Habrの皆さん、こんにちは。 私たちの理解では、乾燥していて人生から遠く離れた高等数学が悪い実際的な結果をもたらさなかった場合、尊敬される読者に例を提示したいと思います。
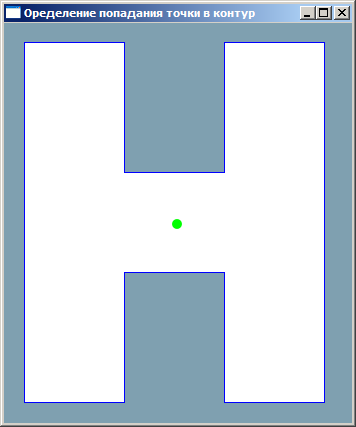
最初のいくつかの思い出
それは、私が90年代に専門大学の1つ、おそらく2番目のコースの学生だったときでした。 一度プログラミングオリンピックに行きました。 そしてまさにこのオリンピックでの課題は、三角形の座標、平面上のテストポイントを設定し、このポイントが三角形の領域に属するかどうかを判断することでした。 一般に、些細な作業ですが、それから私はそれを解決しませんでした。 しかし、それから私は-より一般的なタスクについて-埋め立て地に属すると考えました。 繰り返しますが、90年代半ば、インターネット、コンピュータージオメトリに関する書籍はありませんでしたが、タワーとターボパスカルを備えた286-x研究室についての講義がありました。 それで星が一致しました。ちょうど問題について考えていたとき、塔で複雑な変数の理論を読んでいました。 そして、1つの式(それについて)は肥沃な地面に落ちました。 このアルゴリズムはPascalで発明され、実装されました(残念ながら私の1.5ギグスクリューは死に、このコードと他の若々しい業績を忘れてしまいました)。 卒業後、ある研究所で働きました。 そこで研究所の従業員のニーズに合わせてGISを開発する必要がありました。自分の仕事の1つは、オブジェクトがサーキットに入ったかどうかを判断することでした。 アルゴリズムはC ++で書き直され、動作することが実証されています。
アルゴリズムのタスク
与えられた:
-頂点の座標(xi、yi)およびテストポイントの座標(x0、y0)によって定義される平面上の閉じたポリライン(以降、ポリゴン)
定義:
点が多角形で囲まれた領域Dに属するかどうか。
アルゴリズムのその後の記述のための式の導出は、数学的な完全性および正確性を主張するものではなく
、科学
分野の女王に対する工学(消費者アプローチ)のみを示してい
ます 。
それでは始めましょう

労働者-農民工学の観点からの説明:
-境界Gは、指定された輪郭です。
-z0-テストポイント
-f(z)-複雑な引数の複雑な関数は、回路内のどこでも無限になりません。
これらは、ポイントがコンターに属することを確立するために、積分を計算し、それを特定のポイントでの関数の値と比較する必要があります。 それらが一致する場合、ポイントは輪郭にあります。 注:
Cauchyの
積分定理は、点が等高線上にない場合、被積分関数はどこにも無限に行かず、積分はゼロになると述べています。 これは問題を簡素化します-積分を計算し、それがゼロに等しいことを確認するだけです:非輪郭の点はゼロに等しく、異なる-それは輪郭にあります。
積分を計算しましょう。 f(z)については、単純な関数1を使用します。一般性を失うことなく、z0に対してポイント0を使用できます(常に座標をシフトできます)。

被積分関数の分母にある虚数単位を取り除き、積分を実数部と虚数部に分割します。

第2種の2つの曲線積分が判明しました。
最初を計算します
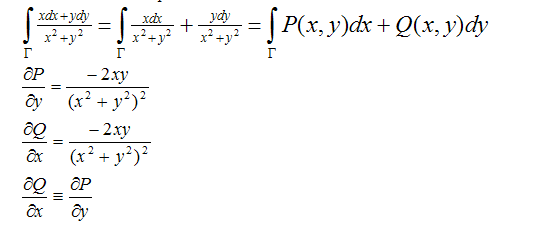
積分がパスに依存しないという条件が満たされているため、最初の積分はゼロであり、計算する必要はありません。
虚数部では、このようなトリックは機能しません。 境界線が線分で構成されていることを思い出してください。

Gi-はセグメント(xi、yi)-(xi + 1、y i + 1)
i番目の積分を計算します。 これを行うには、i番目のセグメントの方程式をパラメトリック形式で記述します

