Now everyone is talking about the new revolution brought by artificial intelligence and machine learning. Smart algorithms penetrate all spheres of life: from searching for the Higgs boson, to choosing a movie for the evening. The most advanced companies are already actively implementing these technologies in their products and marketing. Personalized recommendations, advertising, website interface - all this is not some kind of black magic, but already available technologies.
In the domestic market, without a doubt, Yandex is the most advanced company using the power of machines. In his report to #amoCONF, Yandex Services Marketing Director Andrei Sebrant spoke about the future and the opportunities that open up for each company. Optimize your business for future trends!
Disclaimer . This article is a transcript of Andrei Sebrant’s speech. There are people who save time and love text, there are those who cannot watch videos at work or on the road, but happily read Habr, there are hearing-impaired people for whom the sound track is inaccessible or difficult to understand. We decided for all of them and you to decrypt excellent content. Whoever prefers the video is the link at the end.
Machine intelligence and commoditization of technologies
Good day! Hello, everyone gathered at the Olympic. Thanks for the eyeliner. True, I'm going to talk about the future, using scary words. I suspect that the term “commoditization of technologies” is not widely known to anyone - do not be shy, it is generally not known to many. But it is useful, it is really simple. I’ll talk about him later. And yes, there was the right phrase: I’m going to talk about the future that has come, is coming, some have come so that only scraping remains.
The trouble is that over 20 years of my work on the Internet it seemed to me that everything was awesome, quickly happening - how cool! I now understand that everything that took place over these 20 years was a monstrously inhibitory process, incredibly slow, but it is quickly starting now. In general, the whole report, the story is built on the principle of a strange mosaic, a mosaic that ... Not even, I’d better say it this way: on the principle of a scattered puzzle. If, as a result of looking at these pieces, the picture from these pieces of the puzzle begins to form in your head - the goal is achieved, if not - well, I don’t know, look at the record, try it - maybe it will turn out. Because this is not a cookbook - I will not tell you how to do it. I will tell you in what future, literally in a few years, in 3-4-5 (no more) you have to organize your sales, attract customers, communicate somehow with people who are related to you.
A future that has already come. Two cases are not about the Internet and not about marketing.
But I'll tell you a little bit strange cases. Here is the story of a man from California. It was not by chance that I brought his age on the slide - the peasant is 65 years old, he is even older than me. He has a problem: he has a wife who loves her clean lawn (but this is California, there are no two-meter fences around the lawns); neighboring cats walk on the lawn and crap. How is this task solved in 2016?
Neighboring cats and favorite lawn: how to solve a problem with his wife
In 2016, this person, Robert Bond, buys a little bit of iron to his home computer, connects to it an already standing surveillance camera, which looks out over the lawn and does a somewhat unusual thing further - it downloads affordable, free open-sourced software, which is a neural network and begins to train this neural network to recognize cats in the camera image.
And the task at first seems trivial, because if something is easy to learn, it's cats, because cats are littered with the Internet, tens of millions of cats are on the Internet. If everything was so simple - to recognize such a "daytime" cat can be trained on the "data set", which loads simply with the speed of the throughput channel. But things are worse: in real life, cats go to crap mostly at night. There are practically no pictures of night cats peeing on the lawn on the Internet. Man had, as we do, as any company engaged in normal data-science and training of neural networks does ... Okay, we will dig up the pictures additionally, make them ourselves; the net learned to recognize night cats is also very reliable ...

And after that - the last step: the valve electric control is connected to the output of this computer. The valve stands on the pipe that leads to the sprayer. Therefore, as soon as the cat enters the lawn and wants to adapt, they begin to water it - the cat dumps.
The problem is thus solved, the wife is happy, the cats don’t walk, and all this is a strange miracle - neural networks learning to recognize cats, who found out that on the Internet, hell, there are not enough source images for training. Okay, we will finish you up! She finished her studies. This is probably the only neural network in the world that can recognize night cats.
