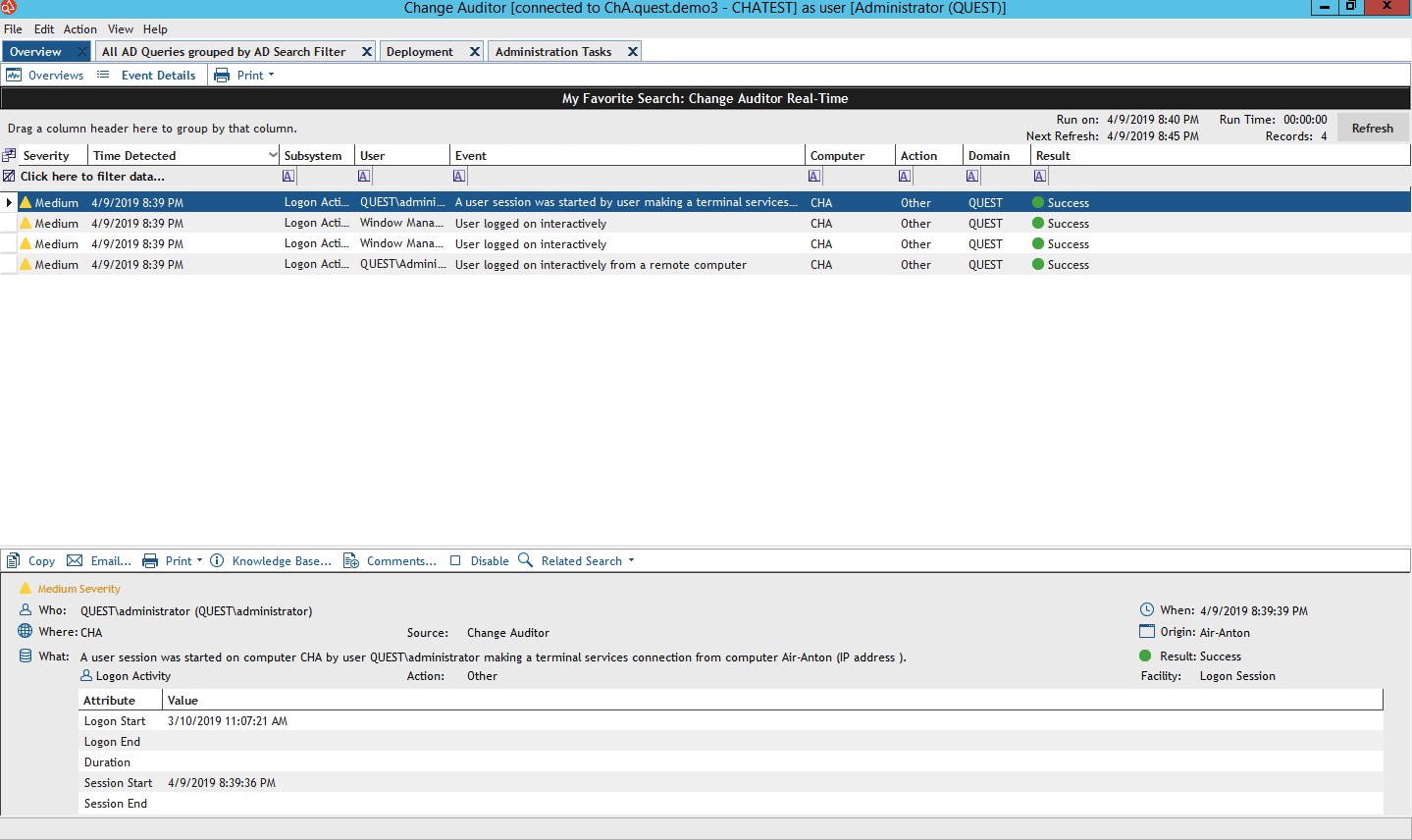 Quest Change Auditor Event Interface
Quest Change Auditor Event InterfaceThis is the main console of Change Auditor. It is needed to control changes and here you can see all the events. Of course, you can apply filters to them and observe only what you need.
There are many ready-made reports that you can modify or create new ones on their basis.
