Finally, I was able to see the data from Magento (categories and products) in the Vue Storefront (VSF) application. This is already the fourth article ( 1 , 2 , 3 ), in which I describe the process of exploring the possibilities of integrating VSF with an Magento 2-based electronic store, and the first where the data from Magento skipped to the customer’s browser.

Under the cat is a link to deployment scripts and a brief description of the steps.
purpose
Display in the client part the category / product data obtained from Magento.
Schematic
Now the dependencies between the application components are presented to me like this:
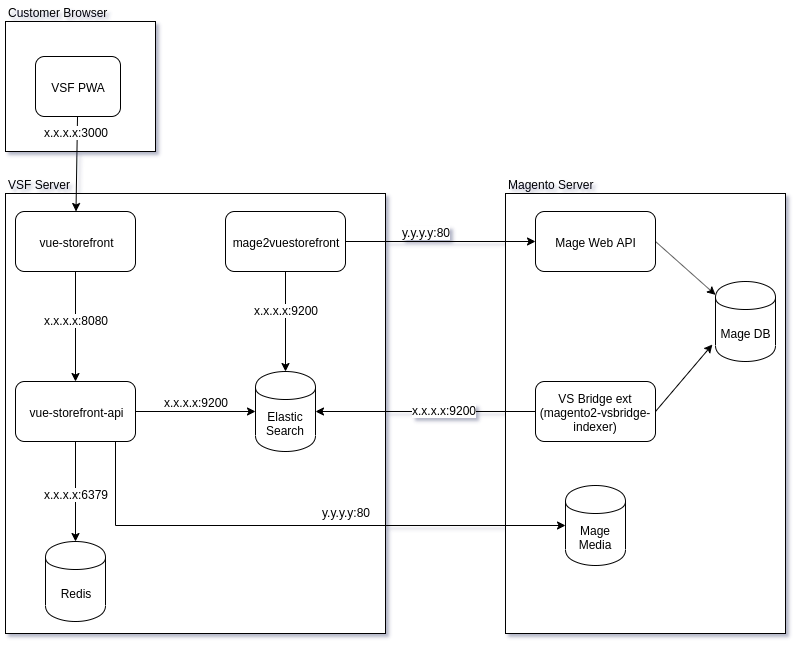
Work environment
In the current iteration, I again used the medium version of the Linux Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 64-bit server (2x 2198 MHz CPU, 4 GB RAM, 10 GB disk) in the Exoscale cloud.
Deployment scripts
I put the scripts for deploying application components into a separate project: flancer64 / vsf_mage2_setup .
Deployment Steps:
- Updating an empty OS, installing additional services and applications (Elasticsearch, Redis, yarn, ...) .
vue-storefront .vue-storefront-api .mage2vuestorefront .- Start data replication from Magento 2 to VSF .
Deployment Configuration
At the time of this writing, the deployment configuration looks like this:
Application Deployment
I clone the scripts for deploying the components on a clean host and set the local deployment configuration:
$ cd ~ $ git clone https://github.com/flancer64/vsf_mage2_setup.git $ cd vsf_mage2_setup/ $ cp cfg.init.sh cfg.local.sh $ nano cfg.local.sh ...
After that I execute the deployment scripts, from the first to the fourth:
$ cd ~/vsf_mage2_setup/ $ bash ./bin/step01_env.sh $ bash ./bin/step02_vsf_front.sh $ bash ./bin/step03_vsf_api.sh $ bash ./bin/step04_mage2vsf.sh
The contents of the scripts can be viewed on github'e. As a result, the following components will be installed and configured on an empty host:
- Elasticsearch
- Redis
- vue-storefront
- vue-storefront-api
- mage2vuestorefront
Component configurations can be seen in the appropriate deployment scripts.
Magento2 Data Replication Script => VSF
In the fourth step, a data replication script ~/mage2vuestorefront/src/run.sh . I give it in its entirety (with the exception of sensitive data):
Data replication
Script ./bin/step05_sync_data.sh :
The script ~/mage2vuestorefront/src/run.sh retrieves data from Magento 2 by accessing the Magento Web API, so it doesn’t work out quite quickly. VSF developers have an alternative ( magento2-vsbridge-indexer ), I used it in a previous article.
After transferring data from Magento 2 to Elasticsearch, you need to update the VSF API configuration.
All this is done like this:
$ cd ~/vsf_mage2_setup/ $ bash ./bin/step05_sync_data.sh
Conclusion
Well, the categories and products from Magento have “infiltrated” the VSF application. Now you need to configure the reverse movement - so that the data from the VSF (basket, orders) gets into Magento 2 and make sure that customers registered in Magento 2 can also log in to VSF.
References