All this is done by a person who is not a hyperprogrammer, who has not worked at Google or Yandex all his life, and with the help of just such hardware, in general, it’s quite cheap, compact and simple.
Japanese cucumbers: how to help mom
Other story. Across the ocean from California, Japanese grow cucumbers on a small home farm. Cucumbers on this form are usually sorted into 9 different categories.
This sorting is done manually by an old mother. It’s hard for her - she stands 8 hours a day near the conveyor, and she’s all her life ... Well, not all, but she devoted the last few years of her life to what she understands, looking at a cucumber (its pimples, color, size and shape), in which out of nine categories it should be attributed. They have trouble - they cannot even hire a temporary worker, because the worker must be taught for several months this glorious process - to recognize cucumbers. Then you probably already guessed.

It was a computer again. This time, however, the grid was in the cloud, because the Raspderry Pi computer is quite low-power. The mesh was taught what mom does as a training sample, they used the action of the mother herself: here is a photograph of the cucumber, where his mother took it. After my mother did this 10 thousand times: “Setochka, here’s a new cucumber for you, do you understand what category he has?” “I understand,” says the setochka.

And all of this was embodied in such a design: the conveyor, cucumbers ride along it before falling onto the conveyor, a camera looks at them, pushers stand along the conveyor and push a cucumber into a box of the corresponding category. Again, this is the 2016 decision. It illustrates a very important point that is now poorly understood. It is written on the screen:

What we used to call information technology, in fact, has ceased to be information. These are operational technologies: the trained machine itself performs actions, and does not inform us; the bell doesn't sound - “The cat has come. What are you going to do? Will you tie it with a towel or what? ” And it displays the category number over a floating cucumber. “Well, now you can push your king’s hand” ... No! There is no person at all in this process after training has ended. This is a very versatile picture that characterizes how the future works, in which machines solve intellectual tasks (to identify a cat, to understand which category a cucumber belongs to).
Information technology has become operational
And actually, this is not our whim. And in general, this is not a property of only the Internet and some virtual things happening on the computer. I specially brought the slide: General Electric is a rather big company working with colossal offline businesses, which believe that 2015 was the year that conversion took place - information technology has become operational, and they determine our future. And in fact, in order to catch up with all this, we need to think about how to set up the same transition in our business processes, because transformation is always a painful and not an instant thing.
But if you do not prepare for this information now, you may find yourself among those who have been stepped on. A good example: they stepped on Kodak, he thought he was well protected (such a technology!). They stepped on the Blackberry - they sincerely thought that it was valuable for people to put pressure on the buttons, and no one would drag their fingers around the screen, dirtying it. Where is the Blackberry? ..
Finally, another reference to the authorities. At the beginning of this year, in Davos, at the World Economic Forum, these very words were officially repeatedly pronounced: we are now in the very center of the fourth industrial revolution. This industrial revolution is mainly due to the frantic speed with which artificial intelligence and machine learning are being introduced.

I hate the words “artificial intelligence” and will now explain why. Because in fact, we are trying to compare the car with ourselves in this place and somehow frighten the car (it’s not afraid): “You will never compare with us! We are thinkers! ” You see, the machine throughout the history of mankind has proven that it can do more - more because we invent it like that.
A car can always do more
Here is a good example that I like to give on a bunch of lectures - this is a story about an artificial bird. We cannot reproduce this. We really have no idea how each feather is arranged in its wing, what function it carries in flight. Moreover, the diversity of these feathered wings in the nature is monstrous! .. And then there are bats.
What is an artificial bird?
True, we cannot and will not be able to reproduce, judging by the development of technology, in the next few years - we cannot fully understand the physics of flight with the accuracy of how each hair in the wing works. But we, since we are still human beings, humanity, were inspired by the bird as an idea of flight. And in this sense, the first artificial bird was a balloon, created many centuries before today. Because he allowed people to take to the air.
Then, after some time, they returned to the idea of a completely different wing, with the profile that the bird is not aware of - it is in static, without swinging movements it can keep the car in the air. But he has a jet engine, and this machine began to haul us across the ocean, which the birds cannot.
