はじめに
人がモナドとは何かを理解していることを知る方法は? 彼自身がコミュニケーションの最初の5分間でこれについてあなたに話し、確実に説明しようとします。 彼はまた、それについてのテキストを書き、可能であればどこかにそれを公開し、他の人もモナドが何であるかを理解します。
特にHaskellの関数型プログラマーの間では、モナドは少しローカルなミームになりました。 彼らはしばしば、特別な場合から始めて、すぐに使用例を示して説明しようとします。 このため、リスナーは概念の主要な本質を把握できず、モナドは黒魔術のままであるか、単に関数型言語の副作用を粉砕する手段にすぎません。
最初にカテゴリー理論の基本概念について説明し、次に実用的な観点からモナドの定義にアプローチし、実際、非常に多くのプログラマーがその表現の1つでこの強力な抽象化を使用することを確認します。
私のプレゼンテーションは、主にBartosz Milewskiの著書「Category Theory for Programmers」に基づいています。これは、一連のブログ投稿として作成され、 PDFで入手でき、最近紙で出版されました。
例はHaskellで提供されており、読者が言語の構文と基本概念に精通していることを前提としています。 前述の本にはC ++の例があり、コードの純度と理解度を比較できます。

カテゴリー
定義
カテゴリ自体は非常に単純な構造です。 カテゴリとは、 オブジェクトとそれらの間の射の集合です。 形態は、オブジェクトを接続する一方向の矢印と見なすことができます。 一般的な場合、オブジェクト自体の本質については何もわかっていません。 カテゴリ理論はオブジェクトではなく、射、またはむしろその構成で機能します。
次の表記が使用されます。
- Ob C-カテゴリーCのオブジェクト。
- Hom C (A、B)-AからBへの射:
- g∘fは、射fとgの合成です。
カテゴリを定義する際、射は追加の制限を受けます。
- 一対の射fとgについて、fがAからBへの射(f∈Hom(A、B))である場合、gはBからCへの射(g∈Hom(B、C))であり、合成g∘が存在するfはAからCへの射である(g∘f∈Hom(A、C))。
- 各オブジェクトに対して、恒等射型id A∈Hom(A、A)が与えられます。
任意のカテゴリーが満たさなければならない2つの重要な特性があります(カテゴリー理論の公理):
- 構成の結合性:h∘(g∘f)=(h∘g)∘f;
- 恒等射による合成:f∈Hom(A、B)の場合、f∘id A = id B∘f = f
カテゴリは、有向グラフとして非常に簡単かつ自然に視覚化されます。 原則として、必要に応じて、射と同一の射の構成を追加することにより、任意の指向グラフをカテゴリに拡張できます。
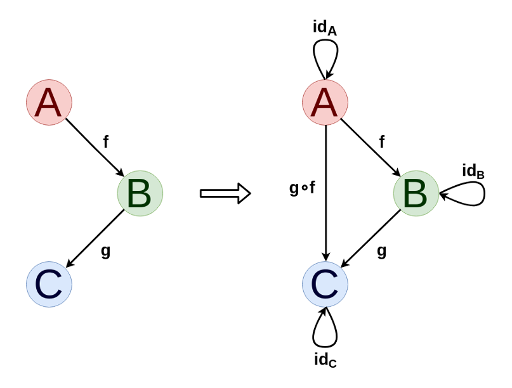
任意のカテゴリーについて、 二重カテゴリーを定義できます( C opで示され、元のカテゴリーの矢印を回すことで射が得られ、オブジェクトは同じです。これにより、二重のステートメントと定理を定式化できます。
オブジェクトと射は必ずしも集合を形成するわけではありません(古典的な意味で、集合論から)。したがって、一般的な場合、「オブジェクトのクラス」というフレーズが使用されます。 オブジェクトのクラスと射がまだ設定されているカテゴリは、 小さなカテゴリと呼ばれます 。 さらに、それらのみで作業します。
タイプと機能
, Haskell, — . , Int Bool — , Int -> Bool — .
id, :
id :: a -> a
id x = x
— , Haskell :
f :: a -> b
g :: b -> c
g . f :: a -> c
(g . f) x = g (f x)
, , — , Set. , — , : . bottom, _|_. , , , bottom. Haskell, , Hask. , Set. , , : HomC(A, B) ∈ C. , a -> b — Haskell.
.