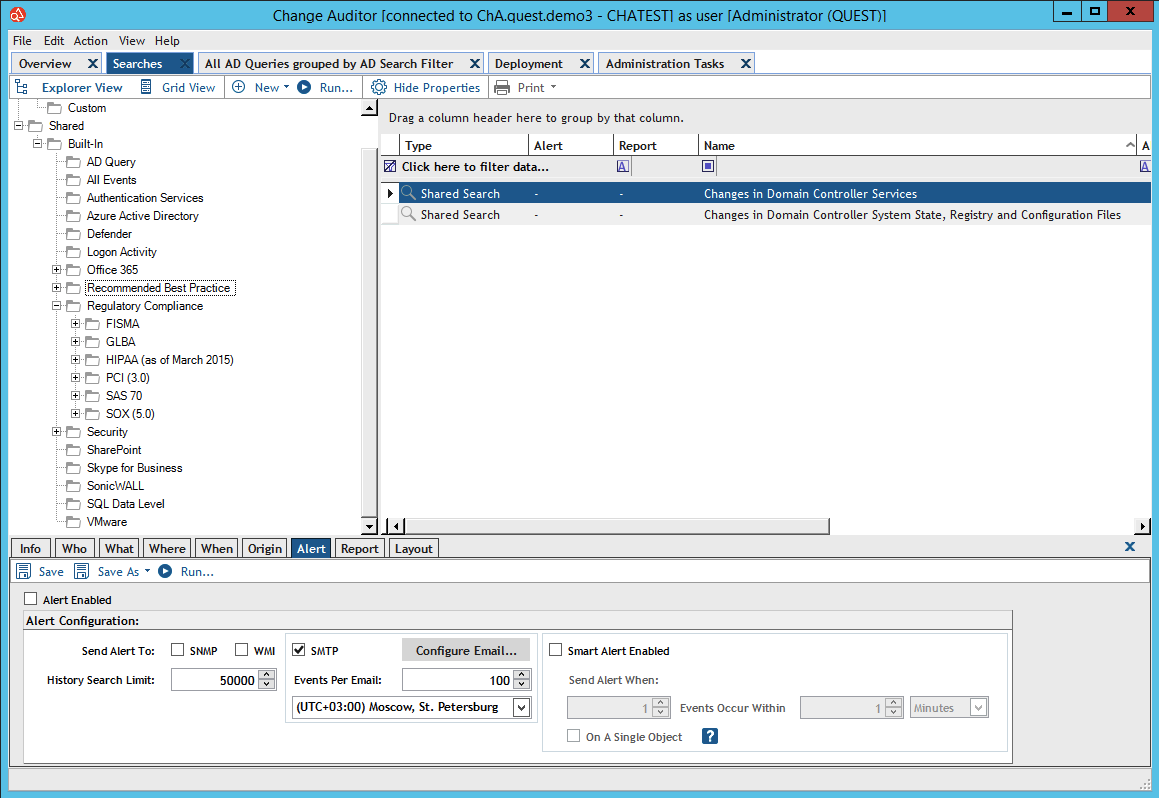 Report Selection Interface in Quest Change Auditor
Report Selection Interface in Quest Change AuditorIn addition to the main consoles, Change Auditor has a special Threat Detection module. It receives events from Change Auditor over the past 30 days and reveals atypical user behavior: entering from an unusual place or at an unusual time, unsuccessful password entry several times in a row on a domain controller, entering a forbidden file resource, etc.
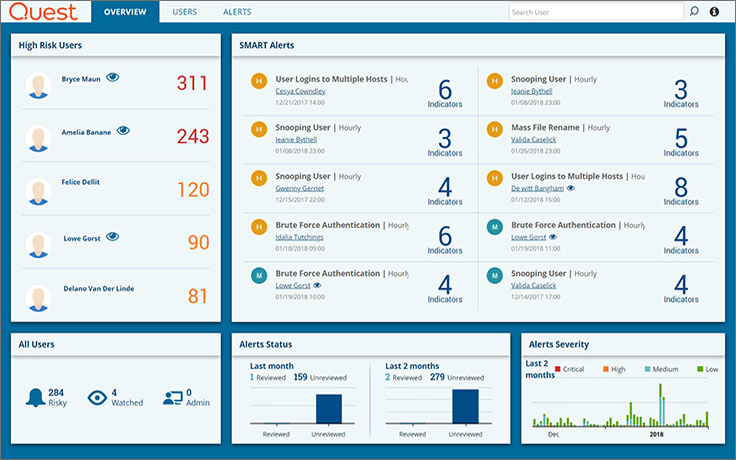
The next console is Enterprise Reporter. It controls the configuration of objects. There are also predefined reports.