Moreover, at some point, we, humanity, flew to the stars ... Okay, to Mars! So far, not to the stars, but this “Curiosity” is crawling along Mars and is transferring selfies from there. The same artificial bird brought him there. You see, what we thought about the idea of flying and what should be an artificial bird.

Listen, when they say to me now about artificial intelligence ... Well, we don’t know how it works (points to the head) ... Yes! Just like we don't know anything about the bird's wing. This did not stop us at the stage when the balloons appeared, come up with an abacus and simplify some kind of operation that animals are not capable of, but we have a verbal account - but, damn it, it's easier. Then technology helped us to make it even simpler, and then technology reached the very neural networks that are trained on their own - this is important! They learn by themselves!
What is artificial intelligence?
If we recall the example of a cat, no one explained to this grid the formal parameters of the difference between a cat and a baby and a dog. Grid studied herself, looking at millions of pictures of cats and eventually learned. We do not know how. Well, how do we learn ourselves?
And actually, what I'm talking about right now, that artificial intelligence (machine speaking is still more correct) will have the same relation to our brain as a rocket to a sparrow - and makes life so interesting. A rocket cannot tweet and shit on our heads. Sparrow can.

At the same time, a rocket, as you might guess, can: a nuclear charge to a neighboring continent, Kuryoshiti to Mars, a satellite to orbit for satellite Internet to work, a lot of things, but this has absolutely nothing to do with sparrows. Exactly the same thing will happen with machine intelligence: it will do things that we cannot figure out, what the brain can do, but it can.

At the same time, another interesting story happened in parallel, which concerns not so many services ... Because I'm talking about specific services now - image recognition, in fact the function around which both examples were built, around which the search for pictures is built, a bunch of some of things. But this is still a specific service. You can say personalization - I will have separate examples about it. This is also a separate service - to understand something about the buyer who came to you. But this is a service.
Not only the services themselves, but also the interfaces
Self-learning systems, neural networks in the first place made it possible to solve another interesting problem that is absolutely like this - across all services. This task is front-end.
Some time ago, there was such a problem (although it did exist): you need to bring the information into machine-readable form so that the machine can start working with it. No more such a problem! Because ... What is a machine-readable view? She can read the text even from the manuscript, even from the screen, even from the cave drawing, if the text is there. She can, moreover, understand what happened in this picture if it is a picture. She can hear what has been said out loud and turn it into printed text if you need it for some reason; worse than that - the meaning of all this is to understand ...
Recognition of speech, images, speech synthesis
And this is the most interesting story that is happening now. What is happening right now is awesomely changing lives, say, in a couple of years. In order for the machine to learn not to stupidly listen and simply translate sounds into letters, it was necessary to teach it some meaning. This is where an interesting task began, a completely practical task, which is not visible from the outside, and this is a huge breakthrough that was solved, for example, by search engines that had to solve the problem ...

You know, for some mental illnesses (if there are psychologists in the room - they know such a test) they give four objects or more and say: “What is superfluous here? Find it. " In many cases, for some diseases, completely surprising, strange answers that seem delusional to us. So, the same task for the car: four objects - find the extra.

And it turns out that in the old, traditional model of linguistic analysis, this is a big ambush. Because, if we look at object No. 2 and object No. 4, it turns out that while this written text and stress are not heard, the LOCK and LOCK are no different. Moreover, even an in-depth analysis of the adjective shows that this is something that describes the material from which this noun is apparently made. And it would seem that these two objects are very close (points to "Stone Castle" and "Iron Castle"), and this one ("Old Fortress") is generally nowhere, there is nothing similar. But you and I understand that the story is completely different: generally speaking, this object is superfluous (the Iron Castle), but these three are the same. How to explain this to a car? Especially when it comes to the fact that there is an image in general and, for simplicity, or rather for realism, we assume that this image does not contain text in pictures - for example, on the page where it is found. Just an image. In the photo album. How to classify it? Should I display it at the request of the "old fortress"?