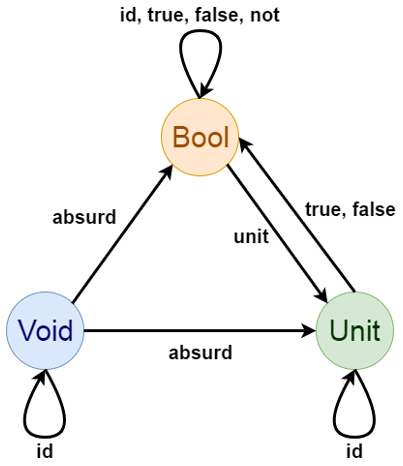
Void, ( ). absurd, , , Void, :
absurd :: Void -> a
Unit, — , (). unit , :
unit :: a -> Unit
unit _ = ()
— Bool:
data Bool = True | False
, Void, Unit Bool.
Void , absurd, Bool, Unit. , Void, , .
Bool -> Unit , unit, . Unit -> Bool . (), True, False. , Unit Bool:
true, false :: a -> Bool
true _ = True
false _ = False
Bool Bool — , 4 ( n — 22n): id, true false, , not:
not :: Bool -> Bool
not True = False
not False = True
, :
Haskell- .
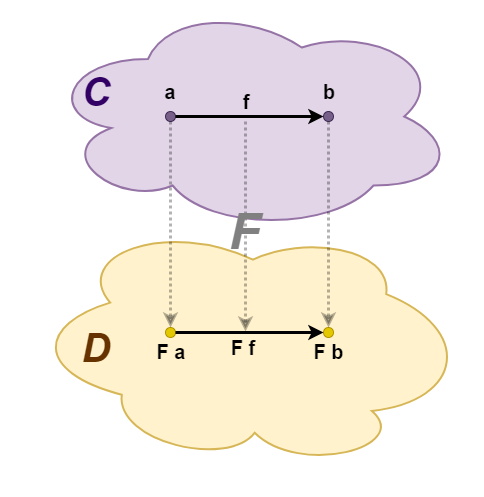
— . , C D, F . -, C D. a — C, F a — D, . -, : f :: a -> b C F f :: F a -> F b D.
, " " :
- h = g ∘ f, F h = F g ∘ F f.
- ida — a, F ida = idF a — F a.
, "" : , , . , , () . , .
. , F :: C -> D G :: D -> E G . F :: C -> E. , , , , . IdC, IdD IdE. , , .
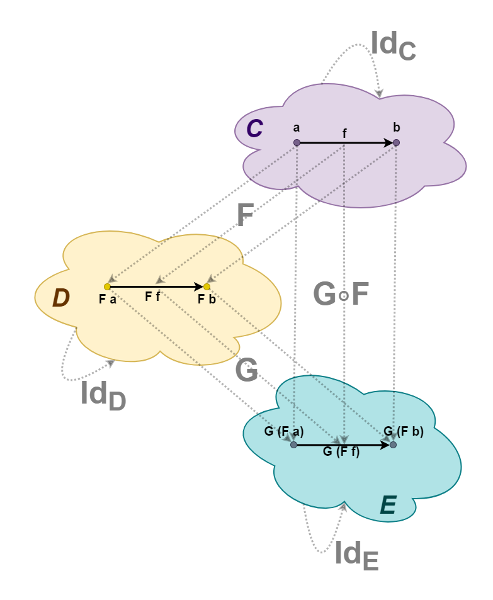
, , -, — (). , Cat ( ).
Haskell . , , - , .
Maybe , a Maybe a ( Maybe !):
data Maybe a = Nothing | Just a
, f :: a -> b F f :: Maybe a -> Maybe b. fmap. , ( ):
-- f F f
-- /------\ /------------------\
fmap :: (a -> b) -> (Maybe a -> Maybe b)
fmap _ Nothing = Nothing
fmap f (Just x) = Just (f x)
, Maybe — . , , Functor. fmap, , ( — ):
class Functor f where
fmap :: (a -> b) -> f a -> f b
— , , fmap . f a -> f b, , .
, , , .. , . : , - .
. , . , , — Haskell.
: upCase, , toWords, . toUpper words:
upCase :: String -> String
upCase = map toUpper
toWords :: String -> [String]
toWords = words
:
processString :: String -> [String]
processString = toWords . upCase
, . , processString "upCase toWords".
— , . -, , , -, , .
