The Internet of Things (IoT) has a great influence on the development of modern medicine: smart bracelets for the elderly, hospitals, whose security is ensured by IoT systems, RFID-marking of medicines and much more. We develop and implement IoT solutions and therefore we follow the key medical discoveries.
We have collected for you several interesting studies and experiments this year: about antidepressants, the impact of video games on aggressiveness, lack of sleep and anxiety, and IoT news for health.Video games with scenes of violence will not make you a maniac

In October 2018, a tragedy occurred in Kerch. One of the students in the college opened fire, killing 20 people. Then, on a transfer from Vladimir Solovyov, invited expert Philip Gross-Dneprov accused the game of DotA 2 (though he called it Doka).
It's not just this expert. Today, both in Russia and around the world, many people think that video games increase impulsiveness and negatively affect the mental abilities of gamers and their memory.
But studies that confirmed the link between gaming and aggressive behavior focused on short-term effects, so their results cannot be called reliable.
In 2019, psychiatrists at the University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf conducted the first long-term study of the consequences of violent video games: not only behavioral indicators of aggression were taken into account, but also sexual life, empathy, performance indicators, levels of depression and anxiety.
For the experiment, 90 healthy participants were selected (average age - 28 years). They were randomly divided into three groups. The first one was offered to play Grand Theft Auto V every day (scientists attributed it to being “cruel”), the second - in the video game without scenes of violence The Sims 3, the third - not to play at all. The experiment lasted two months.
The results showed that the participants in the first group (with violent video games) showed no significant changes in behavior either in comparison with the second group (non-violent video games) or the third, passive group. In addition, there was no difference between the initial and final tests: that is, between the assessment of the participants' aggressiveness before and after the two-month experiment.

But scientists note that only adult participants took part in the experiment, and the study of children's aggressiveness requires additional research.
Read the detailed results of the study
here .
By the way, while we were writing this text, Chinese teens have limited time for online games and banned from playing at night. The new rules, according to the country's leadership, should "protect the mental and physical health of minors."
Are antidepressants not more effective than placebo?
According to the World Health Organization in 2018, more than 300 million people suffer from depression, the disease has become the main cause of disability in the world (with dysthymia - chronic depression - a patient is prescribed a disability of I or II group, depending on the symptoms).
Like most other mental disorders, depression is poorly understood. Until now, the neurobiological causes of the disease have not been found: even the classical monoamine theory, which associates the disorder with a lack of serotonin, has not received convincing evidence.
The scientific community cannot accurately describe the etiology of the disease, so there is no need to talk about effective treatment. Most often, patients are prescribed antidepressants, the effect of which is doubtful.
For several years, Australian scientists tested the work of the antidepressant, which is now considered the most effective - this is fluoxetine, one of the most commonly prescribed drugs for depression and anxiety. 153 patients suffering from various forms of depression were divided into two groups: in one, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) was combined with drug support - the initial dose of fluoxetine was 20 mg; the second group was treated according to the CBT + placebo tablets. After 12 weeks, the first measurements were taken (on the MADRS depression scale).
Both groups showed a positive trend in treatment, but in both groups it was the same (33 points on the MADRS scale in the placebo group and 32 in the fluoxetine group). But in the group with fluoxetine, acts of auto-aggression were more often recorded - patients inflicted physical harm on themselves.
Scientists have not found evidence that adding fluoxetine to cognitive-behavioral therapy alleviates the symptoms of depression in patients.
The scientific publication came out as a refutation of a study of the effectiveness of fluoxetine in 2004 (TADS study - Treatment for Adolescents With Depression Study), the authors of which found supposedly undeniable advantages in prescribing tablets in combination with CBT.
Read the full study
here .
3. Even one night without sleep results in tangible anxiety