And it turned out that there is such a thing that for some time seemed unscientific fiction, like a very multidimensional space of meanings in which you can teach a machine to build some vectors. Pieces of these vectors are shown below the pictures, and even a cursory glance shows that these (the first three pictures) are generally similar - well, guys, there is something 8, 7, 1, 3 ..., and here - brrr, it’s obviously something- it’s not at all. That is, these three stick out somewhere in one place, in one area, approximately in one area of this monstrous multidimensional space of meanings, and the fourth somewhere somewhere there.
And this solves the problem of understanding the meaning, at least from the point of view of what objects are meaningfully close to each other. It’s cool that this task now, for example, to solve problems similar to one another, will allow the same Microsoft to provide excellent simultaneous translation in Skype. Because it was at that moment when instead of the classical linguistic models that stumble on this problem (lock - lock), neural networks were connected - it became meaningful to translate. And then, guys, then they already connect language by language. At that moment, when your space of these meaning vectors is full, its projection into any language is a purely technical operation. At this moment, language problems on our planet disappear as a class.
This is a very non-trivial story! I’m not saying that the ingenious Yandex, the ingenious Microsoft, the ingenious Google are doing it now. I mean that this changes life in a way that we could not imagine, somehow like that - with a half kick. We won’t even see that all of a sudden everything in the interface was shut down. It will look like this - not like some kind of separate super service.
Attempt on traditional science? No, symbiosis with her!
I want to show what is happening with traditional areas specifically on the example of science, and not some commercial product. Look, the science that concerns us all is meteorology. We all want to understand: do we need to take an umbrella, will it rain today? Maybe, in fact, it’s not necessary to have an umbrella, but simply to dress warmer, and there will be no rain, and the bastard is terrible.
And here I’ll say now about the Yandex solution, because it, again ... I don’t want to sell Yandex here, it is large enough without my sales. These things with meteorology are now being done by all the large companies engaged in forecasting weather phenomena in the world: both the Weather Channel and others, IBM has connected in terms of machine learning. Fortunately, we have a forecast inside (one of Yandex services), and, for something, we have enough machine learning.
About the weather forecast and Meteum
So, the Meteum appears. A brief tour of what weather forecast is. This is an awesome completely diverse array of data pouring in real time into supercomputers. Data is taken from what is now on the screen. These are dozens of meteorological satellites, from which information is flowing about the portion of the Earth that is located beneath them, in various parts of the spectrum. These are about ten thousand weather stations that give (but, unfortunately, only on the surface of the earth) information on the state of the atmosphere: its temperature, wind direction, wind speed, humidity, chemical composition, if necessary, the degree of light exposure by the sun - that’s all.

Well, since, generally speaking, the atmosphere is three-dimensional, and in order to simulate all sorts of such processes in it that require still changing something in height (the clouds are at a certain height, and not just a column), there are several more, Unfortunately, stations small enough for the size of our Earth, from where they regularly launch, several hours a day, weather balloons - a hefty balloon filled with helium (so it takes off), which carries a set of sensors that can measure everything the same (temperature, speed, humidity and t aka further).

And the whole set of these data is poured into several hyper-, supercomputer centers that are located around the world, and these data are processed by several constructed by physicists-theorists, specialists in the dynamics of compressible fluid (this is what the atmosphere surrounding us is called in a normal "physical" language) ... These there are a lot of models, they are really few, and harder they were created, for decades, by the work of a bunch of brilliant brains, very strong physicists, and then turned into executable code by no less than brilliant programmers and mathematicians ami.
These models give, in general, give some kind of approximately meaningful forecast. A special example: none of these models in this situation will predict +30 (the sun). But it’s clear that they are lying (the weather is about the same as in our courtyard) - either a little more than zero, or a little less than zero, or it will sprinkle snow, or rain, or what?