, a , .
newtype Writer a = Writer (a, String)
, Writer — , fmap:
instance Functor Writer where
fmap f (Writer (x, s)) = Writer (f x, s)
upCase toWords , , "" Writer:
upCase :: String -> Writer String
upCase s = Writer (map toUpper s, "upCase ")
toWords :: String -> Writer [String]
toWords s = Writer (words s, "toWords ")
, , - . , b , , c c , :
compose :: (a -> Writer b) -> (b -> Writer c) -> (a -> Writer c)
compose f g = \x -> let Writer (y, s1) = f x
Writer (z, s2) = g y
in Writer (z, s1 ++ s2)
processString :
processString :: String -> [String]
processString = compose upCase toWords
. () a -> b a -> Writer b , a b. , .. a -> Writer a:
writerId :: a -> Writer a
writerId x = Writer (x, "")
, , Hask. , a b a -> b, a -> m b, .. "" - m. (embellished). m, Writer — .
C m. K, , C, .. ObK = ObC. a -> b K a -> m b C: HomK(a, b) = HomC(a, m b). , , K — C.
, , , . , m — . Haskell ( Hask):
class Monad m where
--
(>=>) :: (a -> m b) -> (b -> m c) -> (a -> m c)
--
return :: a -> m a
>=>, "fish", : . , , — , , , . Writer — , compose — >=>, writerId — return.
>=> . , -. a, f, , , bind:
f >=> g = \a -> let mb = f a
in (bind mb g)
where
bind :: m b -> (b -> m c) -> m c
bind b " " m , b m c. >=>. : m b -> (b -> m c) -> m c. , . "" Haskell >>=, bind, return:
class Monad m where
(>>=) :: m a -> (a -> m b) -> m b
return :: a -> m a
, - b -> m c b, m b. , m, fmap, (a -> m b) -> m a -> m (m b). >>= m (m b) m b, "" , . join:
ma >>= g = join (fmap g ma)
where
join :: m (m a) -> m a
, Writer :
join :: Writer (Writer a) -> Writer a
join (Writer ((Writer (x, s2)), s1)) = Writer (x, s1 ++ s2)
Monad:
class Functor m => Monad m where
join :: m (m a) -> m a
return :: a -> m a
, m . , fmap >>=:
fmap :: (a -> b) -> m a -> m b
fmap f ma = ma >>= (\a -> return (f a))
, "" .
(.. , ) .
(a -> [b]) -> (b -> [c]) -> (a -> [c]). :
(>=>) :: (a -> [b]) -> (b -> [c]) -> (a -> [c])
f >=> g = \x -> concat (map g (f x))
. a, , — f [b]. , b — g : map g (f x) :: [[c]]. , .
>>= :
(>>=) :: [a] -> (a -> [b]) -> [b]
xs >>= f = concat (map f xs)
return :: a -> [a]. :
return :: a -> [a]
return x = [x]
Monad:
instance Monad [] where
xs >>= f = concat (map f xs)
return x = [x]
, . , , . , — , ..
, , - .
, , Maybe. Just, — Nothing. , , :
(>=>) :: (a -> Maybe b) -> (b -> Maybe c) -> (a -> Maybe c)
f >=> g = \x -> case f x of
Just y -> g y
Nothing -> Nothing
Monad Maybe:
instance Monad Maybe where
(Just x) >>= f = f x
Nothing >>= f = Nothing
return x = Just x
, . , - , , - . Either String a, : , . :
data Either a b = Left a | Right b
, . . :
type WithException a = Either String a
Maybe:
(>=>) :: (a -> WithException b) -> (b -> WithException c) -> (a -> WithException c)
f >=> g = \x -> case f x of
Right y -> g y
err -> err
Monad :
instance Monad WithException where
(Right x) >>= f = f x
err >>= f = err
return x = Right x
, , write-only , . a -> b , , . , , ( , ):
a -> s -> (b, s)
:
newtype State s a = State (s -> (a, s))
s , State s . runState:
runState :: State s a -> s -> (a, s)
runState (State f) s = f s
Functor:
instance Functor (State s) where
fmap f state = State st'
where
st' prevState = let (a, newState) = runState state prevState
in (f a, newState)
, a b, , a -> State s b, State s — . , :
(>=>) :: (a -> State s b) -> (b -> State s c) -> (a -> State s c)
f >=> g = \x -> State (\s -> let (y, s') = runState (f x) s
in runState (g y) s')
Monad. , return, , -:
instance Monad (State s) where
stateA >>= f = State (\s -> let (a, s') = runState stateA s
in runState (f a) s')
return a = State (\s -> (a, s))
, . , Unit s , Unit -> State s s:
get :: Unit -> State s s
get _ = State (\s -> (s, s))
, Unit . , .
, , . , , , s Unit, s -> State s Unit:
put :: s -> State s Unit
put s = State (\_ -> ((), s))
, , /. , " " RealWorld, . RealWorld - , (, ). :
type IO a = State RealWorld a
IO — , Haskell, "". , . , , , -, .