積分で置換
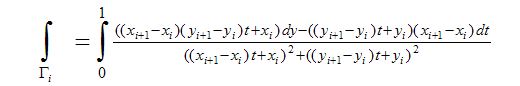
面倒で退屈な変換の後、次の魅力的な式を取得します。
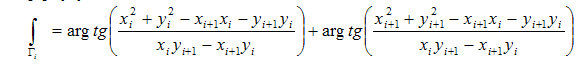
ようやく
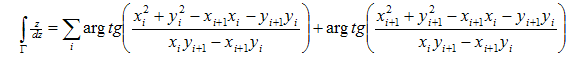
C ++アルゴリズム:
template < class T>
bool pt_in_polygon( const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T last_pt=polygon.back();
last_pt.x-=test.x;
last_pt.y-=test.y;
double sum=0.0;
for (
std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();
iter!=end;
++iter
)
{
T cur_pt=*iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
double del= last_pt.x*cur_pt.y-cur_pt.x*last_pt.y;
double xy= cur_pt.x*last_pt.x+cur_pt.y*last_pt.y;
sum+=
(
atan((last_pt.x*last_pt.x+last_pt.y*last_pt.y - xy)/del)+
atan((cur_pt.x*cur_pt.x+cur_pt.y*cur_pt.y- xy )/del)
);
last_pt=cur_pt;
}
return fabs(sum)>eps;
}
T – , :
struct PointD
{
double x,y;
};
2D : Anti-Grain Geometry (AGG) .
:
–
-
Shift- –
PS
, , . .
forgotten .
template bool pt_in_polygon2(const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
static const int q_patt[2][2]= { {0,1}, {3,2} };
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T pred_pt=polygon.back();
pred_pt.x-=test.x;
pred_pt.y-=test.y;
int pred_q=q_patt[pred_pt.y<0][pred_pt.x<0];
int w=0;
for(std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();iter!=end;++iter)
{
T cur_pt = *iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
int q=q_patt[cur_pt.y<0][cur_pt.x<0];
switch (q-pred_q)
{
case -3:++w;break;
case 3:--w;break;
case -2:if(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x) ++w;break;
case 2:if(!(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x)) --w;break;
}
pred_pt = cur_pt;
pred_q = q;
}
return w!=0;
}
template < class T>
bool pt_in_polygon( const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T last_pt=polygon.back();
last_pt.x-=test.x;
last_pt.y-=test.y;
double sum=0.0;
for (
std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();
iter!=end;
++iter
)
{
T cur_pt=*iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
double del= last_pt.x*cur_pt.y-cur_pt.x*last_pt.y;
double xy= cur_pt.x*last_pt.x+cur_pt.y*last_pt.y;
sum+=
(
atan((last_pt.x*last_pt.x+last_pt.y*last_pt.y - xy)/del)+
atan((cur_pt.x*cur_pt.x+cur_pt.y*cur_pt.y- xy )/del)
);
last_pt=cur_pt;
}
return fabs(sum)>eps;
}
T – , :
struct PointD
{
double x,y;
};
2D : Anti-Grain Geometry (AGG) .
:
–
-
Shift- –
PS
, , . .
forgotten .
template bool pt_in_polygon2(const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
static const int q_patt[2][2]= { {0,1}, {3,2} };
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T pred_pt=polygon.back();
pred_pt.x-=test.x;
pred_pt.y-=test.y;
int pred_q=q_patt[pred_pt.y<0][pred_pt.x<0];
int w=0;
for(std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();iter!=end;++iter)
{
T cur_pt = *iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
int q=q_patt[cur_pt.y<0][cur_pt.x<0];
switch (q-pred_q)
{
case -3:++w;break;
case 3:--w;break;
case -2:if(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x) ++w;break;
case 2:if(!(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x)) --w;break;
}
pred_pt = cur_pt;
pred_q = q;
}
return w!=0;
}
template < class T>
bool pt_in_polygon( const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T last_pt=polygon.back();
last_pt.x-=test.x;
last_pt.y-=test.y;
double sum=0.0;
for (
std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();
iter!=end;
++iter
)
{
T cur_pt=*iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
double del= last_pt.x*cur_pt.y-cur_pt.x*last_pt.y;
double xy= cur_pt.x*last_pt.x+cur_pt.y*last_pt.y;
sum+=
(
atan((last_pt.x*last_pt.x+last_pt.y*last_pt.y - xy)/del)+
atan((cur_pt.x*cur_pt.x+cur_pt.y*cur_pt.y- xy )/del)
);
last_pt=cur_pt;
}
return fabs(sum)>eps;
}
T – , :
struct PointD
{
double x,y;
};