Okay, let's connect a machine learning system here - the one we have called the MatrixNet (with all sorts of dummies yet). And tell me, the machine learning system, you have a task: here are a bunch of heaps of forecasts (say, tomorrow at 9 a.m. in the Olimpiysky area). You write them down now, write down these forecasts - tomorrow you will compare them with the results of actual observations, because tomorrow we will know at 9 am what happened here. And so continuously, and so for the whole Earth. We have large data centers.
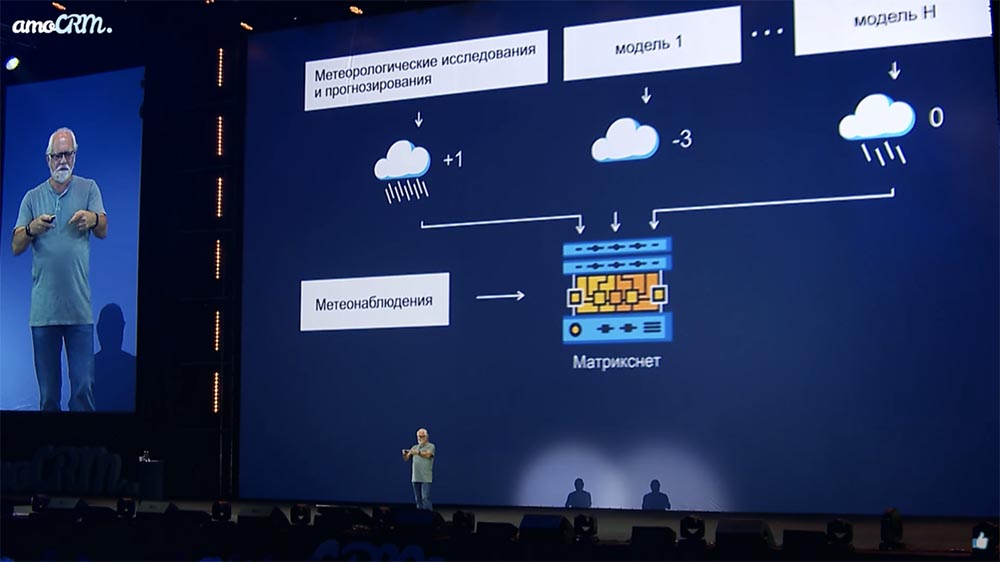
Your task is to learn all the time, comparing how each of these models diverged from actual observation at a given point; learn to minimize this delta, learn to generate your own forecast, which would have a delta (discrepancy with reality, temperature or rainfall or some other metric) less than the discrepancy of any of these models individually.
At the same time, note the important thing: we do not teach this machine physics, we do not have a staff of professors, as in the Institute of Atmospheric Physics of the Academy of Sciences. This machine learns itself to minimize a certain parameter, that is, to make a more accurate forecast. Why? Yes, we have no idea! We are still loading additional data into it that cannot be loaded into the model. For example, for general reasons, we understand that, generally speaking, life in the atmosphere is different for different types of underlying surface, that is, over a lake, over a spruce forest or deciduous forest or urban areas, the atmosphere behaves in very different ways.
But on Yandex.Maps we see pretty up-to-date information, in contrast to these models, in which this information was once, a hundred years ago, laid down, and then this forest was cut down, and there the city was built ... But we have something more- less recent information is available from our satellite maps. We can drive it and eventually force us to generate forecasts that are now on average more accurate than any of the forecasts of these giant models. And since we launched Meteum just less than a year ago, it’ll improve accuracy now, because in order for the machine to learn how to predict well ... Well, the weather is like that - it's a thing with weather cycles. That is, until you survived at least one autumn, it is reliably difficult to somehow predict the autumn weather.
And now she comes to the point where she will survive every season at least once. We launched it just in the late autumn. Now for her, winter will not be a novelty - she once studied winter. And this will increase weather forecasting without improving our understanding of the processes taking place in the atmosphere. Well, you understand, I specifically focus on these words, because this is what will happen to your work. The machine next to you will solve important, smart, intellectual tasks, while completely not understanding what is really happening. Nobody explained to her, as we did not explain anything about physics to this.