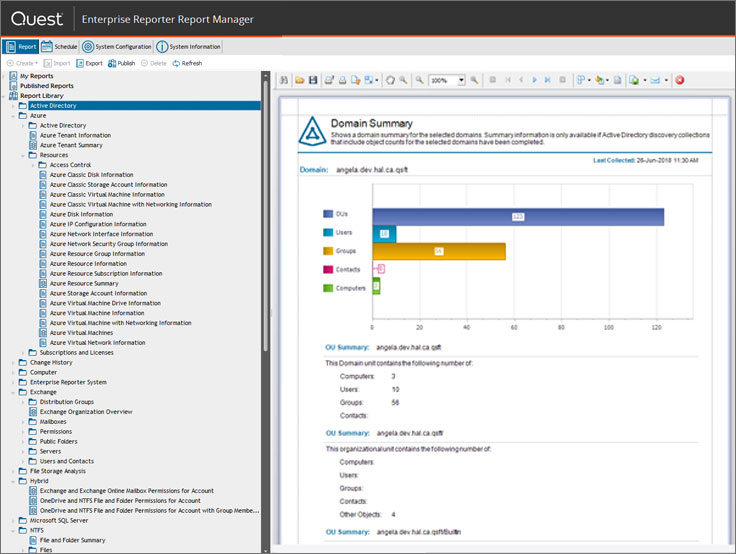 Report Selection Interface in Quest Enterprise Reporter
Report Selection Interface in Quest Enterprise ReporterThe Enterprise Reporter (and Change Auditor, too) has report designers in which you can create an easy-to-understand layout.
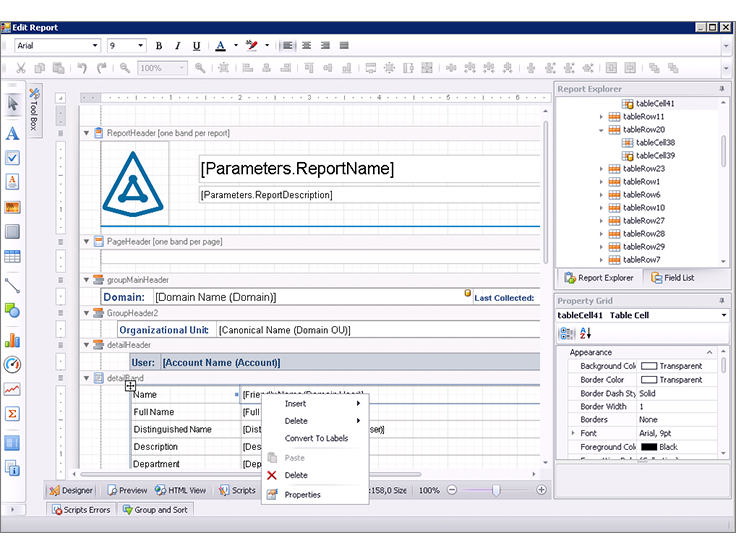 Report customization interface in Quest Enterprise Reporter
Report customization interface in Quest Enterprise ReporterAnd the IT Security Search console to search for events and configuration changes. Here you can find everything that happened with one or another object based on data from Change Auditor and Enterprise Reporter.
 Quest IT Security Search Search Interface
Quest IT Security Search Search Interface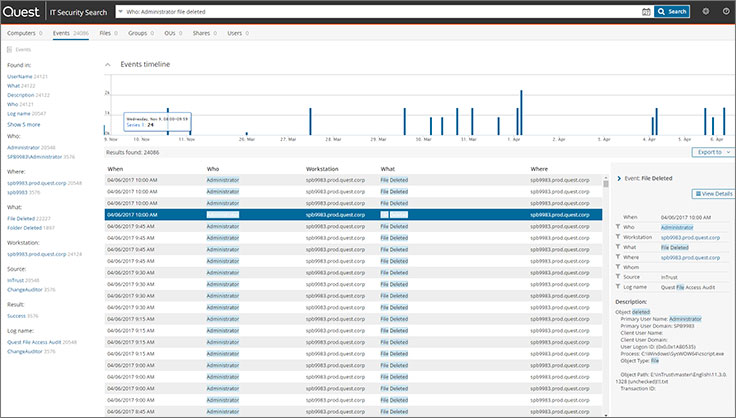 Quest IT Security Search Search Results Interface
Quest IT Security Search Search Results InterfaceNetwrix
We pass to the Netwrix interfaces. The main control panel, from which all the settings and reports in the image below are available.