Lack of sleep, night work, knocked down biorhythms - everyone knows that this is bad for health. But life with deadlines, additional tasks from the boss, the goat, night parties with friends can be quite difficult to organize.
This year, psychologists from the University of California at Berkeley conducted an experiment to find out how much a sleepless night affects the overall psychological state. 18 people took part in the experiment; they spent a week under observation. In the laboratory they had to spend one night without sleep and one usual night for them (they used a polysomnograph to study sleep).
To identify how sleepless night affected the behavior of the participants in the experiment, scientists showed them several videos that were supposed to provoke disgust and anxiety. In this case, brain activity was measured using fMRI. Also, all participants completed a standard questionnaire to identify anxiety.
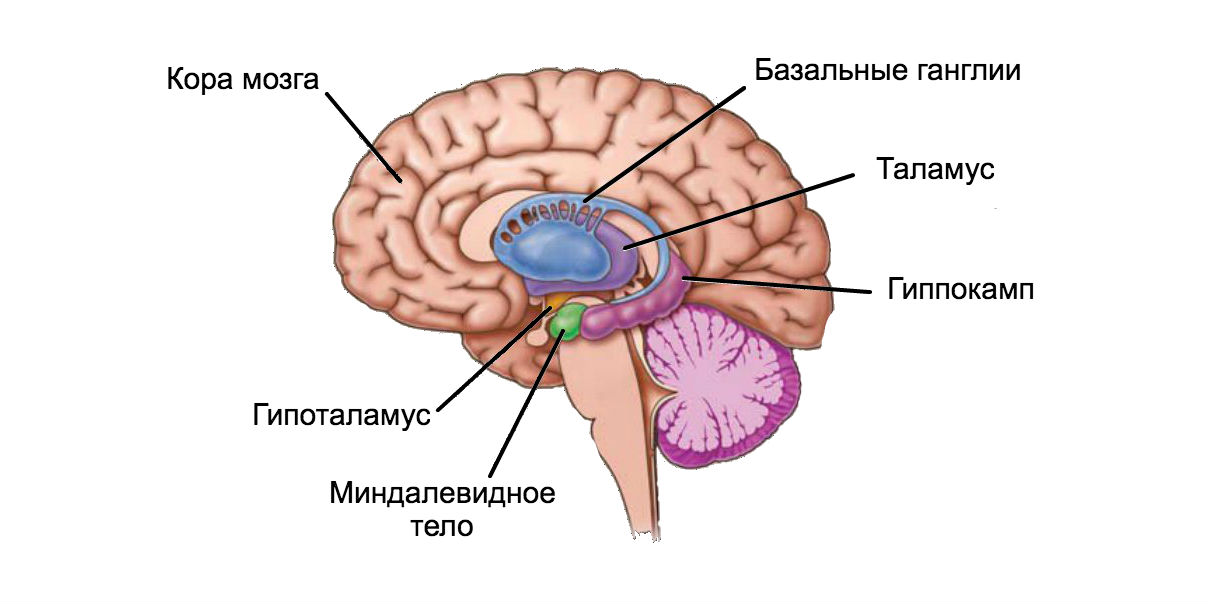
Separate zones are responsible for anxiety in the brain: the insular lobe, the amygdala (processing emotions), the anterior cingulate and prefrontal cortex (mental processes and mental control). The experiment showed that lack of sleep slowed down the work of the departments responsible for cognitive abilities. In addition, he increased the activity of emotional processing zones and disrupted the connections between the work of all departments. As a result, after a sleepless night, the participants recorded a significant increase in anxiety the next day (compared with indicators after a night with normal sleep).
Scientists also found out how the characteristics of sleep affect the general anxiety of people, for this they analyzed it in phases. It turned out that the long phase of slow sleep provides minimal anxiety the next day. This was confirmed by an online study of 280 volunteers, whom scientists offered to take a questionnaire on anxiety symptoms and provide data on sleep quality for four days.
Read more in detail here:
www.nature.com/articles/s41562-019-0754-84. Well, about IoT-innovations: a smart home stethoscope
This year, the Polish company StethoMe launched on sale a smart home stethoscope that allows you to remotely diagnose pneumonia and other respiratory diseases.
A stethoscope is applied to the back (the right places are indicated in the mobile application), the patient must breathe deeply and cough. The device writes all data about sounds to the application and sends it to the server, where it will be processed by artificial intelligence: the algorithm can detect wheezing and warn the patient about the problem.

The creators of the device claim that their stethoscope works three times more efficient than live doctors. The accuracy of determining the diagnosis is 80%.
“The device consists of more than 170 small electronic components paired with a smartphone that sends data to our server, where it is analyzed using an artificial intelligence module,” explains Wojciech Radomsky, chairman of the board of StethoMe.
You can look at the magic stethoscope
here .