Personalization: the inevitable future of customer communication
And so now I’ll still tell you a little bit about what is important for a particular business. Science is science, but we are talking about business. Look, the story about personalization has already sounded here: Mikhail in a very perfect report on the amoCRM update just said that, guys, now you can personally catch up with this person by announcements about something that he has not yet bought from you.
This is correct, it is ideal that this is becoming the norm in a variety of systems, but not everything in the world is controlled only from amoCRM. Here, amoCRM, for example, allows you to catch up with a person on other sites (you may have your own site).
Targeting technologies
Here a funny paradox of 2016 arises: advertising is technologically much more advanced than everything else on the site. Well, you understand: for the sake of simplicity I’m taking now not an application, but just a website - you can have static content hanging on your website that has been hanging there for the last three years, it’s just stupid, without any interactivity, like at the time the Web was born, 20 years ago. And the ad code, a piece of code, Google and Yandex, or some other good grid, is a terribly smart black box, which at that moment, while this page is being drawn, understands everything about the incoming user, accesses the database with hundreds of ads and makes smart, intuitive assumptions which one is more likely to click. Because in fact, the optimized parameter when they show you an ad is the probability of a click. That is a bunch of all kinds of mathematics, “machine learning” and everything else. And the page - as it is, it is.

Machine intelligence learns from people
Do you understand that this will not take so long? You understand that soon enough to have a site that is not as smart as the ads around ... well, kwa ... well, it's disgusting to be on such a site ?! It is disgusting to go to a site whose face is the same for everyone, on a product card that is the same for everyone, and so on, and so on, and so on.

That is the story that personalization will overtake you everywhere. And the farther, the more it will work better and better, because, again: machines learn from people. It is very important that we do not teach her, we do not understand something new and therefore we have nothing to teach the car. Yes, she herself is self-learning all the time, because all the time there are these millions, billions of clicks that she takes for herself.
Crypta
And yes, here it turns out ... A little frightening such a little block diagram made from a more technical presentation. For example, the technology, which we call Crypta, allows you to determine the interests of a person, a lot of things are spinning, and as a result, the “black box” decides what to draw on the “face” of some kind of “market”.
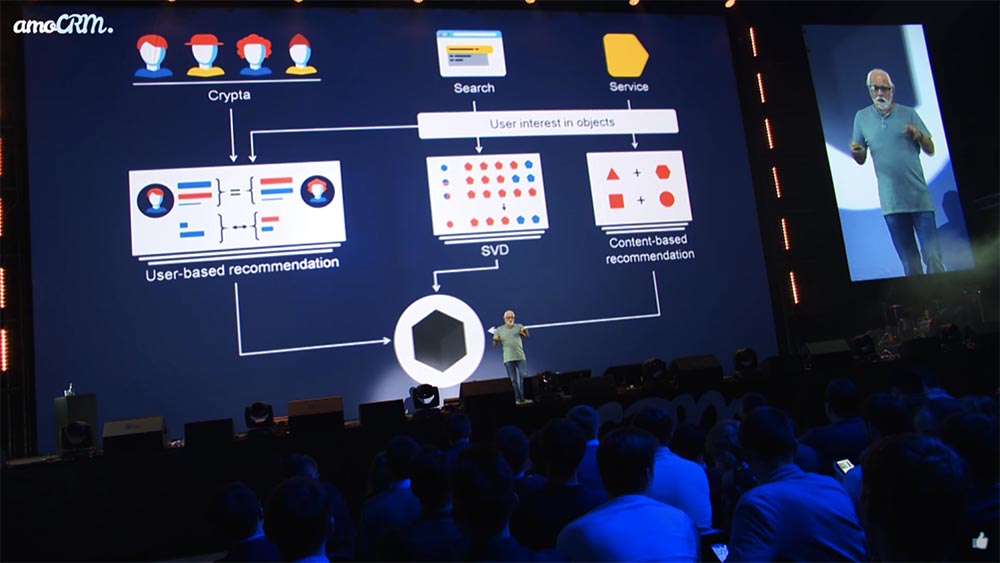
Stop averaging and segmenting!