2D : Anti-Grain Geometry (AGG) .
:
–
-
Shift- –
PS
, , . .
forgotten .
template bool pt_in_polygon2(const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
static const int q_patt[2][2]= { {0,1}, {3,2} };
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T pred_pt=polygon.back();
pred_pt.x-=test.x;
pred_pt.y-=test.y;
int pred_q=q_patt[pred_pt.y<0][pred_pt.x<0];
int w=0;
for(std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();iter!=end;++iter)
{
T cur_pt = *iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
int q=q_patt[cur_pt.y<0][cur_pt.x<0];
switch (q-pred_q)
{
case -3:++w;break;
case 3:--w;break;
case -2:if(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x) ++w;break;
case 2:if(!(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x)) --w;break;
}
pred_pt = cur_pt;
pred_q = q;
}
return w!=0;
}
template < class T>
bool pt_in_polygon( const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T last_pt=polygon.back();
last_pt.x-=test.x;
last_pt.y-=test.y;
double sum=0.0;
for (
std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();
iter!=end;
++iter
)
{
T cur_pt=*iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
double del= last_pt.x*cur_pt.y-cur_pt.x*last_pt.y;
double xy= cur_pt.x*last_pt.x+cur_pt.y*last_pt.y;
sum+=
(
atan((last_pt.x*last_pt.x+last_pt.y*last_pt.y - xy)/del)+
atan((cur_pt.x*cur_pt.x+cur_pt.y*cur_pt.y- xy )/del)
);
last_pt=cur_pt;
}
return fabs(sum)>eps;
}
T – , :
struct PointD
{
double x,y;
};
2D : Anti-Grain Geometry (AGG) .
:
–
-
Shift- –
PS
, , . .
forgotten .
template bool pt_in_polygon2(const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
static const int q_patt[2][2]= { {0,1}, {3,2} };
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T pred_pt=polygon.back();
pred_pt.x-=test.x;
pred_pt.y-=test.y;
int pred_q=q_patt[pred_pt.y<0][pred_pt.x<0];
int w=0;
for(std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();iter!=end;++iter)
{
T cur_pt = *iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
int q=q_patt[cur_pt.y<0][cur_pt.x<0];
switch (q-pred_q)
{
case -3:++w;break;
case 3:--w;break;
case -2:if(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x) ++w;break;
case 2:if(!(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x)) --w;break;
}
pred_pt = cur_pt;
pred_q = q;
}
return w!=0;
}
template < class T>
bool pt_in_polygon( const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T last_pt=polygon.back();
last_pt.x-=test.x;
last_pt.y-=test.y;
double sum=0.0;
for (
std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();
iter!=end;
++iter
)
{
T cur_pt=*iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
double del= last_pt.x*cur_pt.y-cur_pt.x*last_pt.y;
double xy= cur_pt.x*last_pt.x+cur_pt.y*last_pt.y;
sum+=
(
atan((last_pt.x*last_pt.x+last_pt.y*last_pt.y - xy)/del)+
atan((cur_pt.x*cur_pt.x+cur_pt.y*cur_pt.y- xy )/del)
);
last_pt=cur_pt;
}
return fabs(sum)>eps;
}
T – , :
struct PointD
{
double x,y;
};
2D : Anti-Grain Geometry (AGG) .
:
–
-
Shift- –
PS
, , . .
forgotten .
template bool pt_in_polygon2(const T &test,const std::vector &polygon)
{
static const int q_patt[2][2]= { {0,1}, {3,2} };
if (polygon.size()<3) return false;
std::vector::const_iterator end=polygon.end();
T pred_pt=polygon.back();
pred_pt.x-=test.x;
pred_pt.y-=test.y;
int pred_q=q_patt[pred_pt.y<0][pred_pt.x<0];
int w=0;
for(std::vector::const_iterator iter=polygon.begin();iter!=end;++iter)
{
T cur_pt = *iter;
cur_pt.x-=test.x;
cur_pt.y-=test.y;
int q=q_patt[cur_pt.y<0][cur_pt.x<0];
switch (q-pred_q)
{
case -3:++w;break;
case 3:--w;break;
case -2:if(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x) ++w;break;
case 2:if(!(pred_pt.x*cur_pt.y>=pred_pt.y*cur_pt.x)) --w;break;
}
pred_pt = cur_pt;
pred_q = q;
}
return w!=0;
}