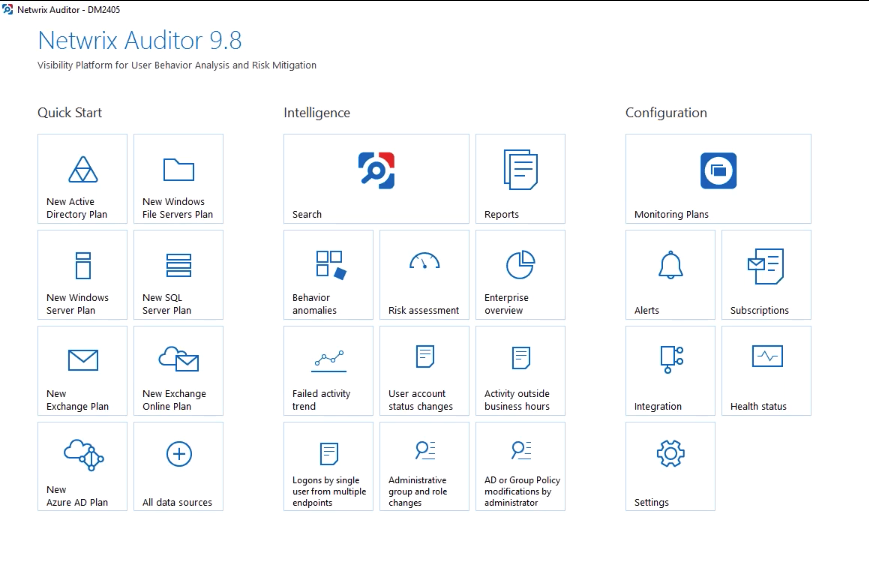 Netwrix Auditor Core Interface
Netwrix Auditor Core InterfaceAmong the Netwrix views, we did not find a traditional event console (similar to monitoring systems or Change Auditor), but there is a special view with event search, called by clicking on the "Search" button.
 Event Search Report in Netwrix Auditor
Event Search Report in Netwrix AuditorThe following image shows an example of a report on possible risks.
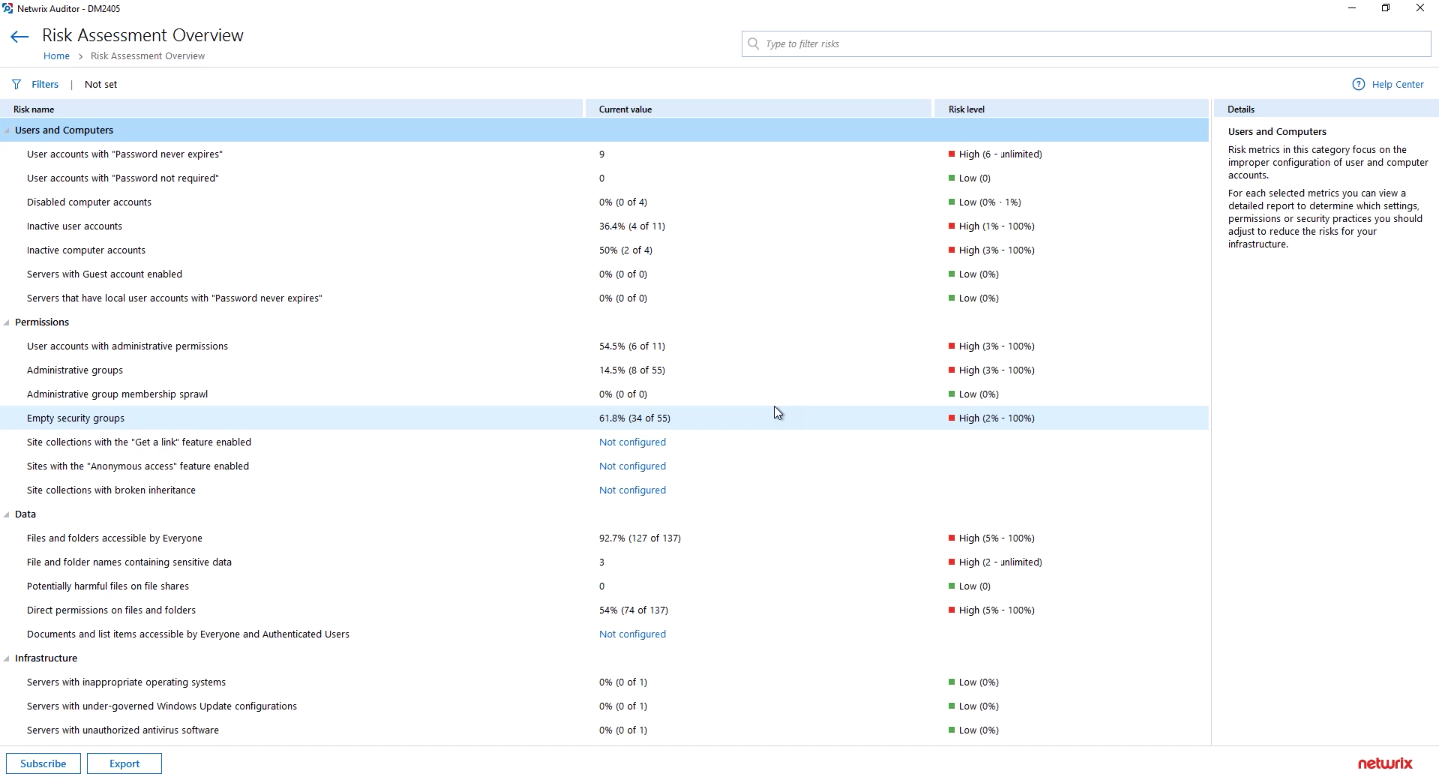 Netwrix Auditor Interface with Possible Risks
Netwrix Auditor Interface with Possible RisksNetwrix Auditor has a set of predefined reports (there are many of them). Each can be modified and created on its basis a new customized report.