Translated into the usual marketing terms, this means: stop averaging, stop segmenting, you can work at the level of personalization. This familiar cocktail of several components is able to keep our weak brain. The car does not need. She does not need to break into ten categories or go to some kind of RFM segmentation, where, again ... Few advanced marketers, just few people can keep more than twenty segments in their head.
And the car doesn’t care, it doesn’t need segments - it works directly with hundreds of millions, as, for example, in our case, various users.At the same time, a smart algorithm shows not only something similar (it will be sad for a person), it can open something, it can show a person - “Wow! How could I not know about this? ” I went to the page - and the text; sticks ...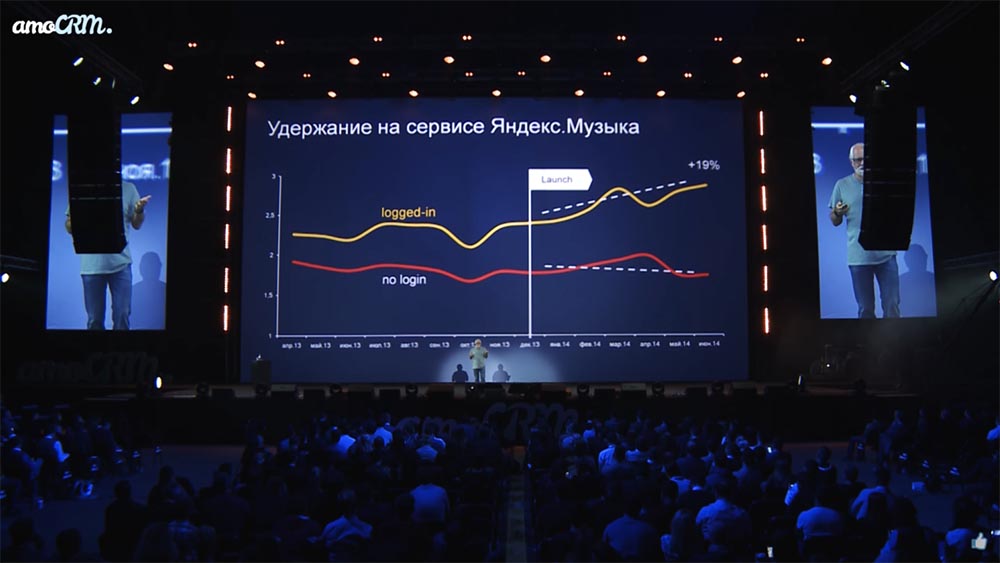
Is it possible to get away from "similarity"?
And this is how, for example, all modern streaming services work, this is how YouTube works. Recommendations begin to adapt to each individual person. As an illustration, there is a graph of how the time spent on the service increases when you turn on the “black box” ... and-and-and ... a person starts to stick because he is recommended songs that he wants to listen to all the time.
Yandex Zen
Or how it happens in our more advanced, most recently launched, and in a bunch of different countries, time killer called "Zen". Such a service. It is either in the “lancer” on the mobile, or in the browser on the mobile. There is a stream of content optimized for each person individually, of a very different kind: news, pictures, cats, recipes - what a person wants to read. But she is personalized for him absolutely automatically. There for the first time we were convinced that we do not care where the service is launched - in Brazil, Indonesia or Russia. We do not need to engage in a long study of cultural features, the characteristics of the consumption of content in this country - this is all done by the algorithm.