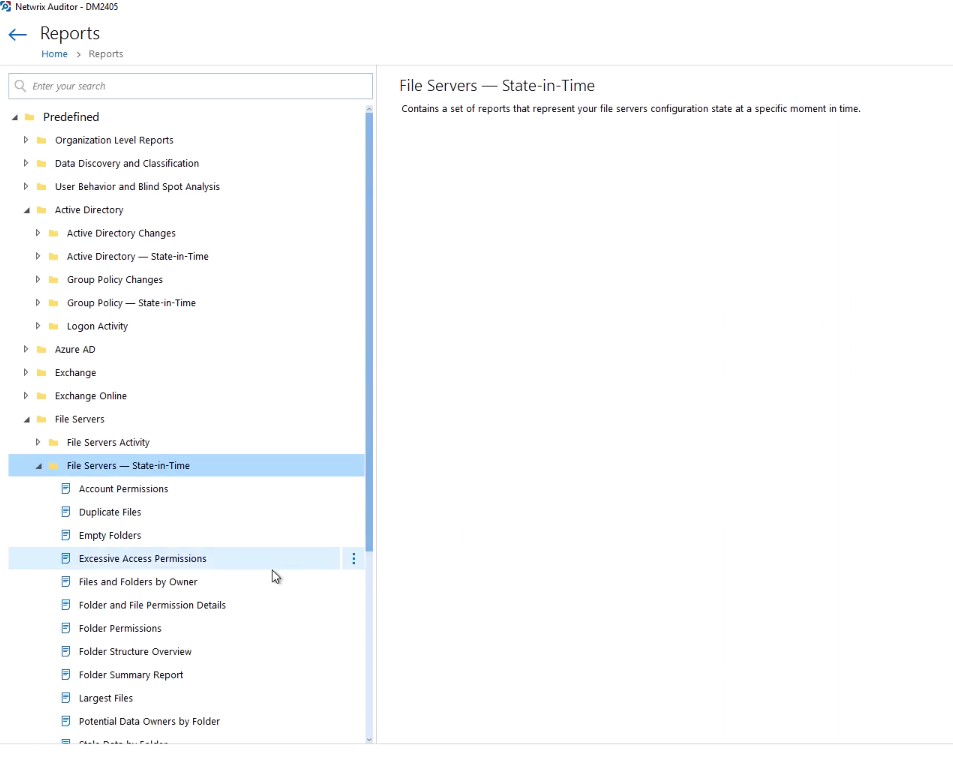 Netwrix Auditor interface with a list of built-in reports
Netwrix Auditor interface with a list of built-in reportsFrom the main interface, a report can be generated with the specified characteristics. At the end of the report there is a “Subscribe” button.
 Netwrix Auditor interface with sample report
Netwrix Auditor interface with sample reportNetwrix Auditor has a special presentation with identified anomalies.
 Netwrix Auditor Interface with Identified Anomalies
Netwrix Auditor Interface with Identified AnomaliesConsole to undo changes. Made in the form of a wizard and runs separately in the Windows menu.
 Netwrix Auditor Console for undoing changes
Netwrix Auditor Console for undoing changesGeneral conclusions
In general, both systems have similar functionality (except for differences in supported technologies). When choosing an audit system, we recommend proceeding from a set of technologies that need to be controlled, individual advantages of systems (for example, blocking changes to objects in Change Auditor or integration through the RESTful API in Netwrix Auditor) and ease of use in the interface (but this is already subjective). Another difference that was not included in any of the sections of the article, but was revealed is the technical support: 24/5 in Netwrix and 24/7 in Quest.
If you are interested in auditing the Microsoft infrastructure and you want to do this in a system specially designed for this and evaluate the capabilities of the systems,
leave a request , we will contact you.
When writing this article, data from open sources were used.