But she is personalized for him absolutely automatically. There for the first time we were convinced that we do not care where the service is launched - in Brazil, Indonesia or Russia. We do not need to engage in a long study of cultural features, the characteristics of the consumption of content in this country - this is all done by the algorithm.Social experiment Yandex
We did this experiment at our marketing conference in Yandex at the end of June this year. We did it at the conference, because there are some legal subtleties and technical subtleties, why we could not take it out onto the street. Well, on the street it will be in a year. Here a man walks past the monitor. The camera does not just show its image, but some garbage is spinning over his head. A person points with the installed application the camera of his smartphone at the people of others in the lobby, and other pictures are spinning above them. These pictures are the interests of these people. We did not ask them about this. And I won’t tell you what kind of magic, then what ...
Here a man walks past the monitor. The camera does not just show its image, but some garbage is spinning over his head. A person points with the installed application the camera of his smartphone at the people of others in the lobby, and other pictures are spinning above them. These pictures are the interests of these people. We did not ask them about this. And I won’t tell you what kind of magic, then what ...To summarize ...
I can imagine what would happen if I now ... In which pocket do I have a smartphone?Well, here it won’t work. But imagine, I spent - and I know what to talk about with each of you.Summing up, I spoke. Look, this slide is just for illustration. When I talked about commoditizing technologies, it means that everything has become available from the outlet, that it has become “commodity”, like electricity. None of us are electricians and none of us knows how to start a diesel generator. Well, most. But we know very well that we have a power outlet in the apartment and you can plug it in: you want a washing machine, you want an iron. So, just like that, now you can work with machine learning, with machine mind, because there is an open source code, there is an API - here is just a list of what is often available for free (so as not to be unfounded).And, as the main result, in fact, the main final, final slide.2020+: the most important managerial skills
Guys, when they asked me to do this slide: “Well, will you tell me something about twenty or twenty?” I say: “Yes, it's easy.” Because it comes down to three main points. You have to work together with creative smart machines (if you want it, if you don’t want to, it will) It's damn hard. I know from my own experience at Yandex. Here (I don’t see you well because of the blinding spotlights) I ask you to answer the question aloud: are there people here who have other employees subordinate (from the audience they say “yes”)? Okay, was it easy for you to delegate to them (“no” from the audience)?
You have to work together with creative smart machines (if you want it, if you don’t want to, it will) It's damn hard. I know from my own experience at Yandex. Here (I don’t see you well because of the blinding spotlights) I ask you to answer the question aloud: are there people here who have other employees subordinate (from the audience they say “yes”)? Okay, was it easy for you to delegate to them (“no” from the audience)? Expected.
U.S. too! Imagine: you have to delegate to the machines, but you won’t go out with a beer in the evening or drink something and say: “Vasya, what are you ... Let’s not be like that anymore”. This machine really can not explain to you why she made this decision. But if you do not learn how to work with it (yes, it will sometimes “fakapit”, like any of us and any of our employees), then it’s just a “cover”.Clark's Law
This is the most recent slide. This is one of Clark's laws. I go out with a gray tail and say some strange things. There is a law that says: if a person of my age comes out, begins to carry something about the fact that - “This will never happen! Man is the measure of all things, so the machine will never be ... (takes a deep breath) This is age conservatism, guys, I'm sorry. ” And when a person says, “Listen, in spite of all my conservatism, it will be!”, He is most likely right if he is an expert in this matter. But I’ve been boiling on the Internet for the last twenty years.So thanks! One way or another, but it will happen!
And when a person says, “Listen, in spite of all my conservatism, it will be!”, He is most likely right if he is an expert in this matter. But I’ve been boiling on the Internet for the last twenty years.So thanks! One way or another, but it will happen!A bit of advertising :)
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending it to your friends,
cloud VPS for developers from $ 4.99 , a
30% discount for Habr users on the unique entry-level server analog that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share a server? (options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have
2 x Intel TetraDeca-Core Xeon 2x E5-2697v3 2.6GHz 14C 64GB DDR4 4x960GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 199 in the Netherlands! Dell R420 - 2x E5-2430 2.2Ghz 6C 128GB DDR3 2x960GB SSD 1Gbps 100TB - from $ 99! Read about
How to Build Infrastructure Bldg. class c using Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 servers costing 9,000 euros for a penny?